The Circulatory System - Garnet Valley School District
advertisement

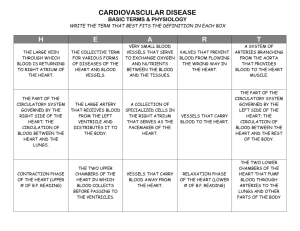
The Circulatory System The Circulatory System • Is the body system consisting of : – the heart, – blood, – and blood vessels called • arteries, • veins, • and capillaries. The Circulatory System • What’s the job of the circulatory system? – To move nutrients and oxygen throughout the body – To remove waste products from the body. • Think of it as your body’s highway – – Specialized vehicles carrying supplies to your body (like a UPS or FedEx Truck) – Vehicles to take the waste away (like a Garbage Truck) Structure of the Circulatory System • Heart: – Receives blood and sends blood away through blood vessels. • Artery: is a blood vessel that carries blood AWAY from the heart. • Vein: is a blood vessel that RETURNS blood to the heart. – Capillaries: tiny blood vessels that connect veins and arteries. Structure of the Circulatory System • Atriums: Receive blood – Right Atrium: • Blood from the body enters the right atrium from two large veins. The blood in these veins is rich in carbon dioxide, a waste product. Right Atrium Structure of the Circulatory System Left Atrium • Atriums Cont’d: – Left Atrium: • Oxygen-rich blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium through two veins. • In review – Atriums receive blood from either veins or the lungs! Structure of the Circulatory System • Ventricles: Send blood to the lungs or the body – Right Ventricle: • This blood flows from the right atrium into the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, blood is pumped through arteries to the lungs. Right Ventricle Structure of the Circulatory System Aorta • Ventricles Cont’d: – Left Ventricle: • This oxygen-rich blood flows from the left atrium to the left ventricle. • The left ventricle pumps this blood to body cells through the aorta, the main artery in the body. Left Ventricle How does our heart work? • http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/ani mations/content/human_heart.html How does our heart work? Blood out to the Body Blood to the Lungs Lungs Blood from the Body Components of Blood • Plasma – 90% Water – Transportation of blood cells – Contains dissolved salts and minerals Components of Blood • Red Blood Cells – Contains Hemoglobin (that gives it its red color) – Hemoglobin is an oxygen magnet on account of its iron. – Hemoglobin transports oxygen to the body’s cells. – BONES produce red blood cells. Components of Blood • White Blood Cells – Oddly shaped and bigger than RBCs – Fight germs and infections – A drop of blood may contain between 4500 and 25000 WBCs at a time. • If you have an infection this number increases. • Consistently high numbers of WBCs in blood may indicate that you have leukemia. – Leukemic patients may have as many as 50000 in every drop. Components of Blood • Platelets – Irregularly shaped. – Clots blood – Scabs and Bruises are examples of platelets at work. – If blood clots inside of arteries, it cuts off the oxygen supply. Blood Types • Types A, B, AB, O • Blood types have to match before a transfusion or the blood cells may clump and cause a fatal blockage. Blood Types • Donors – Type A can donate to A or AB – Type B can donate to B or AB – Type AB can only donate to AB – Type 0 is a Universal Donor • Recipients – Type A can receive A, O – Type B can receive B, O – Type AB can receive all types – Type O can only receive Type O Blood Types • RH factor have to do with blood proteins. • You either have a + or a – • Mothers to be need to know their RH factor because if it doesn’t match their baby’s, the mothers blood may attack the baby’s blood. • Blood exchanges for the baby work. Blood Vessels • Arteries – – – – Carry blood AWAY from the Heart. Tough on the outside, smooth on the inside Muscle can be found in the middle of the artery When the heart relaxes, the artery contracts to push the blood along. Blood Vessels • 5 main arteries 1. Carotid- main artery in the neck 2. Radial- in the wrist 3. Brachial- in elbow 4. Femoral- between hip and groin • The Aorta is the largest artery in the body. Blood Vessels • Veins – Carry blood TOWARDS the heart – Valves prevent back flow of blood and blood can flow from the legs up to the heart – Veins have thin walls. Blood Vessels • Capillaries – Extremely small blood vessels. – Transport blood from arteries to veins – Exchange CO2 and O2, nutrients and wastes – Releases excess heat from body (redness) Reflection • So far, we have learned about: the skeletal system the muscular system and the circulatory system. How do these 3 systems interact with each other?