Save
advertisement
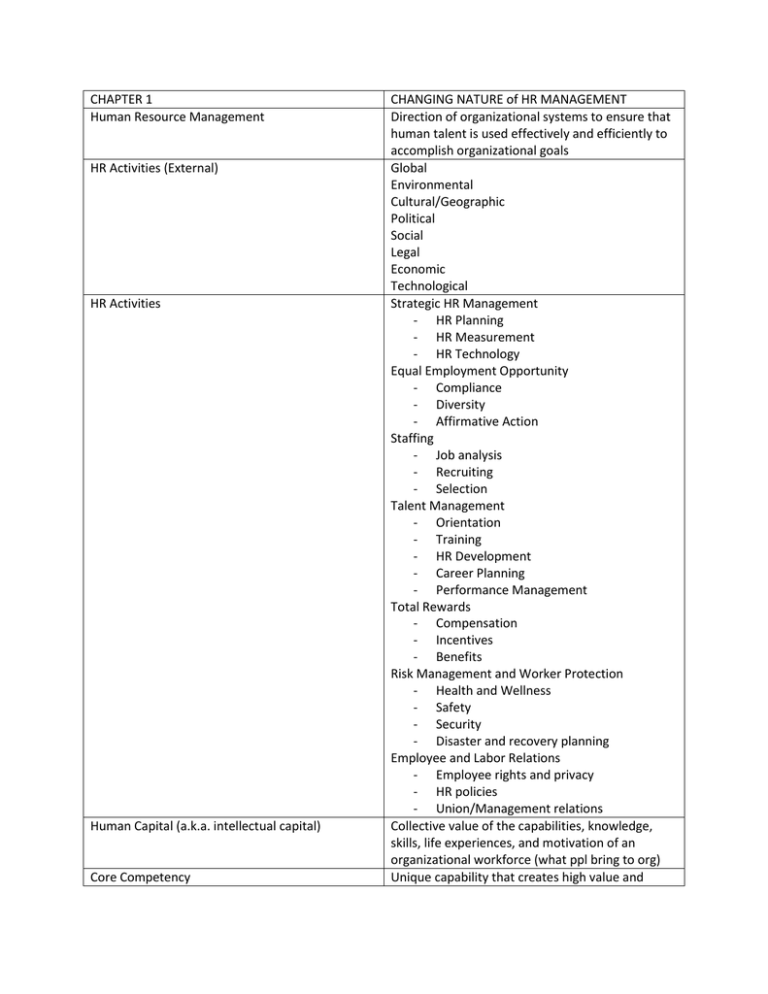
CHAPTER 1 Human Resource Management HR Activities (External) HR Activities Human Capital (a.k.a. intellectual capital) Core Competency CHANGING NATURE of HR MANAGEMENT Direction of organizational systems to ensure that human talent is used effectively and efficiently to accomplish organizational goals Global Environmental Cultural/Geographic Political Social Legal Economic Technological Strategic HR Management - HR Planning - HR Measurement - HR Technology Equal Employment Opportunity - Compliance - Diversity - Affirmative Action Staffing - Job analysis - Recruiting - Selection Talent Management - Orientation - Training - HR Development - Career Planning - Performance Management Total Rewards - Compensation - Incentives - Benefits Risk Management and Worker Protection - Health and Wellness - Safety - Security - Disaster and recovery planning Employee and Labor Relations - Employee rights and privacy - HR policies - Union/Management relations Collective value of the capabilities, knowledge, skills, life experiences, and motivation of an organizational workforce (what ppl bring to org) Unique capability that creates high value and HR Management Challenges HR management roles Human resource management system (HRMS) Four elements of ethics program -> ethical behavior HR Ethics and Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) HR Competencies HR generalist HR specialists Strategic HR Management differentiates an organization from its competition. (strengths that are foundation for creating a competitive adv for an organization) Globalization of Business Economic and Technological Changes Occupational Shifts (from manu and agri to telecom Workforce availability and quality concerns Growth in contingent (temporary) workforce Technological shifts and the internet Workforce demographics and diversity Racial/Ethnic Diversity Women in the workforce Aging workforce Administrative (50% -> 10%) – focus on admin and recordkeeping Operational and employee advocate (30% -> 30%) – HR activities and employee ‘champion’ Strategic (20% -> 60%) – contributor to org results and keeper of org ethics; workforce planning, compensation strategies Integrated system providing information used by HR management in decision making. Emphasizes that making HR decisions, not just building databases, is primary reason for compiling data in information system. - Written code of ethics and std of conduct - Training on ethical behavior - Means for employees to get advice on ethical situations they face - Systems for confidential reporting of ethical misconduct or ques. Behavior Sox was passed by congress to make certain that publicly traded companies followed accounting controls that would reduce the likelihood of illegal and unethical behaviors Strategic contribution Business knowledge HR delivery HR technology Personal Credibility Person who is responsible for performing a variety of HR activities People who have in-depth knowledge and expertise in limited areas of HR Use of employees to gain or keep a competitive adv, resulting in greater organizational Cost Leadership (organizational strategy) Differentiation (organizational strategy) Factors that affect strategic HR management HR management plays sig role in dimensions or organizational effectiveness Approaches to improving Organizational Prod. Unit Labor cost Organizational culture Human Resource Planning effectiveness Approaches competition on the basis of low price and high quality of product or service (Wal-Mart) More appropriate in a more dynamic environment characterized by rapid change, and requires continually finding new products and new markets (Intel or Microsoft) Organizational strategies + Organizational culture - (a) Need for HR: Quantity and skill levels Competitive/financial environment + current organizational situation - (b) Available financial resources A + B - >> - Equal employment - Recruiting and selection - Hr development - Compensation - Performance management - Employee relations - Organizational productivity & hr efforts - Org effectiveness and Fin contributions - Cust Service and quality linked to HR strat - Org culture and org effectiveness Restructuring the organization - revising org structure - reducing staff - aiding in m&a Re-designing work - changing workloads and combining jobs - re-shaping jobs due to tech changes -- Goals INCREASE Org Prod Aligning HR activities - attracting and