Therapeutic Communication (CC)
advertisement

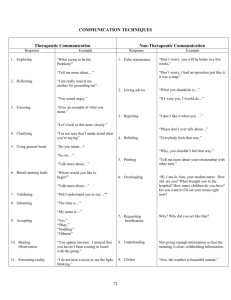
Therapeutic Communication C. Calzolari Therapeutic Communication • Used by nurses and people in the helping professions • Also called “active” or “purposeful” communication • Requires “active listening” or “listening between the lines” Therapeutic Communication • Blocks to therapeutic communication • Impede effective communication • Often due to using the “social” communication techniques • Examples • • • • • • The word “why” Minimizing/belittling False reassurance/social clichés Advising Closed-ended questions Agreeing/disagreeing Clicker Question 3. True or false: The word “why” is a block to communication. Answer Correct answer: True Rationale: The word “why” connotes disapproval or displeasure. Techniques of Therapeutic Communication • Clarifying terms • Reflecting • Open-ended questions (the essence of successful communication) • Require more than a “yes” or “no” answer • Silence Techniques of Therapeutic Communication • Asking for what you need • Identifying thoughts and feelings • Empathy (not sympathy) • Using general leads • Stating implied thoughts and feelings • Giving information (not advice) Clicker Question 4. Nurses must be sure that the terms they choose are correct and mean the same thing to all parties involved in the interaction. This is considered what type of therapeutic communication? A. Reflecting/parroting B. Empathy C. Clarifying terms D. Silence Answer Correct answer: C Rationale: English is a very complex language to learn. Some people use terms very literally. Nursing is a profession that is filled with inference and nuance; it is highly affective. Because of that, it is very important to clarify terms with patients and other workers. Nurses must be sure that the terms they choose are correct and mean the same thing to all parties involved in the interaction. The technique is easy to learn: Simply asking. “When you say ‘I can’t do that,’ what do you mean?” is one way of clarifying a statement. Communicating with Persons who are Experiencing Psychosis • Nurse’s responsibility is to focus on: • Reducing the patient’s anxiety • Decreasing defense mechanisms • Encouraging participation in therapeutic and social events, • Raising feelings of self-worth, • Increasing medication compliance Communicating with Persons who are Experiencing Psychosis • Hallucinations • Hearing voices • First, nurse should seek to understand what the voices are saying or telling the patient to do. • Suicidal or homicidal messages necessitate immediate safety measures. • Approach the patient in a nonthreatening & nonjudgmental way. • Call patient by name, make eye contact, speak simply. • Second, identify the feelings the patient is experiencing . • Third, use distraction techniques. Communicating with Persons who are Experiencing Psychosis • Delusions • • • • Are false fixed beliefs First, assess for safety. Second, clarify reality of patient’s experience. Third, identify the patient’s feelings. • Do not argue with patient. • Do not touch patient. • Fourth, engage patient in reality-based activities. Communicating with Persons who are Experiencing Psychosis • Paranoia • The nurse is to approach the patient in a nonjudgmental, respectful manner. • Use clear and simple language. • Be honest and consistent. • Explain all procedures and policies. • Do not laugh, whisper or talk quietly when the patient cannot hear what is being said. Associative Looseness • Seen with schizophrenia • Autistic Thoughts • Poorly organized thinking • Patient appears confused and disorganized • Increased use suggests increased anxiety and inability to control external and internal stimuli • • • • Tell patient you are having difficulty understanding what he/she is saying. Look for recurring themes in communication. Re-orient Involve patient in reality based activities. Manipulative Behavior • Manipulation can be a defense mechanism. • Recognize splitting. • Be clear with expectations. Anxious Behavior • Gain trust • Be calm • Be honest • Do not discount emotions Aggressive Behavior • Aggressive statements most often begin with the word “you.” • Assertive vs. Aggressive • Crisis Intervention • • • • • Ensure Safety Diffuse the Situation Determine Problem Decrease Anxiety Level Return Person to Pre-Crisis Level Question • Which of the following is an example of a therapeutic, openended question? • A. “Why did you do that, Mrs. Jones?” • B. “How can I help you, Mr. Thompson?” • C. “Can I help you, Ms. Greene?” • D. “Please, can I ask you a question, Mark?” Question • The nurse plans to have a therapeutic communication with the client. To begin that therapeutic communication the nurse must first establish _________________ with the client. Question • The schizophrenic patient tells you, “I know that the man down the hall wants to kill me.” How should you respond? • A. “Don’t worry, I will protect you from him.” • B. “No one will hurt you here, what makes you say that?” • C. “It must be frightening to think that. Let’s walk over here to join in afternoon activities.” • D. “That is not true, you need to go to your room right away.” Question • Your patient has refused all of your attempts to care for him. You say: • A. “I’d like to help you; what can I do?” • B. “Why don’t you like me?” • C. “What is the matter with you?” • D. “You must do this; physician’s orders!” Question • You are one of the nurses monitoring the dining room during dinner. A male patient who has schizophrenia asks a table mate to “please pass the pepper.” When the table mate does so, the first patient throws the pepper shaker at you. He or she screams, “Now look what you’ve done! There are spiders all over my food! I can’t eat this! Get the spiders out of there!” Your best response is: • A. “Those aren’t spiders; that is the pepper you asked for!” • B. “I don’t see any spiders. Let’s go to the game room for a little while before you try eating again.” • C. “Where are the spiders? I am also afraid of them!” • D. “It is inappropriate for you to throw things; you need to go to the locked unit now.” Question • Your patient is commenting that the physician has not been in to visit for two days. You say: • A. “I hate it when that happens!” • B. “What do you need to know?” • C. “Well, he is very busy!” • D. “You feel ignored by your physician?” Question • An example of a therapeutic response conveying support or encouragement is: • A. “That must feel very discouraging.” • B. “Maybe you shouldn’t worry quite so much.” • C. “Why do you say that?” • D. “Nobody would deliberately try to hurt you.” Question • Linda is pacing the floor and appears extremely anxious. The day shift nurse approaches Linda in an attempt to lessen her anxiety. The most therapeutic statement by the nurse would be: • A. How about watching a football game? • B. Tell me how you are feeling today. • C. What do you have to be upset about now? • D. Ignore the client. Question • You observe a patient in the family lounge. She appears to be talking to herself. You want to find out what is wrong. Your best approach to her might be: • A. “Who are you talking to?” • B. “Please stop talking. You are disturbing the other people.” • C. “I saw your lips moving. Can you tell me what you are talking about?” • D. “Why are you talking to yourself?” Question • A nurse is assigned to care for a client who is experiencing disturbed thought processes. The nurse is told that the client believes that the food is being poisoned. Which communication technique does the nurse plan to use to encourage the client to eat? • • • • A. Open-ended questions and silence B. Focusing on self-disclosure regarding food preferences. C. Stating the reasons that the client may not want to eat. D. Offering opinions about the necessity of adequate nutrition. Question • A nurse is providing care to a client admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of anxiety disorder. The nurse is talking with the client and the client says, “I have a secret that I want to tell you. You won’t tell anyone about it, will you?” The appropriate nursing response is which of the following? • • • • A. “No, I won’t tell anyone”. B. “I cannot promise to keep a secret”. C. “If you tell me the secret, I will tell it to your doctor”. D. “If you tell me the secret, I will need to document it in your record”. Question • The nurse in the mental health unit reviews the therapeutic and nontherapeutic communication techniques with a nursing student. Which of the following are therapeutic communication techniques? (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY) • • • • • • A. Restating B. Listening C. Asking the patient, “Why?” D. Maintaining neutral responses E. Giving advice or approval F. Providing acknowledgment and feedback