Introduction to Classification
advertisement

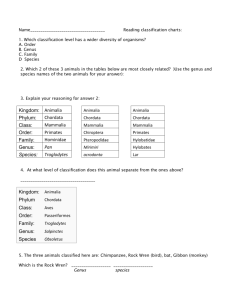
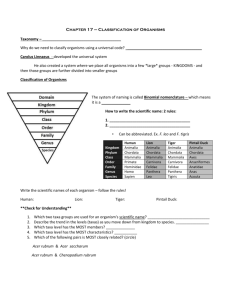
Introduction to Classification Taxonomy Taxonomy: branch of biology dealing with classification – grouping and naming organisms based on different characteristics Field of Taxonomy is continuously changing –more information is being gathered Why Classify? To identify differences in structure, functions, development, and evolutionary history of organisms Over ½ of human proteins are shared with other organisms Generally the more closely related the organism, the more similar the DNA To overcome language barriers – allows people to share information world wide History of Classification Aristotle (~350 B.C.) – developed first classification system of grouping organisms. Not grouped by similar structures or evolutionary similarities Plants versus Animals Carolus Linnaeus (1753 A.D.) – devised current classification system using binomial nomenclature Showed relationships and structural similarities between organisms Binomial Nomenclature 2 word naming system First word: Genus (group of similar species) Always Capitalize Second word: Species (often describes characteristic of the organism) Always lowercase The scientific name is always in latin (no longer used in conversation so it doesn’t change) Scientific name should always be italicized or underlined Why not use common names? Misleading starfish dragonfly Confusing blue jay, blue coat, corn thief dog, perro, chien Why not use common names? Many common names, but they all have only one scientific name! Pyrrhosoma nymphula Cyanocitta cristata Pisaster ochraceus Broader Grouping of Organisms: (Taxa) Domain – new category; broadest; 3 domains are recognized Kingdom – currently 6 are recognized Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species – most specific Acronyms to remember the order: Dearest King Phillip Came Over For Good Spaghetti Or Darling Kids Prefer Cheese Over Fresh Green Spinach Prokaryotes Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaebacteria Kingdom Protist Eukaryotes Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plant Kingdom Animal For a Human: Domain…….Eukaraya Kingdom…….Animalia Phylum…….Chordata Class…….Mammalia Order…….Primate Family…….Hominidae Genus…….Homo Species…….Sapien Linnaeus named humans Homo sapiens means “wise man” — perhaps in a show of hope & optimism Kingdoms Organisms in each Kingdom have similar characteristics: 1) Cell type (Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic) 2) Body form (Unicellular vs multicellular) 3) Method of obtaining food (Autotroph vs heterotroph) 4) Presence of complex organ systems Working through the Taxa Moving from kingdom down to species: The number of species decreases with each level of taxa The amount of similarity increases with each level of taxa What taxa would have a higher quantity of species, family or genus? In which taxa would the species have the most in common, order or class? Organism House cat Red Fox Wolf Gopher Fly Kindgom Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia Animalia Phylum Chordata Chordata Chordata Chordata Arthropoda Class Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Insecta Order Carnivora Carnivora Carnivora Rodentia Diptera Family Felidae Canidae Canidae Geomydiae Muscidae Genus Felis Vulpes Canis Thomomys Musco Species F. V. Fulva Domesticus C. Lupus T. Bottae M. domestica