The Human Genome
advertisement

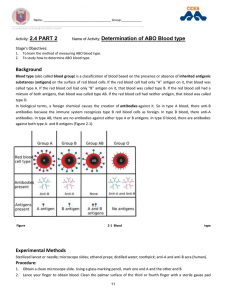
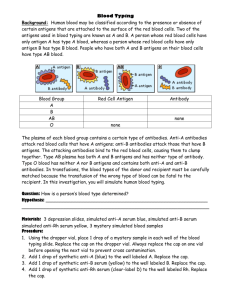
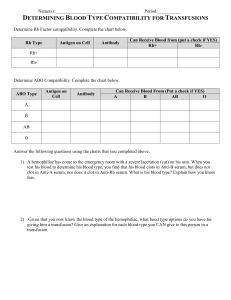
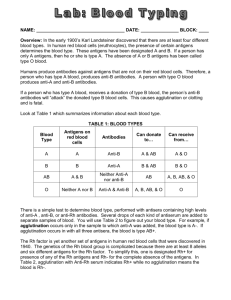
The Human Genome Chapter 12 Karyotypes and Pedigrees The Human Genome In humans, diploid (2n) = 46 That 44 means somatic cells have 46 chromosomes autosomal chromosomes and a pair of sex chromosomes Pedigrees A pedigree is a diagram that traces a single trait through several generations Individuals shaded in have attached earlobes. Is this trait dominant or recessive? RECESSIVE!! Partially shade carriers and label genotypes Solution: A Pedigree for a sex-linked recessive trait: Shade in known carriers and label genotypes. Solution: The Human Genome Chapter 12 Blood Typing and Chromosomal Genetic Disorders Use only to type blood in lab (serum reacts to antigens present) Blood Typing Chart Blood Type A B AB O Rh+ Rh- Genotypes Antigens Antibodies Donate to Receive from Reaction to Anti-A Reaction to Anti-B Reaction to Anti-Rh Use only to type blood in lab (serum reacts to antigens present) Blood Typing Chart Blood Type Genotypes A IAIA, IAi B IBIB, IBi AB IAIB O ii Rh+ ++, +dominant Rh- -recessive Antigens Antibodies Donate to Receive from Reaction to Anti-A Reaction to Anti-B Reaction to Anti-Rh Use only to type blood in lab (serum reacts to antigens present) Blood Typing Chart Blood Type Genotypes Antigens Antibodies A IAIA, IAi A Anti-B B IBIB, IBi B Anti-A AB IAIB AB none O ii none Anti-A Anti-B Rh+ ++, +dominant Rh none Rh- -recessive none *only if exposed to antigen Donate to Receive from Reaction to Anti-A Reaction to Anti-B Reaction to Anti-Rh *Rh- mothers can be exposed to the Rh antigen if the fetus is Rh+ Use only to type blood in lab (serum reacts to antigens present) Blood Typing Chart Blood Type Genotypes Antigens Antibodies Donate to Receive from A IAIA, IAi A Anti-B A,AB A,O B IBIB, IBi B Anti-A B,AB B,O AB IAIB AB none AB AB,A, B,O O ii none Anti-A Anti-B A,B, AB,O O Rh+ ++, +dominant Rh none pos pos or neg Rh- -recessive none *only if exposed to antigen pos or neg neg only Reaction to Anti-A Reaction to Anti-B Reaction to Anti-Rh *Rh- mothers can be exposed to the Rh antigen if the fetus is Rh+ Use only to type blood in lab (serum reacts to antigens present) Blood Typing Chart Blood Type Genotypes Antigens Antibodies Donate to Receive from Reaction to Anti-A Reaction to Anti-B Reaction to Anti-Rh A IAIA, IAi A Anti-B A,AB A,O clumps - B IBIB, IBi B Anti-A B,AB B,O - clumps AB IAIB AB none AB AB,A, B,O clumps clumps O ii none Anti-A Anti-B A,B, AB,O O - - Rh+ ++, +dominant Rh none pos pos or neg clumps Rh- -recessive none *only if exposed to antigen pos or neg neg only - *Rh- mothers can be exposed to the Rh antigen if the fetus is Rh+ Nondisjunction Occurs when a chromosome or chromosomes fail to separate in meiosis Individuals end up with the wrong number of chromosomes ( < or > 46 total) Risk factor increases with age Nondisjunction of Autosome Down Syndrome caused by trisomy 21 (3 copies of chromosome #21) Nondisjunction of Sex Chromosomes Turner Syndrome (karyotype 45, XO): Female; sterile; sex organs do not develop at puberty Klinefelter’s Syndrome (Karyotype 47, XXY): Male; infertility; fewer secondary sex characteristics; variations are 48, XXXY and 49, XXXXY