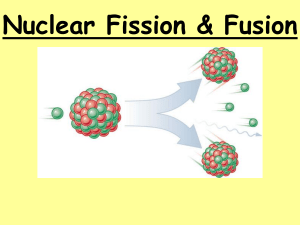
Nuclear Fission and Fusion PowerPoint
advertisement

Fission & Fusion Forces • What holds an atom together? • Why doesn’t the nucleus of an atom fly apart if it’s made of positively charged protons? Forces • Strong Nuclear Forces hold the nucleus of an atom together. Who discovered radioactivity? • In 1896, Henri Becquerel accidentally left pieces of uranium salt in a drawer on a photographic plate. When he developed the plate, he saw an outline of the uranium salt on it. He realized that it must have given off rays that darkened the film. Who discovered radioactivity? • Two years later Marie and Pierre Curie discovered two new elements, Polonium and Radium, both radioactive. Who discovered radioactivity? • Two years later Marie and Pierre Curie discovered two new elements, polonium and radium, both radioactive. • It took them >3 years to get 0.1g of radium from several tons of the mineral pitchblende. Radioactive Elements • Any element over atomic number 83 is radioactive. • Radioactive materials have unstable nuclei (too few or too many neutrons). • When an unstable nucleus decays, it breaks apart emitting particles and energy as it decays. • Three types of nuclear radiation: Alpha particles Beta particles Gamma radiation electromagnetic wave Fission • The process used to release nuclear energy by splitting Uranium-235 nuclei is called fission. + ENERGY What nuclei can split during nuclear fission? • Only large nuclei like U or plutonium can split apart during nuclear fission. Click on image for animation What nuclei can split during nuclear fission? • U-236 is so unstable that it immediately splits into barium & krypton nuclei, several neutrons & a large amount of energy Fission • http://www.atomicarchive.com/Movies/Mov ie4.shtml • http://holbert.faculty.asu.edu/eee460/fissio n.html • Teachers’ Domain: Nuclear Reaction: Fission Chain Reaction • Free neutrons produced by fission can hit other nuclei emitting more neutrons repeating the reaction over and over. • A series of fission reactions is called a chain reaction. • Can only be slowed by using materials that will absorb the neutrons. • http://www.atomicarchive.com/Movies/Mov ie1.shtml Chain Reaction • An uncontrolled chain reaction releases a huge amount of energy in a short time & requires a critical mass of starting material to produce more reactions. Nuclear Power • Nuclear power plants use fission to produce energy. • Nuclear power plants are used in many countries (France is the leader). • There are no nuclear power plants in KY. The nearest is 199 miles away in Tenn. • Ideal location for a nuclear power plant? Take this quiz to test your fear of nuclear power plants. Should you fear? Fusion • The sun is powered by nuclear fusion. • In a nuclear fusion reaction, two small, light nuclei combine to form one larger, heavier nucleus. • Two hydrogen atoms combine under extreme heat and pressure to form a helium atom. (H-2 + H-2→He-4) Fusion • http://www.atomicarchive.com/Fusion/Fusi onMov.shtml • http://holbert.faculty.asu.edu/eee460/fusio n.html Fusion • Why can’t we use the fusion reaction in nuclear power plants? - needs lots of energy - need to overcome electrical forces - difficult to control - never been produced in a nuclear power plant Fusion • Why would we want to use the fusion reaction in a nuclear power plant? 1. Hydrogen is the most common element in the universe. 2. Could meet energy demands for millions of years Let’s Review • Brightstorm Videos fission and fusion and quantitative relationship. • This site is a blog that has good animations for fusion and fission. • Quick Engaging animations How are temperature & fusion related? • How can two nuclei get close enough to combine? They must be moving very fast. • All nuclei positively charged • Thus repel each other • KE must overcome electric force to push them close enough to combine • KE increases as temperature increases • Temp must be millions of °C like Sun & other stars How does the Sun produce energy? • The Sun, made mostly of H produces its energy by fusion of H nuclei • 2 protons (H-1) fuse to make a H isotope (H-2); then H-1 + H-2 form an isotope of He-3. positron neutrino Light light The emission of a positron or a positive electron is referred to as beta decay. The positron is accompanied by a neutrino, a massless and chargeless particle. Positrons are emitted with the same kind of energy spectrum as electrons in negative beta decay because of the emission of the neutrino. How does the Sun produce energy? • To complete the process, 4 H nuclei combine into 1 He nucleus during which a small amount of matter changes into a huge amount of energy. Fusion on the Sun • The heat & light Earth receives comes from this process. • About 1% of the Sun’s hydrogen has been changed into energy. • Sun has enough H to continue fusion reactions for another 5 billion years. Fusion vs. Fission • Fusion combines nuclei & fission splits them apart. Pdf file • Comparison Chart Fission vs. Fission Radiation • Background radiation can come from – Sun – Water – Plants ***Radon is the largest source of radiation in the earth’s crust.*** Radiation Damage • • • • Mutate hemoglobin Mutate cells, lose function Destroy immune system Burn skin, destroy bone Radioactive Tracer • What is a radioactive tracer? - short lived isotope that can be observed with a sensitive detector Radioactive Tracer • How are they used? - Agriculture – measure water flow - Medicine – locate tumors - Medical research – trace drug paths thru body - Geology – trace underground water flow