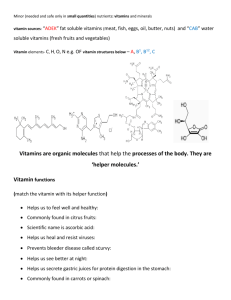
WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS

VITAMINS
• “
VITAMIN” means “vital for life”
• VITAMINS are organic compounds which are necessary in small quantities ( mg or µg
Micronutrients) for everyday healthy functioning of the body
1
Active form
• The structural form that performs its function (exhibits activity) within the organism .
• Human cannot synthesize sufficient quantities of vitamins; thus, vitamins must taken from other sources (diet or pill)
2
The general symptoms of any vitamin deficiency
• Frequent illness
• Slow healing wounds
• tiredness
MACalvey/Teachnet/Vitamins 2006 3
VITAMINS -
Two main categories
Water soluble
B
C
Fat Soluble
E
K
A
D
4
Water soluble
• Have more oxygen and nitrogen in their structure
• Cannot be stored in body
- regular supply needed
Fat Soluble
• Have significant hydrocarbon portions in their structure
• Can be stored in body regular supply not needed
• Excess is excreted in urine - no danger of toxic levels
• Can accumulate to toxic levels if large amounts ingested
• Unstable to heat and light, leach into cooking liquids
• Fairly stable at normal cooking temperatures
5
WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS
Vitamins B and C
• Functions
• Effects of deficiency
• Sources
• RDA
B Vitamins
are important for healthy skin and nervous system
• Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
• Vitamin B2
• Vitamin B3
• Vitamin B5
(riboflavin)
(niacin or niacinamide)
(pantothenic acid)
In general, the B complex is important for healthy skin and nervous system
• Vitamin B6
(pyridoxine, pyridoxal, or pyridoxamine, or pyridoxine hydrochloride)
• Vitamin B7
(biotin)
• Vitamin B9
(folic acid)
• Vitamin
B12 (various cobalamins; commonly cyanocobalamin in vitamin supplements)
7
B complex Vitamins
Vitamin B
1
- Thiamine
Deficiency
Functions
• Essential for release of energy from arbohydrates
(coenzyme)
• Necessary for appetite and good health
• Needed for normal functioning of nervous system
• Beri-beri disease of nervous system
Common in countries where polished rice is staple food
8
Vitamin B
1
Sources
• Meat and liver
• whole-grain
• spinach
- Thiamine
9
Vitamin B
1
- Thiamine
RDA
1mg per day -
Requirement increases with energy expenditure
RDA R ecommended D aily A llowance
10
Vitamin B
2
-Riboflavin
Functions
• Metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats (coenzyme
FMN, FAD)
• Growth, repair, development of body tissues - healthy skin, eyes and tongue
• The principal growth promoting factor in the vitamin B complex
Deficiency
• Loss of appetite
• Swollen tongue, cracked lips, eye infection, dermatitis
11
Vitamin B
2
-Riboflavin
Sources
• liver
• Milk
• Cheese
• Leafy Vegetables
12
Vitamin B
2
-Riboflavin
RDA
1 - 1.5 mg per day
13
Vitamin B3 -Niacin (Nicotinic acid)
Functions
• Metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats (coenzyme
NAD,NADP)
• Needed for normal functioning of nervous system
Deficiency
• Pellagra
Symptoms
• loss of appetite
• mental disorder diarrhea
• possible death
14
Vitamin B 3 -Niacin (Nicotinic acid)
Sources
Liver meat
Yeast extracts
Milk
Cheese
Vegetables grains
MACalvey/Teachnet/Vitamins 2006 15
Vitamin B3 -Niacin (Nicotinic acid)
*RDA
*Related to protein intake
15 - 20mg per day
MACalvey/Teachnet/Vitamins 2006 16
Vitamin B
6
-Pyridoxine
Functions
• Protein metabolism
(coenzyme)
• Involved in formation of haemoglobin, hormones and structural proteins
• Healthy development of nervous system
MACalvey/Teachnet/Vitamins 2006
Deficiency
• Tiredness and
Fatigue, irritability
• Premenstrual tension
17
Vitamin B
6
-Pyridoxine
Sources
Meat
Fish
Nuts bananas
MACalvey/Teachnet/Vitamins 2006 18
Vitamin B
6
-Pyridoxine
RDA
2mg per day
MACalvey/Teachnet/Vitamins 2006 19
Vitamin B
12
- (CyanoCobalamin)
Functions
Vit B12 is necessary for the
• Red blood cell formation
• nervous system function
• the prevention of certain forms of anaemia and neurological disturbances
• functions primarily as a coenzyme in intermediary metabolism
Deficiency
• Pernicious anaemia
• Nerve degeneration
20
Vitamin B
12
- (CyanoCobalamin)
Sources
• Meat Liver
• Fish
• Cheese
• Cereals
This vitamin is stable to cooking
21
Vitamin B
12
- (CyanoCobalamin)
RDA
3-4 µg per day
22
Vitamin B9 -Folic Acid
Functions
• Red blood cell formation
• Essential for synthesis of
DNA and RNA (coenzyme)
• Development of brain, spinal cord and skeleton in foetus
Deficiency
• Fatigue in mild cases
• Anaemia in severe cases
Important to take folic acid prior to pregnancy and vital during first 3 months pregnancy
23
Vitamin B9 -Folic Acid
Sources liver
Fortified cereals
Green leafy vegetables
Potatoes
Milk
24
Vitamin B9 -Folic Acid
RDA
300 µg per day
More during pregnancy
25
Pantothenic acid
Functions
• Nessessary for the biosynthesis of coenzyme A
Deficiency
• Unknown
Sources
Pantothenic derives from
Greek word meaning from every where
26
Biotin
Functions
• A coenzyme important in lipid and carbohydrates metabolism.