retaining employees - Training & dev and eval employees - compensating emp and other HR act Outsourcing - using domestic vendors/contractors opposed to emp - Outsourcing op internationally --Goals – Reduce unit labor costs Useful way of measuring HR productivity; calculate: avg cost of workers/avg levels of output Shared values and beliefs in an organization Process of analyzing and identifying the need for and availability of HR so that the organization can meet its objectives FOCUS OF HR PLANNING Steps in HR planning Process HR strategies Internal Jobs and Skills Audit Forecasting Estimating Internal Labor Supply for given unit Sources Succession planning Worker adjustment and retraining notification (WARN) HR Metrics To have - right number of human resources - with the right capabilities at the right times in the right places - Review organizational objectives and strat o Scan external environment for labor supply changes o Assess internal workforce capabilities - Develop forecasting o Id organizational need for people o Forecast supply of ppl available - Formulate HR strategies and plans Means used to anticipate and manage the supply of and demand for human resources - What jobs exist now? - How many ppl are performing each job? - What are the reporting relationships of jobs? - How essential is each job? - What jobs will be needed to implement future organizational strategies? - What are the characteristics of anticipated jobs? Uses information from the past and the present to identify expected future conditions. – short range, intermediate range (1-5 years) and long range 5+ Current Staffing – Projected outflows + inflows Inflows - External hires - Internal transfers - Promotions - Recalls Outfalls - Promotions - Turnover - Terminations - Demotions - Retirements - Deaths - Layoffs Process of identifying a longer-term plan for the orderly replacement of key employees Requires employers to give 60-day notice before implementing a layoff or facility closing that involves more than 50 people Specific measures tied to hr performance indicators. Developed using costs, quantity, Full-time equivalents (FTEs) Return on Investment (ROI) Economic Value Added (EVA) Strategic and Operational HR Metrics Balance Scorecard (four perspectives) Benchmarking HR Audit CHAPTER 2 Psychological contract quality, timeliness and other designated goals Measure equal to one person working full-time for a year Calculation showing the value of expenditures for HR activities Net operating profit of a firm after the cost of capital is deducted Strategic - Rev. generated/FTE - NI before tax/FTE - Ratio of managers to non-managers - labor costs as % of total Op costs - ROI of human cap ex - HR dept exp as % of total exp - Payroll/benefits costs as % of rev Operational - annual turnover rate - benefits costs as % of payroll - Training ex/FTE - Avg time to fill openings - workers comp costs/FTE - # of applicants per opening - Absenteeism by employee level/dept Financial Internal business process Customer Learning and growth Compares specific measures of performance against data on those measures in other organizations Formal research effort that evaluates the current state of HR management in an organization. Attempts to evaluate how well HR activities in each of the HR areas (staffing, compensation, etc) have been performed, so that management can id areas for improvement ORG/INDIVIDUAL RELATIONS & RETENTION Unwritten expectations employees and employers have about the nature of their work relationships Employers provide: - Competitive compensation and benefits - Career development opportunities - Flexibility to balance work and home life Employees contribute: - Continuous skill improvement and increased productivity Job satisfaction Job dissatisfaction Organizational commitment Employee engagement Continuance Commitment Factors Factors affecting job satisfaction and org commit Absenteeism Measuring absenteeism Rates Approaches to control absenteeism Turnover Types of Turnover - Reasonable time with the organization - Extra effort when needed Positive emotional state resulting from evaluating one’s job experiences Occurs when one’s expectations are not met Degree to which employees believe in and accept organizational goals and desire to remain with the organization Extent to which an employee is willing and able to contribute Suggests that decisions to remain with or leave an organization ultimately are reflected in employee