January 20 – Prenatal Development and Birth
advertisement

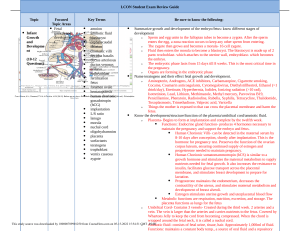
Fundamentals of Lifespan Development JANUARY 20 – PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT AND BIRTH Video Video – 9 Months in the Womb Footage of Baby in the Womb 3D Video of Conception to Birth Life’s Greatest Miracle – PBS NOVA Germinal Stage – Conception and Implantation Implantation: ◦ Amniotic Fluid – Fluid for temperature & protection ◦ Placenta – Food & oxygen & waste ◦ Umbilical Cord – Delivers blood & removes waste ◦ Zygote – New cell produced by combining two gametes ◦ Gamete – Ovum and sperm with 23 chromosomes Milestones of Prenatal Development Trimester Period Weeks Length and Weight Major Events First Zygote – Germinal Stage 1 Conception. One cell multiplies & forms blastocyst. Zygote - Implantation 2 Blastocyst begins implantation Embryo - Organogenesis 3-8 6 mm Primitive brain & spinal cord. Organs begin to grow Embryo 5-8 2.5 cm 4g External body parts grow. Embryo can move. Gonad and genital development. Fetus 9-12 7.6 cm 28 g Rapid increase in size. Internal organs become organized. Second Fetus 13-24 30 cm 820 g Fetus enlarges. Fetal movements felt by mother. Sensitive to light & sound. Third Fetus 25-38 51 cm 3200 g Size increases. Organs mature. Fat is added. Antibodies are transmitted. Fetal Stage Milestones Weeks Major Events 9 – 12 Fingerprints, grasping reflex, facial expressions, swallowing, rhythmic ‘breathing’ of amniotic fluid, urination, genitals appear, activity & rest. 13 – 16 Hair follicles, respond to mothers voice and other loud noises 17 – 20 Fetal movements felt by mother, heartbeat detectable with stethoscope, lanugo covers body, eyes respond to light, eyebrows, fingernails 21 – 24 Vernix protects skin, lungs produce surfactant, vitality possible but problematic 25 – 28 Recognition of mother’s voice, regular periods of rest and activity, good chance a newborn would survive 29 – 32 Very rapid growth, antibodies acquires, fat deposits under skin 33 – 36 Movement of head for birth, lungs mature 37 + Full-Term Pregnancy Summary Genetic Disorders Teratogens Agents that causes damage to an embryo or fetus during the prenatal period. Drugs – Legal and Illegal Alcohol Tobacco Radiation Pollution Infectious disease Nutrition (maternal factor) Stress (maternal factor) Maternal Age Rh factor incompatibility 3 types Mutagenic – Cause alterations to genomic DNA Environmental – Environmental agents that disrupt normal cell development Epimutagenic – Cause alterations with epigenetic structures without changing the DNA Teratogens Childbirth Stages of childbirth: 1. Dilation and effacement of the cervix ◦ First birth = 12 – 14 hours ◦ Second + = 4-6 hours 2. Delivery of the baby ◦ First birth = 50 min ◦ Second + = 20 min 3. Delivery of the placenta ◦ 5-10 min The Apgar Scale Childbirth Key Terms Breech position – When a baby is turned so that the buttocks or feet would be delivered first Anoxia – Inadequate oxygen supply during labour and delivery Isolette – Plexiglas-enclosure to protect preterm babies Cesarean – A surgical birth where a doctor makes an incision in the mother’s abdomen and lifts the baby out of the uterus Discussion How were you born? 1 – In a hospital 2 – In a birthing center 3 – At home 4 – Other Why did your parents chose that location? What did (would) you do if you (or a partner) were going to have a child?