Chapter 2 - TeacherWeb

Chapter 2
Data in Science
Section 1: Tools and Models
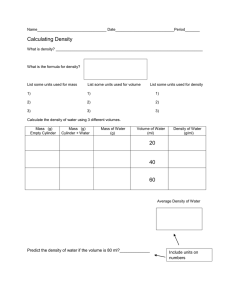
Vocabulary mass amount of matter in an object volume amount of space something occupies measure of the size of an object in a 3D space density amount of a matter in a given volume
D = mass/volume D= m/v
Vocabulary temperature measurement of how hot/cold substance is model representation of object or a system
Vocabulary theory a system of ideas that explains many related observations and is supported by a large body of evidence
Law descriptive statement or equation that reliably predicts events under certain conditions
Tools in Science
Need to be accurate use the proper tool
Making Measurements
International System of Units aka “metric system” based on multiples of 10
Making Measurements
Length meter (m)
Mass kilogram (kg)
1 kg = 2.2 lbs volume liter ( L )
1 mL = 1 cm³
Density ratio of mass to volume amount of matter inside
Models in Science used to simplify complex concepts physical sketch or scale train mathematical weather economics conceptual big bang theory
Models in science
Right size models help to make large items easy to see models brings to life unseen concepts sound waves
Limitations only as good as information put into it
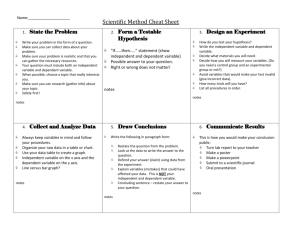
Making Scientific Progress
Models: summarize info tool for communication
Making Scientific Progress
Scientific Theory based upon repeated tests of a hypothesis explains and predicts
Law summary of multiple experiments tells you how things work stronger than theory
Section 2: Organizing Data
Vocabulary independent variable dependent variable axis
Vocabulary independent variable the factor that is deliberately manipulated dependent variable the factor that changes as a result of the independent variable being changed
Vocabulary axis one of two reference lines that mark the borders of a graph.
Dependent Variable
Independent Variable
Creating a Data Table organization is key gather data from research data table with 2 columns independent variable goes on x-axis factor that is changed in an experiment dependent variables goes on y axis changes as a result of the independent variable
Creating a Data Table
Controlled parameter factors that stay constant throughout the experiment variable parameter factors that change in an experiment
Creating a Graph highly visual easy format to see information
Axis x-axis is horizontal x-axis is independent variable y-axis is vertical y-axis is dependent variable
Creating a table
Range the extent of each variable subtract the smallest value from the largest value
Range: x axis:
6 days- 1 days = 5 days y axis
65 deg - 40 deg = 25 degrees
Creating a Table
Scale each axis has its own scale factor
Data Points plot data points first then find line of best fit captures the most data linear
Creating a Table
Labels!
each axis and a title
Patterns Shown by Graphs trend direction or pattern of data straight line = linear curved line = non-linear
Patterns Shown by a Graph
Positive or Negative Relationship
Sec 3: Analyzing Your Data
vocabulary
Mean
Median
Mode
Slope
Vocabulary mean
- the number obtained by adding up the data and dividing by the sum of the occurances.
- aka… AVERAGE
- median
- middle number when data arranged in order from lowest to highest
Vocabulary mode
- most frequently occurring value slope
- measure of the steepness of a line
- ratio of rise over run
Why Mathematics?
• Math is international language
• measures properties
• exact
• patterns can be seen
Accuracy of Data
• make sure tools are functioning correct
• make sure you are using tool properly
Reproducing Data
• data must be reproducible in future experiments
• verifies the results
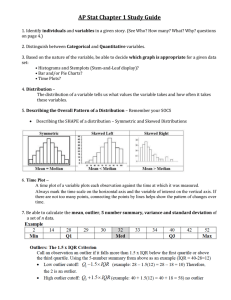
Describing Data Sets
mean
average
find the mean of
26, 20, 15, 27
Describing Data Set
median
the middle number
Describing Data Set
Mode
➔ number that appears most often
Slope of a Line
➔ rate of change
➔ slant of a line
◆ rise over run
◆ change of y values divided by the change of x values
Slope of a Line
Positive, Negative, or horizontal lines