Review Packet - Parkway C-2
advertisement

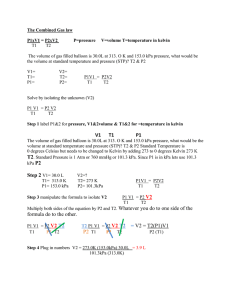
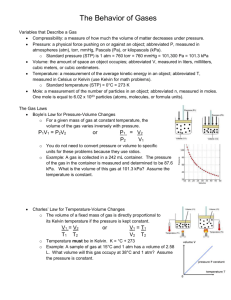
Review Packet Gas Laws Chapters 13.1-2 & 14 WARNING: THIS IS ONLY A SAMPLE OF PROBLEMS FROM THIS UNIT. YOU ALSO NEED TO STUDY FROM YOUR OBJECTIVE SHEET, CLASS NOTES, WORKSHEETS, LABS, ETC!!!!! Make sure you know these relationships for the test: 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023 particles = 22.4 L at STP = Molar Mass (g) use the periodic table 1.00 atm. = 101.3 kPa = 760 mm Hg or torr = 14.7 psi (Standard Temperature) 1oC = 1 Kelvin But in Celsius change to Kelvin ____ oC + 273 = Kelvin (K) For Problems – Please write all work on a separate piece of paper. Include a formula, a number set up and a final answer with the correct significant digits and unit(s). Fill in the blank with the best most correct word choice possible. 1. The physical behavior of a gas depends on its volume, temperature, and _________________________. 2. A gas has random motion because it has ___________________________ energy. 3. Atmospheric pressure _____________________________ with an increase in elevation. 4. If equal volumes of gases are at the same temperature and pressure, the volumes must contain the ___________________________ number of particles. Problem Solving 1. A rigid container of O2 has a pressure of 3.5 atm at a temperature of 713 K. What is the pressure at 1426 K? 2. How many nitrogen molecules are in 5.62 L of nitrogen gas at STP? 3. Which has the greater pressure? Show all conversions to verify your answer. 1.79 atm or 952 mmHg or 195.5 kPa 4. The Combined Gas Equation relates 3 separate gas laws. Draw and label a graph for each law, in addition show a line that illustrates the relationship between the 2 variables. Charles' (Pressure is constant, so the graph will show volume versus temperature, where temperature is the independent variable.) Boyle's (Temperature is constant, so the graph will show pressure versus volume, where volume is the independent variable.) Gay-Lussac's (Volume is constant, so the graph will show pressure versus temperature, where temperature is the independent variable.) 5. A sample of gas under a pressure of 855 kPa has a volume of 3.50 mL. The pressure is increased to 995 kPa. What volume will the gas occupy at the new pressure, assuming that the temperature is constant? 6. A 212 L sample of a gas exerts a pressure of 316.6 mmHg when its temperature is 38oC. What volume would it occupy at 33.3 kPa and 34oC? 7. A gas with a volume of 345 mL at 47oC is heated until its volume is 894 mL. What is its new temperature? 8. A 5.00 L air sample has a pressure of 107 kPa at a temperature of –50oC. If the temperature is raised to 102oC and the volume expands to 7.00 L, what will the new pressure be? 9. If 0.0025 moles of Hydrogen gas is formed by bubbling it up through water. The gases occupy a volume of 45.55 mL at 20.0oC. What is the total pressure of all of the gases and the pressure of the dry hydrogen gas if the PH2O is 2.33 kPa? (Hint: solve for total pressure first using the ideal gas law) 10. What is the total pressure of the gases, in kilopascals (kPa), in a closed rigid container at constant temperature that is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon monoxide gases? The N 2 has a pressure of 125.0 kPa, the O2 has a pressure of 538.5 mmHg, and the CO has a pressure of 0.732 atmospheres. 12. What distinguishes effusion from diffusion? How are these processes similar? 13. Calculate the ratio of the velocity of He atoms to the velocity of fluorine molecules at the same temperature. 14. A certain gas effuses four times a fast as oxygen (O2) gas. What is the molar mass of the gas? 16. Magnesium burns in air to produce magnesium oxide, MgO, and magnesium nitride, Mg 3N2. Magnesium nitride reacts with water to give ammonia. Mg3N2 + 6 H2O (l) 3 Mg(OH)2 (s) + 2 NH3 (g) What volume of ammonia gas at 24oC and 753 mmHg will be produced from 4.56 g of magnesium nitride? 17. How many grams of chlorine (Cl2) exist in a container that has a volume of 2.00 L, and pressure of 19.2 psi and is at a temperature of 25.0oC? 18. At standard conditions, it was found that 1.00 L of a gas weighed 0.760 g. What is the compounds molecular (molar) mass? 19. Sodium hydrogen carbonate is also known as baking soda. When this compound is heated, it decomposes to sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water vapor. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. What volume (in liters) of carbon dioxide gas at 91oC and 756 mmHg will be produced from 35.4 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate? Practice Multiple Choice – be sure to have your logic sketched out so that you know why you arrived at your choice. 1. 2. A gas occupies a volume of 1.50 L at 700 mmHg and 200°C. Which mathematical expression gives the correct volume at 400 mmHg and 100°C? a. 1.50 x 400 100 700 200 c. 1.50 x 400 473 700 337 e. 1.50 x 700 473 400 373 b. d. 1.50 x 400 373 700 473 1.50 x 700 373 400 473 For a gas, which two variables are DIRECTLY proportional to each other (if all other conditions remain constant)? 1. P and V 2. P and n 3. P and T a. d. 1 only 1 and 2 only b. e. 2 only 2 and 3 only c. 3 only 3. 4. Which of the following gases has the greatest density at 2.5 atm and 25°C? a. N2O b. F2 d. C3H8 e. NF3 The The The The The pressure pressure pressure pressure pressure will remain the same. will decrease by a factor of five. will increase by a factor of five. will increase by a factor less than five. will increase by a factor greater than five. Equal volumes (1.0 L) of ozone, O3, and methanethiol, CH3SH, under the same conditions have equal 1. 2. 3. a. d. 6. HNF2 A given mass of gas in a rigid container is heated from 100 to 500°C. Which of the following responses best describes what will happen to the pressure of the gas? a. b. c. d. e. 5. c. numbers of molecules. numbers of atoms. masses. 1 only 1 and 2 only b. e. 2 only 1 and 3 only c. 3 only Three 1.0-L flasks are filled with H2, O2, and Ne, respectively, at STP. Which of the following statements is TRUE? 7. a. b. c. d. All the flasks have the same number of gas molecules. The velocity of the gas molecules is the same in all the flasks. The densities of all the gases are the same. There are twice as many O2 and H2 molecules as Ne atoms. e. None of these is true. For the following reactions consider the reactants, after the reaction has finished (only products exist) and the substances return to the same initial temperature, which system will have an increase in pressure? d. 2 ClF3(g) 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 2 NO2(g) 2 NO(g) + O2(g) 2 CO2(g) + 3 H2O(l) C2H6O(l) + 3 O2(g) e. C(s) + O2(g) a. b. c. 8. Cl2(g) + 3 F2(g) CO2(g) Which of the following gases will have the slowest rate of diffusion (assume they are all at the same temperature): a. d. CF4. Ne. b. e. F2. SO3 c. H 2.