absenteeism and turnover stats The Individual (Ability + Motivation + Support) The Job (Design + Job Elements) - Job satisfaction/dissatisfaction - Organizational commitment Absenteeism/Turnover Any failure to report for work as scheduled or to stay at work when scheduled (cost ~$645/emp/yr) Voluntary (avoidable) Involuntary – illness, death in family (# of person-days lost through job absence during period / (Avg # employees) X (# workdays)) X 100 Incidence Rate - # of absences / 100 employees each day Inactivity Rate - % of time lost to absenteeism Severity Rate – Avg time lost/absent employee during specified period (month or yr) Attendance reward programs “no fault” policies Paid time off programs Unused leave buy-back Illness verification Disciplinary actions Occurs when employees leave an organization and have to be replaced. – related to job satisfaction and organizational commitment Involuntary Turnover – terminated for poor performance or work rule violations Voluntary Turnover – leave by choice Functional turnover – lower performing or disruptive employees leave Dysfunctional turnover – key individuals and high performers leave at critical times Measuring Turnover (Separations = departures) Determining Turnover Costs Individual Performance factors Performance (P) Formula Motivation Organizational Culture Myths of retaining employees Drives of Retention Uncontrollable Turnover –reasons outside the control of the employer Controllable – could be influenced by the emp # of emp separations during month/Total # employees at midmonth X 100 Separation Costs – HR staff/supervisor time to prevent separations, exit int time, unemployment exp, legal fees, accrued vacation, cont benefits Replacement Costs – recruiting/advertising exp, search fees, staff time salaries, emp referral fees, relocation, testing Training Costs – paid orientation, training staff time Hidden Costs – lost productivity, decreased customer service, other employee turnover 1. Individual ability to do the work 2. Effort expended 3. Organizational support Ability (A) X Effort (E) X Support(S) Desire within a person causing that person to act; usually act for one reason: to reach a goal Pattern of shared values and beliefs of a workforce Money is the main reason people leave Hiring has nothing to do with retention If you train people you are only training them for another employer Do not be concerned about retention during a merger If solid performers want to leave, the company cannot hold them Job design and work - Job/person matching - Time flexibility - Work/life balancing Career Opportunities - Training/development and mentoring - Career planning/advancement Rewards - Competitive pay and benefits - Performance and compensation - Recognition Employee relationships - Fair, nondiscriminatory treatment - Supervisory/management support - Coworker relations Characteristics of the employer - Culture and values Job design Job enlargement Job enrichment Person/job fit Characteristics of People and Jobs Flex time Job sharing Work/Life balancing Exit Interview Keys to managing retention - Management - Job security Organizing tasks, duties and responsibilities into a productive unit of work. Can influence: performance, job satisfaction, physical and mental health Broadening the scope of a job by expanding the # of different tasks to be performed Increasing the depth of a job by adding responsibility for planning, organizing, controlling or evaluating the job. Examples – giving an entire job rather than piece, providing more freedom and authority, increasing accountability etc. Important concept of matching characteristics of people with characteristics of jobs Job Characteristics (mgmt can control) - tasks, authority/responsibility, policies/procedures, tools, variety, time requirements, social opportunities, working conditions, stress People Characteristics (mgmt cannot control) - motivation, interests, energy level, personality variables, physical characteristics, honesty, intelligence Employees work a set number of hours a day but vary starting and ending times Two employees perform the work of one FT job Different work arrangements Leave for children’s school functions Compressed workweek Job sharing On-site child/adult care Telecommuting Employee assistance plans On-site health services Wellness programs Fitness facility Individuals are asked to give their reasons for leaving the organization Measurement and Assessment - Absence/turnover