ACTIVE TRANSPORT: Transport of Large molecules using energy
advertisement

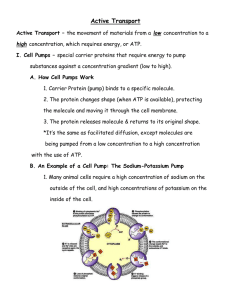
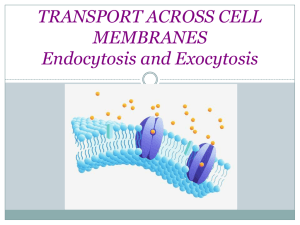
ATP Active Transport Requires energy or ATP Can move materials from LOW to HIGH concentration AGAINST concentration gradient ACTIVE TRANSPORT EXAMPLE #1: Proteins can pump molecules against the concentration gradient (flow). The protein uses ATP energy to push the molecules where the cell NEEDS them to be, regardless of the concentration. Label the protein pump on your cell membrane! ACTIVE TRANSPORT EXAMPLE #2: ENDOCYTOSIS Very large or bulk material (a lot at once) can be moved INTO the cell by a process called ENDOCYTOSIS. “en” like “enter” There are two forms: PHAGOCYTOSIS PINOCYTOSIS Endocytosis – Phagocytosis Used to engulf large items (biomolecules or pathogens) or bulk by creating a vesicle. Called “Cell Eating” Phagocytosis Capture of a Yeast Cell (yellow) by membrane extensions of an Immune System Cell, or white blood cell (blue) Endocytosis – Pinocytosis Used to engulf large amounts of liquid by creating a vesicle. Called “Cell drinking” ACTIVE TRANSPORT EXAMPLE #2: EXOCYTOSIS Very large or bulk material (a lot at once) can be moved OUT the cell by a process called EXOCYTOSIS. “ex” like “exit” Moving the “Big Stuff” Exocytosis - moving things out. Molecules are moved out of the cell by vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with one another. Exocytosis Exocytic vesicle immediately after fusion with plasma membrane.