2/1: Atomic Structure
advertisement

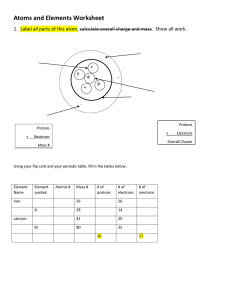
Atomic Structure- History and The Nucleus Philosophers and Scientists • Know how the following contributed to the history of the atom: Philosophers from History of the Atom video – Empedicles – Leucippus – Aristotle – Gassendi Modern Day scientists – Dalton • atoms could not be divided • all elements of a given element are the same • different atoms could join to form compounds – Thomson • the plum pudding model • negatively-charged "plums” surrounded by positively-charged "pudding” – Rutherford • atom is made up of a central charge surrounded by a cloud of orbiting electrons – Bohr • electrons are in levels around the nucleus Next week Structure of the Atom Particle Charge Mass (atomic mass units) 1 Location Proton positive + Neutron neutral Ø 1 nucleus Electron negative - 0.0006 orbit, level, cloud nucleus • The nucleus – the center of the atom composed of protons and neutrons – 99.9% of the atom’s mass is here – about 100,000 times smaller than the entire atom – the atomic number of an atom is the number of protons (+ charged) in the nucleus • The # of electrons (- charged) equals the # protons in a neutral atom. – the atomic mass or mass number of an atom is the sum of the protons and neutrons – Isotopes • atoms with the same number of protons (and therefore the same element) but with a different number of neutrons.