Continuity and Change Over Time
advertisement
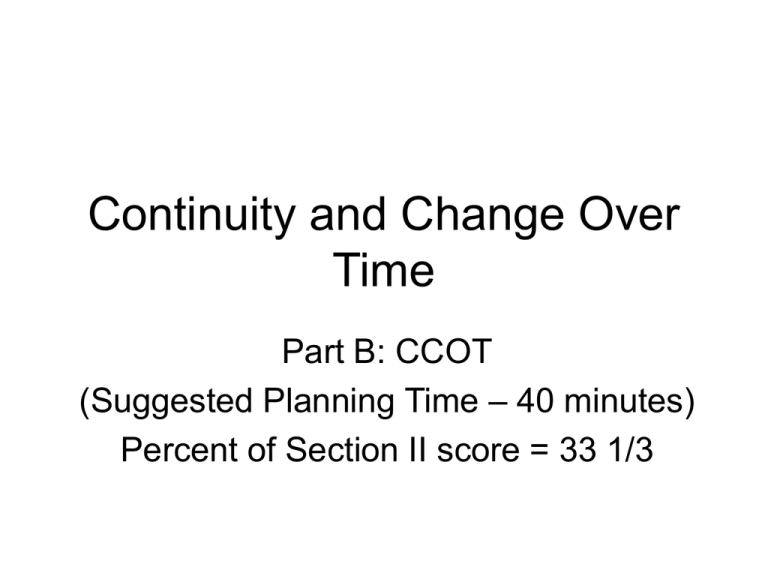
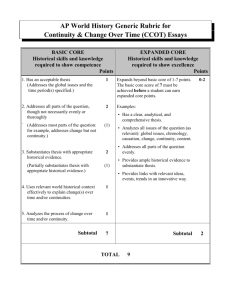
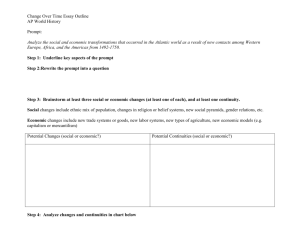
Continuity and Change Over Time Part B: CCOT (Suggested Planning Time – 40 minutes) Percent of Section II score = 33 1/3 What It Is • Analyzes continuity and change over time • Covers at least one time period • Addresses a theme such as trade, culture, technology, migration, environment • Analyzes the process and causes of change using specific examples • Analyzes the process and causes of continuities using specific examples Generic Rubric • Has an acceptable thesis. (Addresses the global issues and the time period specified.) • Addresses all parts of the questions, though not necessarily evenly or thoroughly. (Addresses most parts of the question: for example, addresses change but not continuity) • 1 point • 2 points • Substantiates thesis with appropriate historical evidence. (Partially substantiates thesis with appropriate evidence) • Uses relevant world historical context effectively to explain continuity and change over time • Analyzes the process of continuity and change over time • 2 points • 1 point • 1 point • Basic Core points - 7 Expanded Core • Clear, analytical and comprehensive thesis • Analyzes all issues of the question: global context, chronology, causation, change, continuity, effects, content • Ample historical evidence • Links to relevant ideas, events, trends in innovative ways • 0 – 2 points Directions: You are to answer the following question. You should spend 5 minutes organizing or outlining your essay. Write an essay that: • Has a relevant thesis and supports that thesis with appropriate historical evidence. • Addresses all parts of the question • Uses world historical context to show change and continuity over time • Analyzes the process of change and continuity over time 2. Analyze the social and economic transformations that occurred in the Atlantic world as a result of new contacts among Western Europe, Africa and the Americas from 1492 to 1750. Thesis • Must be at the beginning of the essay. • Must explicitly address social and economic changes and continuities • “Between 1492 and 1750, a period marked by exploration and European imperialism, a global economy emerged in which Africa, the Americas and Europe all interacted and exchanged goods through commerce. The social hierarchies and demographics of these areas were also dramatically altered by globalization and contacts with the New World, although the basic political structures were left largely unchanged.” Addresses all parts of Question • Students must accurately describe six social and economic changes or continuities, at least one social and one economic. • Students may address transformations within the Atlantic World, or within specific regions: Western Europe, Africa, Americas • “The most radical change . . .revolved around the new global economy, which was marked by the system of Triangular trade which took raw materials from Africa and the Americas across the Atlantic to be transformed into manufactured products in Western Europe.” Historical evidence • Nine pieces of historical evidence, at least one on social and one on economic changes • “European economy boomed with the introduction of New World crops such as potatoes and corn, and the population increased dramatically.” Historical Context • Uses historical context to effectively show change and continuity in the Atlantic world • Placing the Atlantic world in the context of world history • Connecting the Atlantic world to global processes • Describing the interaction between two regions • “This exchange led to dramatic social changes in West Africa, where millions of men and women were exported across the Atlantic to be used as slaves in the Americas.” Analyzes the process of change and continuity • Explain the causation of exchange around the Atlantic world • “Since this sort of labor involving sugar cane was highly demanding and required great physical force, men were generally needed and women were left back in Africa.”