Baby Book Chap. 3 the Fetus
advertisement

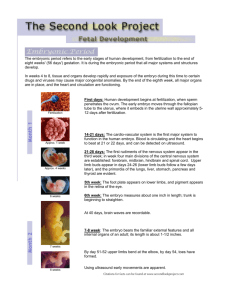
The Fetus Chapter 3 1. At what point in a baby’s development is the sex, color of hair and eyes as well as other physical characteristics determined? At conception 2. How is the sex of the baby determined? The egg carries two X chromosomes and the sperm carries both an X chromosome and a Y chromosome. If the egg is fertilized with an X chromosome it is a female; if it is fertilized with a Y chromosome it is a male 3. List four factors that affect the chances of having twins: • A. Age – twins are less common in younger mothers • B. Number of children – Twins are less common in first pregnancies • C. Race – People of African descent are more likely to have twins • D. Family History – do twins run in your family? 4. What is the difference between fraternal and identical twins? • Fraternal Twins occur when 2 eggs are fertilized with two sperm. There are two separate embryos. It is possible to have different sex fraternal twins. • Identical Twins occur when 1 egg is fertilized by one sperm and then divides into two separate embryos. Identical twins are always the same sex. 5. Why is the unborn baby not likely to feel anything if the mother falls during pregnancy? • The baby is buoyant and is protected by the amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. 6. What is “quickening”? The mother feels fluttering movements – they are faint at first and may be mistaken for “gas”. Eventually they become stronger and more frequent as the baby grows. The baby has been active long before the mother first feels this movement When does the mother first feel this movement? 18 – 20 weeks 7. Why does it not bother a baby to be upside down in her mother’s uterus? The baby is weightless and does not feel the pull of gravity. This is very similar to astronauts in space. a. What is the fetal position? It is when the fetus curls up in the womb because there is no longer enough room to stretch out. 8. Why does the skull remain flexible and the final fusion of the skull bones happen just before puberty? The Baby must get through the birth canal at birth and the brain is not fully developed and does not stop growing until puberty. Fetal Developmental Chart First Month: In the first 2 weeks: • The fertilized egg is called a zygote. • During this time the zygote reaches the uterus and attaches to the lining of the uterus. • Attachment of the zygote signals the uterus that nutrition from the lining of the uterus is needed and it is not shed and the woman misses her first period and does not usually resume having a period until after the birth of the child. • Although the zygote is experiencing tremendous growth at this time, it is only the size of a pinhead In the next 2 weeks: •Internal organs and the circulatory system begin to form •The heart begins to beat •By the end of the month small bumps indicate the beginning of arms and legs •The eyes, brain, and spinal cord are beginning to form •The fetus is the size of a pea Second Month (8 weeks) • • • • • At 5 weeks the embryo is about ¼” long Face, eyes, ears, and limbs take shape Bones begin to form Internal organs begin to form Brain is developing rapidly Third Month (12 weeks) • As the month begins the fetus is about 1” long • Nostrils, mouth, lips, tooth buds, and eyelids form • Fingers and toes are almost complete • Has finger- and toe- nails • All organs are present but immature • Fetus begins to move a little • Hair may begin to appear Fourth Month (16 weeks) • The fetus is about 3” long and weighs about 1 ounce • The fetus can suck its thumb, swallow, hiccup and move around • Facial features become clearer • Secondary sexual characteristics are formed • There is a tiny chin • Eyes seem too far apart • At the end of this month the development period is over and the growth phase begins Fifth Month (20 weeks) • The fetus is about 6.5 – 7” long and 4 – 5 ounces in weight • Hair, eyelashes, and eyebrows appear • Teeth continue to develop (inside the gums) • Organs continue to mature • The fetus becomes more active Sixth Month (24 weeks) • The fetus is now 8 – 10 inches long and weighs between 8 and 12 ounces • Fat is being deposited under the skin, but the fetus still appears wrinkled • Breathing movements begin • Taste buds appear • Lungs are immature Seventh Month (28 weeks) • The fetus is 10 – 12 inches long and 1.5 to 2 pounds • Periods of fetal activity are followed by period of rest and quiet • The fetus is covered by vernix – a cheese-like secretion to prevent the skin from becoming water-logged • Organs are still immature • Umbilical cord has reached its maximum length Eighth Month (32 weeks) • Weight gain continues rapidly • The fetus is 14 – 16 inches long and 2.5 – 3 pounds • The fetus may react to loud noises with a reflexive jerking action • In most cases the fetus moves into a head down position • The fetus becomes less active as they grow and have less room to move • Lungs are developing Ninth Month (36 weeks) • At the beginning of the 9th month the fetus is about 17 – 18 inches long and weighs about 5 – 6 pounds • Skin becomes smooth as fat deposits continue to build • Fetal movements decrease as the fetus has less room to move around • The fetus acquires disease-fighting antibodies from the mother’s blood • The fetus descents into the pelvis, ready for birth