Nonmetals, inert gases, and semimetals
advertisement

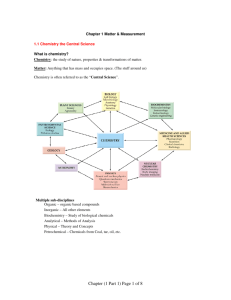
Nonmetals, inert gases, and semimetals Exploring the right side of the periodic table. Properties of non metals • Nonmetals lack the properties of metals. • Most nonmetals are poor conductors of both heat and electricity. • Nonmetal solids are brittle and are dull in color. (Sulfur) • Many nonmetals are common Earth elements. Physical properties • Four nonmetals are gases at room temperature (oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, and chlorine). • Other nonmetals are solids at room temperature (carbon, iodine, and sulfur). • Bromine is the only nonmetal which is a liquid at room temperature. Chemical properties • Atoms of nonmetals either gain or share electrons when they react with other elements. • Examples of these types of reactions are salt (NaCl) and rust (Fe2O3). Families of the Non metals (The Boron Family) • These elements usually share or donate their three electrons in the valence shell. • The family extends from Boron to Ununtrium (#113). • One of the most commonly used elements from this family is Aluminum. (The carbon family) • The elements in the carbon family all like to share, gain, or lose four electrons. • The Family extends from carbon through lead. • Carbon is the basis of all of the life on the planet Earth. Why is Carbon so important to life on planet Earth? • Because carbon has the unique ability of being the only nonmetal which can generate four bonds it can form long chains to produce many different substances. • Proteins, oil, carbohydrates, and coal are examples of important substances which are made of long chains of carbons. The nitrogen family • This group contains two nonmetals nitrogen and phosphorous, which are both important to plants and agricultural growth. • The elements in this family usually share or gain three electrons. • The Earths atmosphere is about 80% nitrogen gas. • Nitrogen occurs in nature as N2 which is called a diatomic molecule. In this form the N2 gas is not very reactive. • Some bacteria use nitrogen as the basis to form compounds to keep themselves alive (Nitrogen fixation). • Match heads are made of phosphorous which is very reactive when struck and lit. The oxygen family • The oxygen family contains three nonmetals (oxygen, sulfur, and selenium). • These elements usually gain or share two electrons. • Oxygen is one of the most important elements which keeps the human species alive. • Oxygen, like nitrogen is a diatomic molecule (O2), and can also form a triatomic molecule (O3) called ozone. • Oxygen is very reactive and can combine with most other elements. • Oxygen is the most abundant element in the Earths crust and the second most abundant in the atmosphere. • Sulfur which is another member of the Oxygen family which is used to make Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) The halogen family • Group 17 contains fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. • Halogen actually means “salt forming” • Halogens gain or shares only one electron with other elements to make compounds. • Halogens are very dangerous when in a pure form. • Example of dangerous halogens are bromine which can cause significant burns, bromine also reacts with silver to produce photos and images on xray film. Inert gases • The elements in group 18 are the inert gases. • The other name for the inert gases are the “noble gases” • These gases do not usually share, gain, or lose any electrons. • The inert gases tend to be very unreactive. • These gases are so unreactive they were not discovered until the late 1800s’. • Common uses for noble gases are neon signs (also xenon, and argon). • Also helium is used in helium balloons. Hydrogen • Hydrogen lacks a neuron and contain only one proton. • Although it makes up 90% of the universe, it actually makes up less that 1% of the Earths crust. • Most hydrogen is bound to oxygen to produce water. • Because hydrogen has some unique properties it is not placed in a particular group. Hydrogen can combine with most every other element, so it is reactive, but it is a gas, so it is placed in the far left corner of the periodic table by itself. Semimetals • Semimetals are between metals and nonmetals. • These elements have characteristics of both groups. • The most common metal is silicon (Si). • The most common place to find silicon is at the beach which is silicon dioxide or SiO2, which is called sand. • Semimetals are semiconductors which means they conduct electrical current under certain conditions. • The semiconduction characteristic of the semimetals is the reason why elements like Silicon and Gemanium are used for computer chips, lasers, and transistors.