Water Soluble Vitamins ppt
advertisement

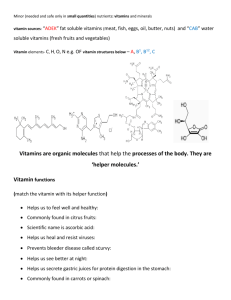
Water Soluble Vitamins! Objectives After reading Chapter 6, completing a concept map and class discussion, you will be able to Identify water soluble vitamins Distinguish water soluble vs fat soluble Describe the concert role of B vitamins Describe concert deficiencies Identify vitamin imposters and non-B vitamins Water Soluble Vitamins: Characteristics Essential Organic Structure Non-energy Producing Micronutrients Stability Bioavailability Toxicity Water Soluble Vitamins vs. Fat Soluble Vitamins The B Vitamins Coenzymes Vitamin Concept Map FUNCTIONS Food Sources Vitamin Other Facts Thiamin Functions SOURCES Sources Thiamin Other Facts Thiamin Other names: Vitamin B1 1998 RDA men: 1.2 mg/day women: 1.1 mg/day Chief functions in the body Part of coenzyme TPP (thiamin pyrophosphate) used in energy metabolism Easily destroyed by heat Thiamin Sources Pork Whole Grain or Enriched Grains Ribovlavin Functions SOURCES Sources Riboflavin Other Facts Riboflavin Other names: Vitamin B2 1998 RDA Men: 1.3 mg/day Women: 1.1 mg/day Chief functions in the body Part of coenzymes FMN (flavin mononucleotide) and FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide) used in energy metabolism. Easily destroyed by ultraviolet light and irradiation Riboflavin Copyright 2005 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning Riboflavin Sources Milk products Yogurt Cheese Enriched or whole grains Liver Niacin Functions SOURCES Sources Niacin Other Facts Niacin Other names Precursor: dietary tryptophan 1998 RDA Nicotinic acid Nicotinamide Niacinamide Vitamin B3 Men: 16 mg NE/day Women: 14 mg NE/day Upper level for adults: 35 mg/day Niacin Chief functions in the body Part of coenzymes NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (its phosphate form) used in energy metabolism Toxicity symptoms Painful flush, hives, and rash (“niacin flush”) Excessive sweating Blurred vision Liver damage, impaired glucose tolerance Niacin Sources All protein foods Milk, eggs, meat, fish, poultry Whole grain Enriched grains Nuts Vitamin B6 Functions SOURCES Sources Vitamin B6 Functions Other Facts Vitamin B6 Other names Pyridoxine Pyridoxal Pyridoxamine 1998 RDA Adults (19-50 years): 1.3 mg/day Upper level for adults: 100 mg/day Vitamin B6 Chief functions in the body Part of coenzymes PLP (pyridoxal phosphate) and PMP (pyridoxamine phosphate) used in amino acid and fatty acid metabolism Helps to convert tryptophan to niacin and to serotonin Helps to make red blood cells Vitamin B6 Deficiency symptoms Scaly dermatitis Anemia (small-cell type) Depression, confusion, abnormal brain wave pattern, convulsions Vitamin B6 Sources Meat, fish, poultry, liver Potatoes Legumes Non-citrus fruits Fortified cereal Soy products Vitamin B12 Functions SOURCES Sources Vitamin B12 Functions Other Facts Vitamin B12 Other names: cobalamin (and related forms) 1998 RDA Adults: 2.4 g/day Chief functions in the body Part of coenzymes methylcobalamin and deoxyadenosylcobalamin used in new cell synthesis Helps to maintain nerve cells Reforms folate coenzyme Helps to break down some fatty acids and amino acids Vitamin B12 Activates Folate Absorption requires HCl Pepsin Intrinsic factor Vitamin B12 Easily destroyed by microwave cooking Deficiency disease: pernicious anemia Difficult for vegetarians to obtain Toxicity: none reported Vitamin B12 Sources Animal products Meat, poultry fish, shellfish Milk, cheese Eggs Fortified cereals Folate Functions SOURCES Sources Folate Functions Other Facts Folate Other names Folic acid Folacin Pteroylglutamic acid (PGA) 1998 RDA Adults: 400 g/day Upper level for adults: 1000 g/day Folate Folate Folate Chief functions in the body Part of coenzymes THF (tetrahydrofolate) and DHF (dihydrofolate) used in DNA synthesis and therefore important in new cell formation Neural tube defects Spina Bifida Anencephaly Folate Supplementation Decrease in neural tube defects with supplementation of cereals Critical Periods Folate Sources Fortified Grains Leafy Green Vegetables Legumes, Seeds Liver Biotin Functions SOURCES Sources Biotin Functions Other Facts Biotin 1998 adequate intake (AI) Adults: 30 g/day Chief functions in the body Part of a coenzyme used in energy metabolism, fat synthesis, amino acid metabolism, and glycogen synthesis Significant sources Widespread in foods Also produced by GI bacteria Biotin Sources Widespread in foods Organ meats, fish Egg yolks Soybeans Whole grains Pantothenic Acid Functions SOURCES Sources Pantothenic Acid Functions Other Facts Pantothenic Acid 1998 adequate intake (AI) Adults: 5 mg/day Chief functions in the body Part of coenzyme A, used in energy metabolism Easily destroyed by food processing Pantothenic Acid Sources Widespread in foods Organ meats Mushrooms Avacado Broccoli Whole grains Non-B Vitamin Controversial other dietary compounds Still under scientific investigation May be “conditionally” essential Supplements NOT necessary Widespread in foods Non-B Vitamin Choline Contains N2; made from methionine Used to make lecithin & acetylcholine Adequate Intake (AI) established 1998 Men=550 Inositol mg/day; Women=425 mg/day Part of cell membrane structure Carnitine Transports long-chain fatty acids Vitamin Imposters Not essential for humans; essential only for bacteria or other forms of life PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid) Vitamin P (hesperidin)-a bioflavonoid Ubiquinone (Coenzyme Q10) Pyrroloquinoline quinone (methoxatin) Orotic acid Lipoic acid Vitamin Imposters Vitamin O (oxygenated salt water) Vitamin B15 (Pangamic acid) Vitamin B17 (Laetrile) Alleged “cancer cure” Potentially dangerous Vitamin B5 Simply another name for Pantothenic Acid Conclusions 1. 2. 3. 4. Vitamins are derived from a variety of foods. That is why variety is so important. Vitamin deficiencies rarely occur in this country. If they do, it is usually in conjunction with severe illness, stress, or trauma that is superimposed on prolonged inadequate intake. If there is deficiency, usually several vitamins (especially in the case of B vitamins) are involved. Conclusions 1. 2. Toxicity is also rare but a possibility Toxicity is rarely associated with food Toxicity results from supplements Vitamin imposters are used Variety is the Key