Midterm Final Review
advertisement

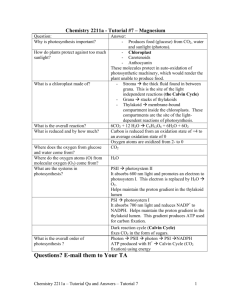
AP Bio Exam Review: Cell Energy (Respiration & Photosynthesis) • Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds • C6H12O6 +6O2 6H2O + 6CO2 +E • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones • 6H20+6CO2 + E C6H12O6 +6O2 Concept 8.3 ATP powers cellular work by coupling exergonic reactions to endergonic reactions • A cell does three main kinds of work: – Mechanical – Transport – Chemical • To do work, cells manage energy resources by energy coupling, the use of an exergonic (energy releasing) process to drive an endergonic (energy absorbing) one Concept 8.4: Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by lowering energy barriers A catalyst is a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction An enzyme is a catalytic protein Hydrolysis of sucrose by the enzyme sucrase is an example of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction Substrate Specificity of Enzymes • The reactant that an enzyme acts on is called the enzyme’s substrate • The enzyme binds to its substrate, forming an enzymesubstrate complex • The active site is the region on the enzyme where the substrate binds Cofactors Cofactors are nonprotein enzyme helpers such as minerals Coenzymes are organic cofactors such as vitamins Enzyme Inhibitors Allosteric Regulation • a protein’s function at one site is affected by binding of a regulatory molecule at another site • Allosteric regulation may either inhibit or stimulate an enzyme’s activity Feedback Inhibition • In feedback inhibition, the end product of a metabolic pathway shuts down the pathway Energy Harvest • Energy is released as electrons “fall” from organic molecules to O2 • Broken down into steps: Food NADH ETC O2 – Coenzyme NAD+ = electron acceptor – NAD+ picks up 2e- and 2H+ NADH (stores E) – NADH carries electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC) – ETC: transfers e- to O2 to make H2O ; releases energy Cellular Respiration Mitochondrion Structure Citric Acid Cycle (matrix) ETC (inner membrane) Glycolysis Without O2 Fermentation • Occurs in plants and animals • Occurs in cytosol • Keep glycolysis going • No oxygen needed • Creates alcohol [+ CO2] or lactic acid O2 present Respiration • Release E from breakdown of food with O2 • Occurs in mitochondria • O2 required (final electron acceptor) • Produces CO2, H2O and up to 38 ATP (NADH, FADH2) Types of Fermentation Alcohol fermentation Lactic acid fermentation • Pyruvate Ethanol + CO2 • Ex. bacteria, yeast • Used in brewing, winemaking, baking • Pyruvate Lactate • Ex. fungi, bacteria, human muscle cells • Used to make cheese, yogurt, acetone, methanol • Note: Lactate build-up does NOT causes muscle fatigue and pain (old idea) PURPOSE = NAD+ recycled for glycolysis Various sources of fuel • Carbohydrates, fats and proteins can ALL be used as fuel for cellular respiration • Monomers enter glycolysis or citric acid cycle at different points ENERGY aerobic (with O2) glycolysis anaerobic (without O2) (cytosol) Respiration (mitochondria) Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) electron transport chain chemiosmosis fermentation Oxidative Phosphorylation ethanol + CO2 (yeast, some bacteria) lactic acid (animals) Leaf cross section Sites of Photosynthesis Vein Mesophyll • mesophyll: chloroplasts mainly found in these cells of leaf • stomata: pores in leaf (CO2 enter/O2 exits) • chlorophyll: green pigment in thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts Stomata CO2 O2 Mesophyll cell Chloroplast 5 µm Outer membrane Thylakoid Thylakoid Stroma Granum space Intermembrane space Inner membrane 1 µm Photosynthesis = Light Reactions + Calvin Cycle “photo” “synthesis” Light Reactions Both respiration and photosynthesis use chemiosmosis to generate ATP Calvin Cycle = produce 3C sugar (G3P) Photorespiration: low carbon-fixation when stomata closed in hot, dry climate C3 C4 CAM C fixation & Calvin C fixation & Calvin in C fixation & Calvin at together different cells different TIMES Rubisco PEP carboxylase Organic acid (normally fixes CO2) fixes CO2 Mesophyll cells Mesophyll: fix CO2 Bundle Sheath: Calvin Cycle Night: fix CO2 in 4C acids Day: Calvin Cycle Ex. rice, wheat, soybeans Ex. sugarcane, grass Ex. cacti, pineapple, succulent Comparison RESPIRATION PHOTOSYNTHESIS • Plants + Animals • Needs O2 and food • Produces CO2, H2O and ATP, NADH • Occurs in mitochondria membrane & matrix • Oxidative phosphorylation • Proton gradient across membrane • Plants • Needs CO2, H2O, sunlight • Produces glucose, O2 and ATP, NADPH • Occurs in chloroplast thylakoid membrane & stroma • Photorespiration • Proton gradient across membrane