IS IT BLOOD?
advertisement
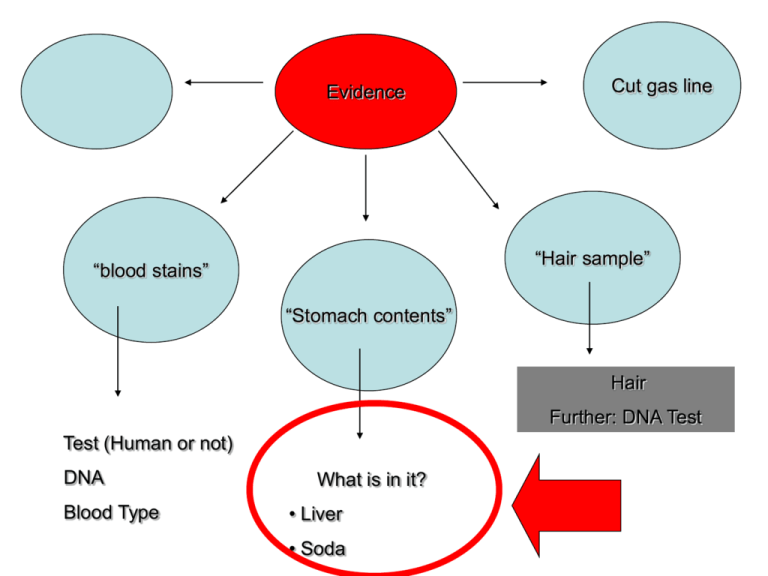
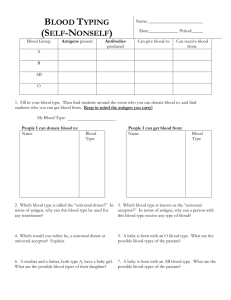
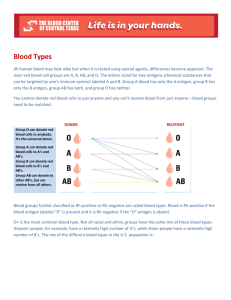
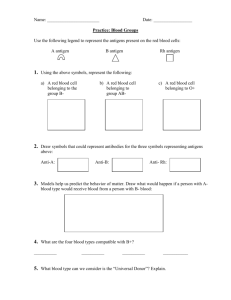
Evidence Cut gas line “Hair sample” “blood stains” “Stomach contents” Hair Further: DNA Test Test (Human or not) DNA Blood Type What is in it? • Liver • Soda Who’s blood is it? Forensic Characterization of Bloodstains Three questions to answer: 1. Is it blood? 2. From what species did the blood originate? 3. If the blood is human, how closely can it be associated with a particular individual? How can a Blood Sample be used for identification? 1. IS IT BLOOD? Presumptive Tests suggests but does not confirm the presence of blood; indicates that other tests should be performed • negative result means the substance IS NOT blood • positive result means the substance IS LIKELY blood (could be) https://ecrimescenechemistrymiller.wikispaces.com/notes+on+serology Kastle-Meyer Test (phenolphthalein/peroxidase test) when a blood stain, hydrogen peroxide and phenolphthalein reagent are mixed, Sensitivity: 1:10,000 (if 1 drop of blood were present in a bucket with 10,000 drops of water, the PHTH test would still turn pink) hemoglobin - Blood contains hemoglobin (carries oxygen and makes blood red) which contains a heme group which contains an Fe which can catalyze the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide the oxidation of the hemoglobin in the blood produces a deep pink color Who’s blood is it? Stephen Sasz Evan Roberts David Host Student Spencer Rhodes Black hair Blond hair Red hair The cell membrane of RBCs has molecules in its surface that act as identification badges so immune system can recognize it as a normal component. Normal Red Blood Cell ANTIBODIES Foreign IMMUNE SYSTEM CHEMICAL MARKERS BLOOD TYPES Blood can be classified by either: A. Blood Type ABO identified by the type of antigen (antigen A or antigen B) B. Rhesus Factor another type of antigen (Rhesus positive or Rhesus negative) So, what is an ANTIGEN? The differences in human blood are due to the presence or absence of certain chemicals called antigens. Individuals have different types and combinations of these chemicals. Antigen = Antibody Generating Agent Antigens are located on the surface of the red blood cells and the antibodies are in the blood plasma. Blood Group A If you belong to blood group A, you have A antigens on the surface of your red blood cells Blood Group B If you belong to blood group B, you have B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells Blood Group AB If you belong to blood group AB, you have both A and B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells Blood Group O If you belong to blood group O, you have no antigens on the surface of your red blood cells Blood Group Notation According to the above blood grouping systems you can belong to any of the following 8 blood groups A Rh+ A RH- B Rh+ B Rh- AB Rh+ AB Rh- O Rh+ O Rh- Blood transfusions who can receive blood from whom? Type O is the universal donor It has no antigens, so will not start the production of any antibodies. Type B can donate to other type Bs but can also donate to type AB. However, an O recipient can only accept blood from an O donor. Type B can accept blood from other type Bs but also from a type O donor Type A can donate to other type As, but can also donate to type AB. Type AB can only donate to other type ABs. Type A can accept blood from other type As but also from a type O donor However, Type AB can accept any type of blood (universal acceptor). Donor Type Receiver O A B AB O A B AB Donating blood – The Rh factor Source : http://nobelprize.org/educational_games/medicine/ The Rh factor on the red blood cell's surface is also an antigen. Those who have it are called Rh+. Those who haven't are called Rh-. Blood Typing 1. Place a drop of the blood sample in each well of the blood typing slide. Replace the cap on the dropper vial. Note: Always replace cap before opening next vial to prevent contamination. 2. Add a drop of anti-A (Blue) serum to the well labeled A. Replace cap. 3. Add a drop of anti-B (Yellow) to the well labeled B. Replace cap. 4. Add a drop of anti-Rh (clear) to the well labeled Rh. Replace cap. 5. Using a different color mixing stick for each well (blue for anti-A, yellow for anti-B, white for anti-Rh), gently stir the blood sample and anti-serum drops for 30 seconds. Discard each mixing stick after use to avoid contamination. 6. Carefully examine the thin films of liquid mixture left behind. Observe for: RESULT (-) + Appearance Film remains uniform in appearance Granules present Positive result indicates the blood type 7. Record results in the data table. Answer with a YES or NO. Type A blood Blood Typing Activity to find out 3 Suspect’s Blood Types Sample 1 (Demo) Sample 2 Evan Anti-A Anti-B Rh Blood Type EVIDENCE BLOOD: TYPE O+ Sample 3 Stephen Sample 4 David