Classification of Living Organisms
advertisement

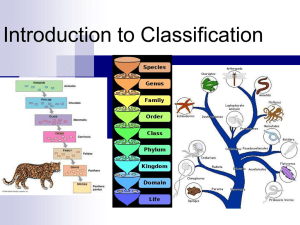
Put these in the correct order. • • • • • • • Order Class Species Genus Phylum Kingdom Family Classification of Living Organisms TAXONOMY _______________ = branch of biology that names and groups organisms Early Taxonomist Aristotle Linnaeus (300 B.C.) Image from: The first person to group or classify organisms was the Greek teacher & philosopher ARISTOTLE _______________ more than 2000 years ago. http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/history/aristotle.html Aristotle’s Classification - Two groups - Plants - based on size - Herbs - Shrubs - Trees - Animals – where they lived - Land - Air - Water Image from: http://www4.d25.k12.id.us/ihil/images/Cougar.jpg Common names can vary Example: puma, catamount, mountain lion, cougar . . . are all names for same animal By using a universally accepted scientific name, scientists can be sure they are discussing the same organism Common names vary Chipmunk Streifenhornchen (German) Tamia (Italian) Ardilla listada (Spanish) Image from: http://www.entm.purdue.edu/wildlife/chipmunk_pictures.htm Common names can be misleading Ex: A jellyFISH isn’t a fish, but a seaHORSE is! Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jellyfish Sea cucumber sounds like a plant but… it’s an animal! Image from: http://www.alaska.net/~scubaguy/images/seacucumber.jpg By mid 19th century, scientists recognized that using common names was confusing. Scientists agreed to use ____________ to give a Latin and Greek single name to each species. Linnaeus’s System Based on physical and structural similarities Developed the two word system of naming organisms • Binomial Nomenclature • First word = Genus • Second word = Species Linnaeus’s System Organisms are grouped in a hierarchy of 7 different taxonomic levels OR ____________ TAXONS Each organism has a two part scientific name = BINOMIAL _________________________ NOMENCLATURE Modern Classification System Based on Evolutionary relationships DNA comparisons Physiological comparisons (biochemistry) Anatomic comparisons (structure) Breeding behaviors Taxonomic Rankings Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Largest The more taxonomic rankings two organisms have in common the more alike those organisms are. Scientific Name Most Specific King Phillip came over from great Spain. Keep people close or fights get started. Kids prefer cheese over fried green spinach What has been added in the recent years that is missing? Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Class Mammalia Order Carnivora Family Felidae Genus Panthera Species leo http://www.vetmed.wisc.edu/dms/fapm/personnel/tom_b/2004-lion.jpg BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE (2-name naming system) 1st name = _______________ GENUS NAME – Always capitalized 2nd name = _________________ SPECIES NAME –Always lower case UNDERLINED or Both names are ______________ ITALICS written in ____________. GENUS = group of closely related species GENUS = Ursus Ursus arctos (Includes many kinds of bears) Ursus maritimus Ursus americanis SPECIES = unique to each kind of bear http://www.macecanada.com/images/bears/kodiak_bear.gif http://students.cs.byu.edu/~tole/Virtual%20Zoo/polar-bear.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Black_bear_large.jpg Binomial nomenclature Humans Homo sapiens Homo sapiens Image from: http://www.earlylearning.ubc.ca/images/photo_baby.jpg Which two organisms are the most closely related? Grizzly Bear White Tail Deer Bobcat Red Fox Polar Bear Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia Chordata Chordata Chordata Chordata Chordata Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Carnivora Artiodactyla Carnivora Carnivora Carnivora Ursidae Cervidae Felidae Canidae Ursidae Ursus Odocoileus Lynx Vulpes Ursus arctos virginianus rufus vulpes maritimus Cladograms Used to show the evolutionary relationships of derived characteristics Derived Characteristics – appear in recent organisms but not older organisms Bull Frog Snapping Turtle Kangaroo Tuna Lamprey Mammary Glands Amnion Dorsal and Ventral nerve cord Backbone Paired Legs The Three Domains Bacteria Kingdom Eubacteria Archaea Kingdom Archaebacteria Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Protista Characteristics of Living Things Organization Reproduction Adaptation Growth and Development Response Homeostasis In order to be classified organism must be alive Why Viruses are not Classified DNA surrounded by protein coat: Viruses are not living no reproduction The Prokaryotes Kingdom Eubacteria Prokaryotes - true bacteria Found everywhere Kingdom Archeabacteria Prokaryotes – ancient bacteria Found in hot springs, sulfur springs, salt lakes, inhospitable places The Eukaryotes Kingdom Protista Most diverse kingdom Mostly microscopic Most Unicellular Lacks a complex organ system May be autotrophic or heterotrophic Eukaryotes con’t Kingdom Fungi Heterotrophs May be multicellular or unicellular Absorbs nutrients from organic material in the environment Eukaryotes con’t Kingdom Plantae Eukaryotes con’t Kingdom Animalia