An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 1
advertisement
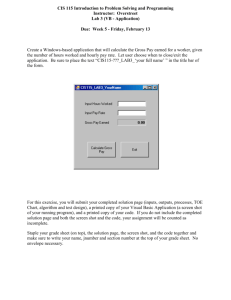
An Overview of Visual Basic .NET Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 1 Methods of Programming Procedural Languages Constructed as a set of procedures (operational, functional units) Often used in text-based environments Object-Oriented Constructed as a set of objects Objects have data elements (i.e. properties) and perform actions (i.e. methods) Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 2 Object-Oriented/Event-Driven Languages Simplifies the task of programming GUI applications. In object-oriented/event-driven languages, the emphasis of a program is on the objects included in the user interface (such as scroll bars and buttons) and the events (such as scrolling and clicking) that occur when those objects are used Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 3 OOP Terminology OOP is an acronym for object-oriented programming It means that you are using an object-oriented language to create a program that contains one or more objects OOD is an acronym for object-oriented design Like top-down design, which is used to plan procedure-oriented programs, OOD is also a design methodology, but it is used to plan objectoriented programs OOD divides a problem into one or more objects Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 4 Object An Object: Is Anything that can be seen or touched Has attributes (properties) that describe it Has behaviors(events) that the object can either perform or have performed on it Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 5 Types of Controls Ch1\Program2 on p.10 (This application can be found in the student data files) Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 6 Starting and Customizing Visual Studio .NET Visual Studio .NET is Microsoft’s newest integrated development environment (IDE) Includes programming languages such as Visual Basic .NET, C++ .NET, C# .NET and J# Can Create: A Windows-based application has a Windows user interface and runs on a desktop computer A console application A Web-based application, on the other hand, has a Web user interface and runs on a server Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 7 Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 8 .NET Framework New Concepts Common Language Runtime (CLR) Execution engine Memory management Intermediate Language (IL) VB.NET compiles to IL Just-in-time compilation Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 9 Language Interoperability .NET: Type System Standard C# Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET VB.NET 10 The Programming Process (1.5) The Programming Process Consists of Several Steps, Which Include Design, Creation, Testing, and Debugging Activities Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 11 Example of an Object This is a GUI object Data includes number-ofhours-worked, hourly-payrate, and gross-pay-earned Action is to calculate and display gross-payearned, given number-of-hours-worked and hourly-pay-rate Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 12 Step 1 of Developing an Application Clearly define what the program is to do For example: Purpose: To calculate the user’s gross pay Input: Number of hours worked, hourly pay rate Process: Multiply number of hours worked by hourly pay rate (The result is the user’s gross pay) Output: Display a message indicating the user’s gross pay Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 13 Step 2 of Developing an Application Visualize the application running on the computer and design its user interface Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 14 Step 3 of Developing an Application Make a list of the controls needed Partial list: Type TextBox TextBox Label Name txtHoursWorked txtPayRate lblGrossPay Button btnCalcGrossPay Button btnClose Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET Description Allows the user to enter the number of hours worked. Allows the user to enter the hourly pay rate Displays the gross pay, after the btnCalcGrossPay button has been clicked When clicked, multiplies the number of hours worked by the hourly pay rate When clicked, terminates the application 15 Step 4 of Developing an Application Define the Values of Each Control's Relevant Properties: Control Type Form Label Label Label Label TextBox TextBox Button Button Control Name (Default) (Default) (Default) (Default) lblGrossPay txtHoursWorked txtPayRate btnCalcGrossPay btnClose Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET Text "Wage Calculator" "Number of Hours Worked" "Hourly Pay Rate" "Gross Pay Earned" "$0.00" "" "" "Calculate Gross Pay" "Close" 16 Step 5 of Developing an Application Make a list of methods needed for each control: Method Description btnCalcGrossPay_Click Multiplies the number of hours worked by the hourly pay rate These values are entered into the txtHoursWorked and txt-PayRate TextBoxes The result is stored in the lblGrossPay Text property btnClose_Click Terminates the application Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 17 Step 6 of Developing an Application Create a pseudocode version of each method: Pseudocode is a combination of English and a programming language For this application: Store Number of Hours Worked times Pay Rate in grossPay. Store the value in grossPay in lblGrossPay.Text. Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET Hourly 18 Step 7 of Developing an Application Check the code for errors: Go step by step through the code, running it in your head as though the computer is running it Keep track of where in the code is being executed Keep track of the values of all of the variables Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 19 Step 8 of Developing an Application Use Visual Basic .NET to create the forms and other controls identified in step 3 This is the first use of Visual Basic .NET, all of the previous steps have just been on paper Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 20 Step 9 of Developing an Application Use Visual Basic .NET to write the code for the event procedures and other methods created in step 6 This is the second step on the computer Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 21 Step 10 of Developing an Application Attempt to run the application - find syntax errors Correct any syntax errors found and repeat this step as often as necessary All of the syntax errors must be removed before Visual Basic .NET will create a program that you can actually run on the computer Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 22 Step 11 of Developing an Application Run the application - once all syntax errors are fixed Run the program with a variety of test data Check the results to be sure that they are correct Correct any errors found Repeat steps 10 and 11 as many times as necessary Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 23 Visual Studio .NET Recent Projects Toolbox Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET Solution Explorer Dynamic Help 24 Starting a New Project Installed .NET Products Name and Location Of Project Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET Type of Project Name of Project 25 Toolbox (autohidden) Visual Basic .NET Project information Windows Form object Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET Properties window 26 The Visual Basic .NET Environment Design Window Solution Explorer Window Dynamic Help Window Properties Window Docked and Floating Windows Toolbox Overview-An Overview of Visual Basic .NET 27