Principles of Business & Marketing Chapter 5 Notes Chapter
advertisement

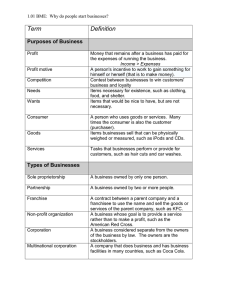
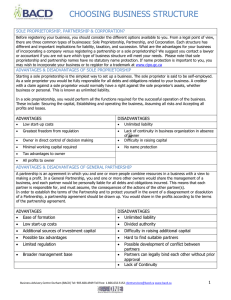
Principles of Business & Marketing Chapter 5 Notes Chapter Overview: To examine the forms of business ownership 5.1 Business in the US economy 5.2 Forms of Business ownership 5.3 Organizational Structure for Businesses 5.1 3 Goals: Describe the changing status of US Employment; discuss the role of business in the US economy, and Describe 3 major types of businesses. Key Terms: Contingent worker, intermediaries and service business. Notes: Jobs are shifting from manufacturing and agriculture to service jobs Employment data: Timeline- 9/11/2001 to 2003 recession- 2003 to 2008 6% economic growth- 2009 to present recession. Baby boomers: born 1946-1964. Largest age group ever 2020 average age of US worker will be 50 Growth segments of jobs are 20-30 year olds, Asian, Hispanic, and African-American workers. Caucasian is dropping from 68% in 2009 to 64% by 2018 Women fast growing also: 1960’s was 35%. By 2018 will be almost 50% Pressures on employees Economic downturn and downsizing, full time to part time, working long hours to keep job, wage cuts, benefits losses, 7-10 feel they do not spend enough time with their kids Contingent worker: one who has no explicit or implicit contract for long term employment. Temporary or on call workers. 5% of labor force expected to double in 10 years. Some like for flexibility of schedule. Sizes of US Businesses: 2009 all businesses worldwide produced more than 70 trillion dollars. US were responsible for almost 20 percent of this. 25 million full and part time businesses making these goods In US 19.5 million businesses have no employees other than the owner. 6.5 million employ fewer than 20 people 886,000 employ 20-100 people 182,000 employ 100 or more 890 employ more than 10000 Our economy has small business as the foundation for success. Roles of business: Most important to make and distribute products and services needed by consumers, government and other businesses. Provides employment. Wages paid purchase goods and services. Businesses pay taxes so governments can spend and provide services Impact on Community: Wages used to buy goods and services. Creates more jobs, housing needs, taxes to community. Small businesses locate near large ones. 6 activities performed by all businesses: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Generating ideas for new business. Make sure competitive Raising capital. Needed to start or grow business. Loans. Investors Employing and training personnel: recruiting, hiring and training Buying goods and services: all businesses buy goods and services. Marketing Goods and Services: bring awareness to users Maintain business records: needed to run business. Verification and tax reporting. 3 types of businesses: 1. Producers: create products and services used by individuals and businesses. Producers include: Extractors: take resources from nature. Oil, coal… Farmers: cultivate land and other resources to grow crops and raise livestock for consumption Manufacturers: get supplies from other producers and convert into products. 2. Intermediaries: businesses that sell goods and services. They are retailers and wholesalers. 3. Service Businesses: offer something that is intangible. No products. Dentists, Dr., painters, massage. Service fastest growing. 60% of US employment. 5.2 Forms of Business Ownership 3 Goals: Understand the 3 major forms of business ownership, Determine when each form of business ownership is appropriate, Recognize other specialized business ownership forms. Key terms: proprietorship, partnership, corporation, partnership agreement, articles of incorporation, franchise 3 major forms of ownership: 1. Proprietorship: a business owned and run by 1 person. Easiest form to start and end. Sole control. All profits. All liabilities. Must common. 2. Partnership: a business owned and controlled by 2 or more people. Similar to proprietorship. Partnership agreement needed. Each partner liable for all debts if fail. 3. Corporation: separate legal entity formed by documents filed with a state. Owned by one or more shareholders and managed by board of directors. More difficult to form and legal requirements. Protected from liability to only amount invested. Choosing a proprietorship: want total control. Easy to start. Tax advantage as take rate is your tax rate versus high corporation tax rates. Can take personal assets if fail. Choosing a partnership: can be a verbal agreement but better to be a written partnership agreement. Describes business, partner roles, investments, profit distribution, responsibilities. Advantage is extra expertise and funding with partners. Must work well together. Choosing a corporation: most popular for large businesses. Also can be for very small. Articles of incorporation: a written document that defines ownership and operations Corporate by-laws: operating procedures of corporation Board of Directors: people who make major policy decisions and financial decisions Advantage is liability is limited to your investment. Disadvantages: lots of record keeping, more laws, tax rate high Specialized Partnerships: Limited liability partnership: limits your liability to investment but cannot participate in day to day operations Joint Venture: 2 businesses operate for a limited time for a specific project Specialized Corporations: S Corporation: limited liability but all income passes through to owners and is taxed at lower personal tax rate LLC (Limited Liability Company) best features of partnership and corporation. No articles of incorporation needed. Non-profit: company that benefits the public and are free from taxes. Must be government approved. Cooperative: owned by a group that serves their needs. Purchase goods and services cheaper as a group. Large number of small businesses working together. Franchise: written contract granting permission to operate a business to sell products and services in a set way. Franchiser: company that owns and grants the rights (McDonalds, Subway,) Franchisee: the company purchasing the rights. 5.3 Organizational Structure for Businesses 2 Goals: Understand important principles in designing effective organization, Compare alternative organizational structures for businesses. Key terms: mission statement, goal, policies, procedures, organization chart An effective business has a clear purpose 1. Mission statement: a specific written statement of the reason a business exists and what it wants to achieve. Usually 2-3 sentences. 2. Goal: statement of expected or desired results. What needs to be achieved? 3. Policies: guideline used in making consistent decisions and actions 4. Procedures: descriptions of the way work is to be done. Guidance and direction for people in organization. Principles that guide effective organizations: 1. 2. 3. 4. Responsibility: obligation to complete specific work Authority: right to make decisions about how things should be accomplished Accountability: taking responsibility for the results achieved Unity of Command: a clear reporting relationship for all the staff. Who is the leader and how decisions will be made 5. Span of Control: number of employees assigned to a particular task and manager Organization Chart shows structure of an organization, classifications of work, and the relationships. Who reports to whom? Functional Organization Structure: work arranged by functions: production, operations, marketing and human resources. Report to managers who are responsible for that function. Same skills. Matrix Organizational Structure: work structured by specific projects, products or customer groups. Varied backgrounds are assigned together. Interesting and motivating. Work with many different people.