Protein Structure
advertisement
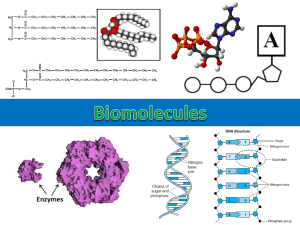
Protein Structure FDSC400 Protein Functions • Biological? • Food? Protein Structure 20 Amino Acids Coded in DNA Primary Secondary Self assembly to a single (native) structure. Depends on primary structure and solution conditions Tertiary ( Quaternary Denatured ) Common in foods. Many nonnative forms depending on protein structure, solution conditions (& history) and ingredient interactions Amino Acids • The monomer unit of proteins R O C C H NH2 HO Chiral carbon (L-series) •R is the side chain. •One of 20 different chemical compounds •Some R-groups are acid (other alkali) •Some R-groups are water soluble (others are not) Amino Acids Polar • Uncharged. Ser, Thr, Asn, Gln, Cys • Positive (basic). Arg, Lys, His • Negative (acidic). Asp, Glu, Non-Polar • Aliphatic. Ala, Ile, Leu, Met, Pro, Val • Aromatic. Phe, Trp, Tyr Example Amino Acids Alanine Phenylalanine Glutamic acid Peptide Bonds R O C R C H NH2 HO O C C H NH2 Amino acids R O HO R C O C C H NH HO Water C H NH 2 Peptide Bonds O H N : C N H N H O + N H R O H + N OC O O + R N H Disulfide Bonds C SH H2 HS C H2 [O] C S S C H2 H2 • Two cysteine molecules under oxidizing conditions • Intermolecular or intramolecular crosslink a-Helix • N-H to C=O hydrogen bonds in 4th succeeding A.A. • Hydrogen bonds parallel to axis • Typically amphiphilic Amphiphilic 2° Structures Hydrophilic Hydrophobic b-Sheet • C=O and N-H perpendicular to chain form inter-segment H-bonds • Parallel or antiparallel b-strands typically 5-15 A.A. • More stable than a-helix b-sheet Protein Folding Hydrophobic amino acids Peptide chain Tertiary Structure Types of Tertiary Structure Globular Disordered Fibrous Many insoluble amino acids, protein tends to minimize surface/volume ratio Interacts well with water and takes up a random configuration Strong secondary structure allows protein to retain a non-spherical shape Quaternary Structure Folded protein unable to contain some hydrophobic residues Dimerized protein shields the hydrophobic amino acids from water