measurement - Employee surveys - Exit interviews - Data analysis Managing Retention - Recruiting and selection - Orientation and training CHAPTER 4 Staffing process Job analysis in perspective Task based job analysis Task Duty Responsibilities Competency based job analysis Competencies Essential Job Functions (required by ADA) Marginal job functions Job description Performance standards - Compensation and benefits - Career development and planning - Employee relations Evaluation and follow-up - Regular review of turnover data - Tracking of intervention results - Adjustment of intervention efforts STAFFING Matches people with jobs through job analysis, recruiting and selection JOB ANALYSIS - Methods (Questionnaires, interviews, observation, logs/diaries) - Sources of data (employees, supervisors, managers, job analyst) - Conducted by (job analyst (HR), outside consultant, supervisor/manager USED FOR –> Job Descriptions and Job Specifications LEADS TO USE FOR – EEO/ADA, HR planning, recruiting, selection, compensation, training, performance management, health, safety, and security, employee/labor relations Most common and focuses on tasks, duties and responsibilities performed in a job Distinct, identifiable wk activity comp of motions Larger work segment composed of several tasks that are performed by an individual Obligations to perform certain tasks and duties Considers how the knowledge and skills are used Individual capabilities that can be linked to enhanced performance by individuals or teams - Technical competencies – specific knowledge and skills employees have - Behavioral competencies – customer focus, team orientation, technical expertise, results orientation, communication effectiveness, leadership, conflict resolution, innovation, adaptability, decisiveness Are the fundamental duties of a job Duties that are part of a job but are incidental or ancillary to the purpose and nature of the job Identifies the tasks, duties, and responsibilities of a job (what, why, where and briefly it is done) Flow directly from a job description and indicate Job specifications Recruiting Labor markets Flexible staffing Job posting External Recruiting sources Advantages/Disadvantages of Internal Recruiting Adv/disadv of external recruiting what the job accomplishes and how performance is measured in key areas of the job description List the knowledge, skills and abilities (KSAs) an individual needs to perform a job satisfactorily (education, experience, work skill requirements, personal abilities, mental and physical requirements) Process of generating a pool of qualified applicants for organizational jobs The external supply pool from which employers attract employees Uses workers who are not traditional employees. Allows an employer to avoid some of the cost of full-time benefits such as vacation pay and pension plans, as well as to recruit in a somewhat different market. System in which the employer provides notices of job openings and employees respond by applying for specific opening. Colleges, universities and schools Labor unions Employment agencies Competitive and media sources Job fairs and special events Advantages - morale of the promotee is usually high - Firm can better assess a candidates ability - lower recruiting costs for some jobs - process is a motivator for good performance - causes a succession of promotions - firm has to hire only at entry level Disadvantages - ‘inbreeding’ results - those not promoted may experience morale problems - employees may engage in ‘political’ infighting for promotions - mgmt development program is needed Advantages - new blood brings new perspectives - training new hires is cheaper and faster b/c of prior external exp. - new hire has no group of political supporters in organization - new hire may bring new industry insights Disadv - firm may not select someone who will fit the job Advantages and Disadvantages of Internet Recruiting Recruiting Evaluation and Metrics Evaluating the cost of recruiting Yield ratio Selection rage Selection and Placement Truisms Placement Person/job fit Selection criteria Job Performance, Selection Criteria Validity or org - process may cause morale problems for internal candidate not selected - new employee may require longer adjustment time Advantages – saved money vs newspaper ad, employment agencies and search firms – save time Disadvantages – more unqualified applicants, additional work for HR staff, just browsers, new legal