CUSTOMER_CODE SMUDE DIVISION_CODE SMUDE
advertisement
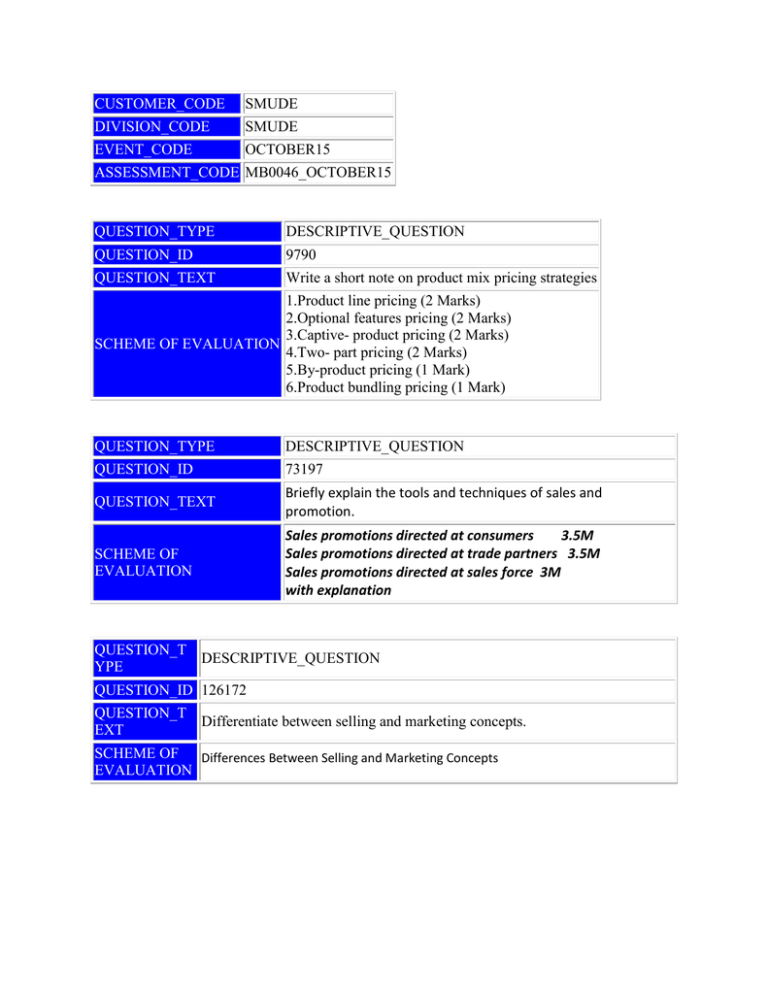
CUSTOMER_CODE SMUDE DIVISION_CODE SMUDE EVENT_CODE OCTOBER15 ASSESSMENT_CODE MB0046_OCTOBER15 QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 9790 QUESTION_TEXT Write a short note on product mix pricing strategies 1.Product line pricing (2 Marks) 2.Optional features pricing (2 Marks) 3.Captive- product pricing (2 Marks) SCHEME OF EVALUATION 4.Two- part pricing (2 Marks) 5.By-product pricing (1 Mark) 6.Product bundling pricing (1 Mark) QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 73197 QUESTION_TEXT Briefly explain the tools and techniques of sales and promotion. SCHEME OF EVALUATION Sales promotions directed at consumers 3.5M Sales promotions directed at trade partners 3.5M Sales promotions directed at sales force 3M with explanation QUESTION_T DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION YPE QUESTION_ID 126172 QUESTION_T Differentiate between selling and marketing concepts. EXT SCHEME OF Differences Between Selling and Marketing Concepts EVALUATION QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 126177 Explain the stages in the new product development. QUESTION_TEXT SCHEME OF EVALUATION 1. Concept generation and market structure identification Idea generation The first stage of new product’s evolution begins with an idea for the product. Hence this stage is also termed as ‘idea generation’. Ideas may originate from the following sources: Sales personnel Marketing personnel Research and development department Top management executives Production department Customer service decisions Employee suggestion system Customers Competitive products Foreign products Market structure analysis The next step in the process of new product development process is to implement a market structure. This process delineates the consumer’s perception of market by building a map outlining the critical consumer dimensions, positioning existing brands on the perceptual map, and indicating favourable new product opportunities. Sales potential In this step, the potential of a new product entry into the market structure is estimated. The purpose of developing such a model helps in establishing a rough estimate of the size of the business potential. It also helps in establishing a base case for using this model for continuous monitoring of the sales forecast and its advances throughout the new product development process. Concept screening At this stage, the ideas collected are scrutinised to eliminate those inconsistent with the product policies and objectives of the firm. The main intention of this phase is only to eliminate unsuitable ideas as quickly as possible. 2. Advertising development This stage of new product development involves the development of advertising and formulation of the product. All the advertising and technical developments of the product concept have a greater focus due to the results from the earlier stages. This stage typically involves two activities, viz. development of advertising strategy and product formulation. The main objective of advertising is to create advertising copy, which can reflect the product’s points of difference to the consumer. Asking the client servicing and creative team to observe the focus group discussion helps in initiating advertising strategy development process. Both the teams get a chance to look at the real consumers and listen to their opinion about the product category and product proposition. 3. Product formulation and testing The product formulation happens in the laboratory. During this stage, the ‘idea-on-the-paper’ is turned into a ‘product-on-hand’. In other words, the idea is converted into a product that can be produced and demonstrated. This stage is also termed as technical development. It is during this period that all developments of the product, from idea to final physical form, take place. The final decision whether a product should be developed on a commercial scale or not is decided at this stage because the time-lag required to attain this stage is long and it is possible that some adverse developments might have taken place during this period. 4. Testing the product In this stage of product testing, the new product manager can check the feasibility and accuracy of product performance. Thus, commercial experiments are necessary to verify earlier business judgments. The objective of this stage is to assess whether the product meets the technical and commercial specifications developed at various levels of concept development for ascertaining product acceptability. 5. Commercialisation and final launch In this stage, the product is submitted to the market and thus commences its lifecycle. Commercialisation is also the phase where marketing is most active in connection with the new product. This stage is considered to be a critical one for any new product and should therefore be handled carefully. For instance, it should be checked whether advertising and personal selling have been done effectively and whether proper outlets have been arranged for the distribution. Despite the care with which the previous development stages have been planned, unforeseen events can impair commercialisation seriously. The following activities are usually undertaken during this stage: Completing final plans for production and marketing Initiating coordinated production and selling programs Checking results at regular intervals All the stages explained above stress the fact that the development of a new product must pass through certain logical stages. Innovation is necessarily an orderly and predictable process and can be performed only in a sequence. For example, commercialisation cannot precede the development stage of a product. QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 126184 QUESTION_TEXT SCHEME OF EVALUATION What is retailing? Briefly explain the most important types of retailing? Retailing is the final connection in the marketing channel that brings goods from manufacturers to consumers. In other words, retailing is the combination of activities involved in selling or renting consumer goods and services directly to ultimate consumers for their personal or household use. Types Mom and pop stores and kirana stores Department stores Discount stores Category killers Specialty stores Superstores and hyper markets QUESTION_TYPE DESCRIPTIVE_QUESTION QUESTION_ID 126185 QUESTION_TEXT What are the differences between Macro and Micro Environment? Macro Last in size Macro environment cannot be controlled It is very unpredictable & SCHEME OF EVALUATION highly uncertain Very complex in nature It includes political, social, cultural, technological, demographic, economic, and natural environment Micro Small in size Can be controlled Not very unpredictable & low in uncertainty It simpler It includes customer, publics, competitions, suppliers and intermediaries