organizational structure - Home
advertisement

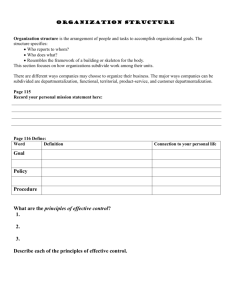
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE Organizational chart An organizational chart taht margaid a si: dna noitazinagro na fo erutcurts eht swohs sti fo sknar evitaler dna spihsnoitaler eht .sboj/snoitisop dna strap It usually shows the managers and subworkers who make up an organization. It shows the relationships between the the organization's staff members. organizational chart Line roirepus neewteb pihsnoitaler tcerid : .etanidrobus dna • Lateral tnereffid neewteb pihsnoitaler : .level lacihcrareih emas eht no stnemtraped • Staff laireganam a neewteb pihsnoitaler: a ot ecivda reffo ot saera rehto dna tnatsissa reganam enil • Functional tsilaiceps neewteb spihsnoitaler .saera rehto dna snoitisop • Organizational structure It refers to the way that an organization arranges people and jobs so that its work can be performed and its goals can be met. The relationships among these positions are illustrated graphically in an organizational chart ,The best organizational structure for any organization depends on many factors including the work it does; its size in terms of employees, revenue, and the geographic dispersion of its facilities; and the range of its businesses . Manager’s basic decisions Researchers generally identify four basic decisions that managers have to make as they develop an organizational structure, The organization's work must be divided into specific jobs . Departmentalization. Number of people and jobs that are to be grouped together must be decided. Number of people and jobs that are to be grouped together must be decided. Limitations of an organizational chart There are several limitations with organizational charts: It only shows 'formal relationships' and tells nothing of the pattern of human (social) relationships which develop . It shows nothing about the managerial style adopted (e.g. autocratic or democratic) It very quickly becomes out-of-date, especially in large organizations which change their staff regularly . The Benefits of Organizational Charts Organizational charts provide managers with specific departmental information that can then be used as a baseline for planning, budgeting and workforce modeling. charts can be linked directly to spreadsheets or budgeting tools for interactive what-if analysis, making planning and decision making easier. Org charts are ideal for sharing the organization's strategic vision, as well as defining responsibilities, dependencies and relationships. allow you to organize your team with clear responsibilities, titles and lines of authority. Unity of Command Unity of Command laudividni hcae: ylno ot stroper noitarepo eht ni gnitapicitrap .rosivrepus eno It eliminates the potential for individuals to receive conflicting orders from a variety of supervisors. Increasing accountability. Preventing freelancing. improving the flow of information, helping with the coordination of operational efforts, and enhancing operational safety. Span of Management: Span of management (sometimes called span of control) refers to the number of people one supervisor should be in charge of. Chain of Command Chain of Command : The chain of command is best known in the military, where you must have approval from your supervisor for each decision you make! Types of organization charts: There are three different types of organization charts: Hierarchical Matrix Flat Traditional bureaucratic structures there is a tendency to increase task specialization as the organization grows larger . In grouping jobs into departments, the manager must decide the basis on which to group them Basis For Departmentalization There are four commonly used bases: Functional departmentalization. Geographic departmentalization Product departmentalization. Customer/market departmentalization. Departmentalization by function Organizes by the functions to be performed. The functions reflect the nature of the business. The advantage of this type of grouping is obtaining efficiencies from consolidating similar specialties and people with common skills, knowledge and orientations together in common units. Functional Departmentalization. Using such functions as the basis for structuring the organization . Grouping jobs that require the same knowledge, skills, and resources allows them to be done efficiently and promotes the development of greater expertise . A disadvantage : is that people with the same skills and knowledge may develop a narrow departmental focus and have difficulty appreciating any other view of what is important to the organization . Geographic Departmentalization. Groups jobs on the basis of territory or geography. Organizations that are spread over a wide area may find advantages in organizing along geographic lines so that all the activities performed in a region are managed together. Product departmentalization Organized according to product . All the activities necessary to produce and market a product or group of similar products are grouped together. Advantage : personnel in the group can focus on the particular needs of their product line and become experts in its development, production, and distribution . A disadvantage : the duplication of resources Customer/market Departmentalization An organization may find it advantageous to organize according to the types of customers it serves. Consumers. government. Matrix Organizational Structure It is the combination of two or more different structures. Functional departmentalization commonly is combined with product groups on a project basis. Advantage of a matrix structure is that it facilitates the use of highly specialized staff and equipment. It fosters cross-fertilization of ideas. Disadvantage: problems of matrix organization arise from the dual reporting structure utilize functional and divisional chains of command simultaneously in the same part of the organization, commonly for one-of-a-kind projects. It is used to develop a new product, to ensure the continuing success of a product to which several departments directly contribute, and to solve a difficult problem. Matrix Structure · Matrix designs have a duel authority structure with both a functional manager and a project manager. · Product and functional structures are integrated and results in a dual organizational focus. · Shared governance, based on participatory management uses a committee structure whereby staff make either managerial or clinical decisions. · Professional practice or self-governance allows staff to govern themselves using specific councils with decision authority. · allows participation in decision making but the power over the final decision remains with the top executive. Decentralization Decentralization : fo ssecorp eht si -noisiced gnisrepsid ecnanrevog gnikam elpoep eht ot resolc sedulcni tI .nezitic ro fo lasrepsid eht ro noitartsinimda ni ecnanrevog .saera ro srotces Centralization Centralization si : yb ssecorp eht seitivitca eht hcihw ,noitazinagro na fo esoht ylralucitrap -noisiced gnidrager emoceb ,gnikam nihtiw detartnecnoc noitacol ralucitrap a puorg ro/dna