concerns Quantity and quality of applicants; time to fill Recruiting expenses/number of recruits hired – problem what else should be included…background checks, relocation etc. Other methods: - Cost benefit analysis - Yield ratios - Selection rate Compare the number of applicants at one stage of the recruiting process with the number at another stage Percentage hired from a given group of candidates Hire hard, manage easy Good training will not make up for bad selection Ultimate purpose of selection. Fitting a person to the right job Simple but important concept that involves matching the KSAs of people with the characteristics of jobs Characteristic that a person must have to do a specific job successfully Elements of job performance (qty of work, quality of work, compatibility with others, presence at work, length of service, flexibility) Selection criteria for employee characteristics (Ability, motivation, intelligence, conscientiousness, appropriate risk for employer, appropriate permanence) Predictors of selection criteria (experience, past performance, physical skills, education, interests, salary req, degrees, test scores, personality measures, work references, prev job and tenure, drug test, police record) Correlation between a predictor and job performance. Occurs to the extent that a predictor actually predicts what it is supposed to predict Reliability Realistic job preview (RJP) Application forms – Purposes Selection process flow chart Selection testing Cognitive Ability Tests Physical Ability Tests Work sample tests Big five personality characteristics Situational judgment tests Structured Interviews Extent to which it repeatedly produces the same results over time – consistency of predictors used in selection Applicants are provided with an accurate picture of the job, including organizational realities so they can better evaluate their own job expectations. Prevent unrealistic expectations - Record of the applicants desire - Provides interviewer with a profile - Basic employee record for hired people - Can be used for research on effectiveness of selection process Application job interest Preemployment screening Application form Tests & interview Background investigation Additional interview (optional) Conditional job offer Medical exam/drug test Job placement Ability Tests Personality tests Honesty/integrity tests Measures an individuals thinking, memory, reasoning, verbal and mathematical abilities Measure an individuals abilities such as strength, endurance, and muscular movement Require an applicant to perform a simulated task that is part of the target job Agreeableness (cooperative, good-natured, softhearted, tolerant, trusting) Extroversion (sociable, talkative) Emotional Stability (NOT these characteristics – Neurosis, depression, anger, worry, insecurity) Openness to experience (flexibility in thought, open to new ideas, broad minded, curious, original) Conscientiousness (achievement – oriented, careful, hardworking, organized, responsible) Designed to measure a persons judgment in work settings – situation and list of possible solutions Uses a set of standardized questions asked of all applicants so that comparisons can more easily be made. EFFECTIVE INTERVIEWING – plan the interview, control the interview, use effective questioning techniques Less Structured interview Problems in the interview Background screening (four goals) Negligent hiring Negligent retention Occurs when the interviewer wings it asking questions that have no identified direct purpose such as tell me about yourself Snap judgments Negative emphasis Halo Effect – occurs when interviewer allows a prominent characteristic to overshadow other evidence Baises and stereotyping Cultural noise – comes from what the applicant believes is socially acceptable rather than knows is factual Show that the employer exercised due diligence in hiring Provide factual information about a candidate Discourage applicants with something to hide Encourage applicants to be honest on applications and during interviews (costs $100-200/applicant) When an employer fails to check an employees’ background and the employee later injures someone on the job; hired an unfit employee, background check was insufficient or did not research potential risk factors that would have prevented the positive decision Employer becomes aware that an employee may be unfit for employment but continues to employ the person and the person injures someone