Science-UNIT-4-vocabulary-flash-cards
advertisement
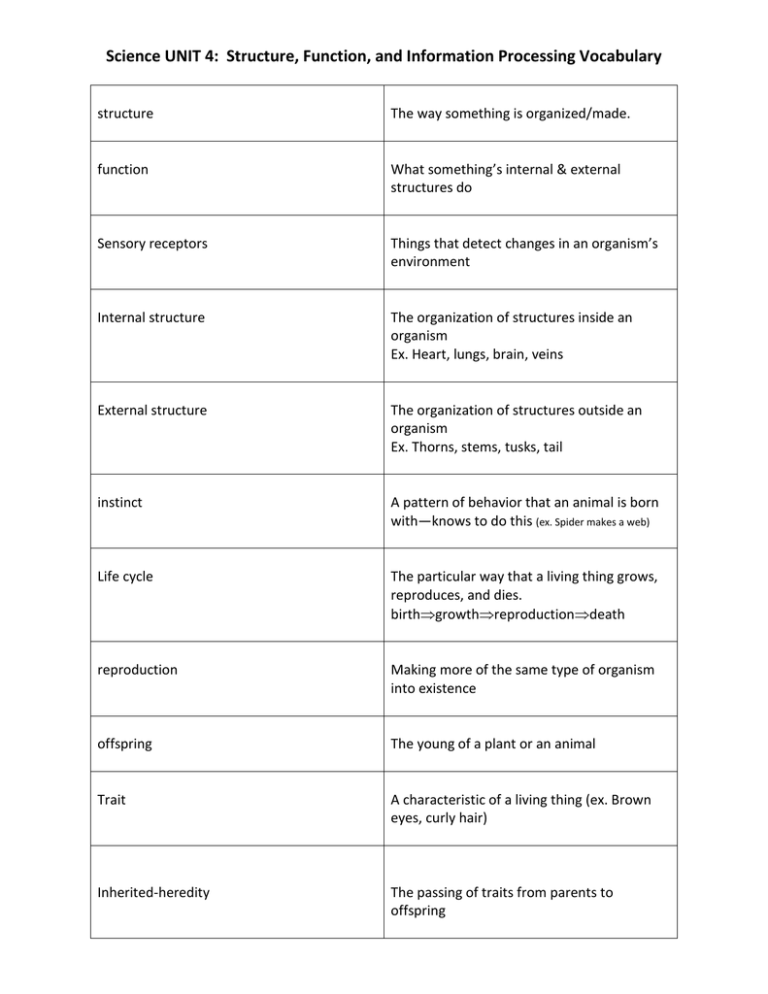
Science UNIT 4: Structure, Function, and Information Processing Vocabulary structure The way something is organized/made. function What something’s internal & external structures do Sensory receptors Things that detect changes in an organism’s environment Internal structure The organization of structures inside an organism Ex. Heart, lungs, brain, veins External structure The organization of structures outside an organism Ex. Thorns, stems, tusks, tail instinct A pattern of behavior that an animal is born with—knows to do this (ex. Spider makes a web) Life cycle The particular way that a living thing grows, reproduces, and dies. birthgrowthreproductiondeath reproduction Making more of the same type of organism into existence offspring The young of a plant or an animal Trait A characteristic of a living thing (ex. Brown eyes, curly hair) Inherited-heredity The passing of traits from parents to offspring organism A single, self-contained living thing adaptation A specific trait or behavior that helps an organism to survive (ex. Camouflage, beak shape) prey An animal that is hunted by another animal predator An animal that hunts other animals migration Seasonal movement of animals to find food, lay eggs, give birth, breed, etc. hibernation A deep sleep that allows some animals to survive through the winter metamorphosis The process of changes in form during an animal’s development. egglarvapupaadult (ELPA sometimes EN(nymph)A) vertebrates Animals with backbones: 5 classificationsfish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, birds (FARM B) invertebrates Animals without backbones: ex. Sponges, worms, crabs, insects, spiders Behavioral adaptation The way an animal acts to survive Physical adaptation Everything that makes up an animal’s body and helps it to survive Social interaction The way an animal behaves in a group in order to survive photosynthesis When a plant uses energy from the sun, water, and carbon dioxide gas to make its food Learned behavior A behavior that an organism doesn’t begin life with. A behavior that is usually taught by parents or adults of the species. Ex. Talking, hunting chlorophyll Made in special cells inside a plant and help the plant trap energy from the sun to make its food germination When a seed begins to grow/sprout pollination The transfer of pollen from one plant to another fertilization When plant cells join to make a seed(s) begin to form and grow The main structures of a plant are: Roots-anchor the plant; transport nutrients Stem-support plant; transport nutrients Leaves-make food for the plant Flower/fruit-makes seeds & holds and protects seeds









