Visual Basic Application
advertisement

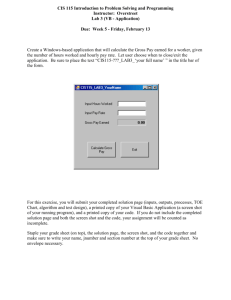
CIS 115 Lecture 4 Create a Windows-based application that will calculate the Gross Pay earned for a worker, given the number of hours worked and hourly pay rate. Clearly define the problem and identify what the program is to do Purpose: To calculate a worker’s gross pay Input: Number of hours worked, hourly pay rate Process: Multiply number of hours worked by hourly pay rate (result is the user’s gross pay) Output: Display a message indicating the user’s gross pay Traditional Procedural Approach - Develop an algorithm: Display message: "How many hours did you work?" Allow user to enter number of hours worked Store the number the user enters in memory Display message: "How much are you paid per hour?" Allow the user to enter an hourly pay rate Store the number the user enters in memory Multiply hours worked by pay rate and store the result in memory Display a message with the result of the previous step This well-defined, ordered set of steps for solving a problem is called an algorithm. VB (GUI) Approach – Identify required controls and events/handlers Inputs - entered into the program via Controls: Hours Worked Hourly Pay Rate Processes - initiated by Events and carried out by the code contained in the corresponding Event Procedures: Calculate Gross Pay ▪ Gross Pay = hoursWorked * hourlyPayRate Output - displayed to the user via Controls: Gross Pay Inputs (controls): Hours Worked Textbox, Label (title/prompt) Hourly Pay Rate Textbox, Label (title/prompt) Processes (events/event procedures): Calculate Gross Pay Button(click) ▪ Gross Pay = hoursWorked * hourlyPayRate Exit Program Button(click) ▪ End Outputs (controls): Gross Pay Earned Label (display result), Label (title) Design the Interface – TOE Chart Task, Object, Event Plan the interface BEFORE creating in VB Examines all of the tasks involved in solution Task (T) Object (O) Event (E) Input Hours Worked Textbox, Label None Input Pay Rate Textbox, Label None Output Gross Pay Label (display), Label (title) None Calculate Gross Pay Button Click Exit Program Button Click Make a list of the controls needed Define values for each control's relevant properties: Control Type Form TextBox Label TextBox Label Label Label Button Button Control Name (Default) txtHoursWorked (Default) txtPayRate (Default) lblGrossPay (Default) btnCalcGrossPay btnExit Text "Wage Calculator" "" "Number of Hours Worked" "" "Hourly Pay Rate" "$0.00" "Gross Pay Earned" "Calculate Gross Pay" “Exit" Make a list the events/procedures needed Develop an algorithm for each procedure Event btnCalcGrossPay_Click Event Procedure Code Algorithm Get hours worked from txtHoursWorked Get hourly pay rate from txtPayRate Multiply hours worked by hourly pay rate Assign result to lblGrossPay btnClose_Click End the application Visualize the application running on the computer and design its user interface Creating the Visual Basic Application - Event Driven Programming Steps Create the Interface / Window first ▪ Input ▪ Output Set the Properties ▪ Configure the appearance and behavior of the controls Then Code the Application ▪ Processes - Event Handing Methods Create the Interface - Use Visual Basic to create the forms and other controls identified in the previous step This is the first use of Visual Basic, all of the previous steps have just been on paper In this step you develop the portion of the application the user will see Label Label Label 2 Buttons Text Box Text Box Label Set Properties - Use Visual Basic to set properties for the forms and other controls from list you made earlier In this step you still developing the portion of the application the user will see Control Type Form TextBox Label TextBox Label Label Label Button Button Control Name (Default) txtHoursWorked (Default) txtPayRate (Default) lblGrossPay (Default) btnCalcGrossPay btnExit Text "Wage Calculator" "" "Number of Hours Worked" "" "Hourly Pay Rate" "$0.00" "Gross Pay Earned" "Calculate Gross Pay" “Exit" Create the Events/Procedures - Use Visual Basic to create and write the code for the event procedures identified earlier In this step you develop the methods behind the click event for each button Unlike the interface, this portion of the application is invisible to the user btnCalculate Button Click Event Assignment statement lblGrossPay.text = Val(txtHoursWorked.text) * Val(txtPayRate.text) ▪ Gets data from txtHoursWorked.text and txtPayRate.text ▪ Assigns results from hours * rate calculation to lblGrossPay.text Val changes the text input from the text box into a number btnExit Button Click Event End 3 Major Types of Errors Syntax Errors – Language Errors Caught by the Compiler & Interpreter Visual Basic – wavy line under problem code Run-Time Errors Program will not run to normal completion Program Crashes Logic Errors Program Runs but produces incorrect results Attempt to run the application - find syntax errors and runtime errors Correct any syntax errors found – indicated by wavy blue line All syntax errors must be removed before Visual Basic will create a program that actually runs Find and correct and correct any runtime errors until program runs to normal completion Run the application using test data as input Run the program with a variety of test data Must test for expected and unexpected input ▪ negative numbers, blank text box, etc. ▪ will talk about how to deal with invalid input later Check the results to be sure that they are correct Correct any logic errors found Repeat this step as many times as necessary Homework 2 Visual Basic Application See handout for details and due date Questions?