chapter 5 study guide
advertisement

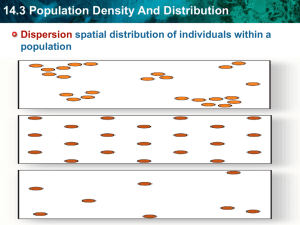
AP Environmental Science Name__________________________ Chapter 5 Study Guide 5-1 How do species interact? CORE CASE STUDY. A. Why are otters important to the marine ecosystem on the west coast of the US? B. What is their current status? 1. Five basic species interactions are: A. B. C. D. E. 2. Define interspecific competition: 3. What must happen for competition to stop? 4. How does competition help drive evolution? 5. What is resource partitioning? 6. Explain the different ways predators attempt to catch prey: 7. Explain the different ways prey species escape predators: AP Environmental Science Name__________________________ SCIENCE FOCUS: A. Why are sea otters important to kelp forests? B. What are the threats facing the kelp forests? C. Why are kelp forests important to the ecosystem? 8. What is coevolution? 9. What is symbiosis? 10. Define the following symbiotic relationships and give an example of each A. Parasitism, B. Mutualism C. Commensalism 5-2 What limits the growth of populations? 11. In what ways can populations change? 12. Describe each of the three general patterns of population distribution occurring in a habitat, and when they might occur: A.Clumping B. Uniform C. Random 13. Most organisms tend to live in groups, what are the advantages of this? AP Environmental Science Name__________________________ 14. Describe the four variables that influence/govern population size: A. Birth B. Death C. Immigration D. Emigration 15. What are the three general categories of age structure of a population? Describe each: A. B. C. 16. Explain range of tolerance: 17. What is the limiting factor principle? SCIENCE FOCUS: A. Why have sea otters been so slow to recover from the human activities that have affected their population numbers? 18. Describe the reproductive patterns of rapidly growing populations: 19. What is environmental resistance? 20. What is exponential growth? Draw a graph representing it. AP Environmental Science Name__________________________ CASE STUDY. A. Why were white tailed deer populations in decline a century ago? B. How were population numbers able to rebound? C. What problems has this increase in numbers caused? 21. What is logistic growth? 22. What is overshoot? 23. Why does overshoot often occur? 24. What is dieback? 25. Define carrying capacity? 26. Describe some of the different reproductive patterns exhibited in nature: 27. What is population density? 28. What is a density-independent population control? Give an example. 29. What is a density-dependent population control? Give an example. 30. Describe the four general types of population fluctuations in nature. Diagram Each. A. Stable AP Environmental Science Name__________________________ B. Irruptive C. Cyclic D. Irregular 31. What are some examples of human population crashes? 5-3 How do communities and ecosystems respond to changing environmental conditions? 32. What is ecological succession? 33. Describe primary ecological succession: 34. Describe secondary ecological succession: 35. How do forest fires or deforestation affect ecological succession? 36. How has ecological succession been viewed classically? 37. How does actual ecological succession work compared to the classic view? AP Environmental Science Name__________________________ SCIENCE FOCUS: A. Describe each of the three factors that affect ecological succession: 1. Facilitation 2. Inhibition 3. Tolerance 38. Define each of the following in ecological terms: A. Stability B. Inertia C. Resilience