Deficiency
• Unknown
Sources
Bacteria in the intestine synthesize biotin in sufficient quantities
27
Vitamin C -Ascorbic Acid
Functions
• Formation of connective tissue, collagen
• Critical to immune system
• Helps absorption of iron
• Prevents scurvy
• Promotes healing of wounds and healthy blood vessels
• Acts as antioxidant, protects HDL cholesterol
Deficiency
• Weakening of connective tissue
• Susceptibility to infection
• Incomplete iron absorption
• Delayed healing of wounds
28
Vitamin C -Ascorbic Acid
Sources
• green peppers
• Kiwi
• Citrus fruits, strawberries,
• Spinach
• broccolli
29
Vitamin C -Ascorbic Acid
Properties
• Acts as an antioxidant
RDA
30-60 mg per day
Least stable of all vitamins
30
FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
Vitamins A,D,E,K
• Functions
• Effects of deficiency
• Sources
• RDA
MA Calvey/Teachnet/Vitamins 2006 31
Vitamin A - Retinol and Beta-Carotene
Retinol Beta-Carotene
Named because of its concern with retina of eye
Only found in animal foods
Present with chlorophyll in plants, converted to
Vitamin A in gut wall
Vitamin A - Retinol and Beta-Carotene
Functions
• Important to vision
Necessary for production of Rhodopsin - pigment in retina, helps eye adapt to dim light
• Regulates growth
• Promotes healthy skin
• Maintenance of healthy epithelial tissues
Effects of deficiency
• Night blindness
• Retarded growth, malformed bones
• Dry mucous membranes
• Xerophthalmia - dry eye membrane
• Susceptibility to infection
Vitamin A - Retinol and Beta-Carotene
Sources
Retinol - liver oil, Liver,
Dairy products, Egg yolk
Beta-Carotene
Dark green leafy vegetables, Broccoli,
Carrots, Deep orange fruits and vegetables
Carotene
Go for Color!
Think
Yellow , Orange ,
Red, Deep Green
Vitamin A - Retinol and Beta-Carotene
Properties
• Powerful antioxidant
RDA
600 µg per day
90% of
Vitamin A in the body is stored in the liver
Vitamin D - Calciferols
Cholecalciferol
Ergocalciferol
The sunshine
Vitamin!
The sun activates Provitamin
7 dehydro cholesterol present in fat under skin
Formed by action of ultra violet light on fungi and yeasts
Manufactured synthetically for use as vitamin supplement
Provitamin 7 dehydro cholesterol
Cholecalciferol
Vitamin D -Calciferols
Functions
• Absorption and laying down of calcium and phosphorous in bones and teeth
• Regulates calcium balance between bones and blood
• Prevents rickets
Effects of deficiency
• *Rickets in children and
*osteomalacia in adults
* Conditions where bones are soft and cannot weight of body
• **Osteoporosis
**Bones become light, less dense and prone to fractures
• Dental caries
Vitamin D -Calciferols
Sources
Sunlight conversion
Fish liver oils
Dairy products
Oily fish
Margarine
Vitamin D -Calciferols
Properties
RDA
7 -10 µg per day
Probably the most stable of the vitamins
Vitamin E -Tocopherols
Anti coagulants and anti oxidants
Functions
• Powerful antioxidant
• May reduce risk of heart disease, stroke, cancer
• Improves absorption of vitamin A
Effects of deficiency
• Deficiency is rare
• Linked to conditions associated to malabsorption of fat
Vitamin E -Tocopherols
Sources
Wheatgerm
Oatmeal
Oils and animal fats
Leafy greens
Eggs
Vitamin E -Tocopherols
Properties
• Acts as antioxidant, delays rancidity and oxidation
RDA
Based on polyunsaturated fatty acid intake
Sometimes called
“Coagulation” vitamin
Vitamin K
Functions
• Constituent of prothrombin which is necessary in blood clotting
Effects of deficiency
• Abnormal clotting, bleeding and haemorrhaging
• Deficiency is rare because intestinal bacteria produce sufficient quantities
Vitamin K
Sources
• Dark green vegetables
• Liver
• Lean meat
• Eggs
• Manufactured by bacteria in intestine
RDA
No established recommendation
How vitamins help each other
• Vitamin E keeps Vitamin A from being destroyed in the intestines
• Vitamin D enables the body to absorb calcium and phosphorous
• Vitamin C helps folate build proteins
• Vitamin B
1 works in digestive system with niacin, pantothenic acid acid and magnesium