Looking Inside Cells

WEDNESDAY 9/23/15
• Learning Goal:
• Identify cell parts and explain their function
• Homework:
• Packet pages 29-
32 due on Friday!
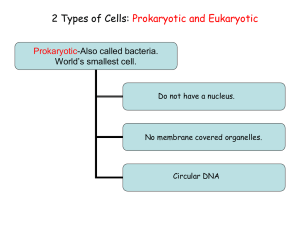
Warm-up:
Turn to page 29 of your packets.
Write two questions you have about the illustrations.
WARM-UP
LOOKING INSIDE CELLS
C H A P T E R 2 S E C T I O N 4
INTRODUCTION
• Organelles
• Tiny structures that carry out specific functions within the cell
• Compare to organs in your body…
CELL WALL
• Rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of PLANTS
• Function: helps to protect and support the cell
• Made of cellulose
• Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls
CELL MEMBRANE
• In cells with cell walls, the cell membrane is located just inside the cell wall
• In other cells, the cell membrane forms an outside boundary
• Function: controls what substances come into and out of a cell
PARTS OF THE NUCLEUS
• Nucleus
• Acts as the “brain” of the cell
• The cell’s control center, directs cell’s activities
• Nuclear envelope
• Nucleus is surrounded by this membrane
• Materials pass in and out of the nucleus through pores in this structure
• Chromatin
• Contains instructions that direct the functions of a cell
• Thin strands, contain genetic material
• Nucleolus
• Where ribosomes are made
THE NUCLEUS
ORGANELLES IN THE CYTOPLASM
• Cytoplasm
• The region between the cell membrane and the nucleus
• Clear, thick, gel-like fluid
• Many organelles are found in the cytoplasm
MITOCHONDRIA
• Convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions
• “powerhouse”
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
• Passageways carry proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another
• Mail truck
RIBOSOMES
• Function as factories to produce proteins
• Sometimes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or float in cytoplasm
GOLGI BODIES
• Receive proteins and other newly formed materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, package them, and distribute them to other parts of the cell
• Mail room
CHLOROPLASTS
• Capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell
• Only in plant cells
VACUOLES
• Storage area of cells (food and other materials)
• Plants cells have ONE large vacuole
• Animal cells have many small vacuoles, or none at all
LYSOSOMES
• Small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials in the cell
• “garbage truck”
SPECIALIZED CELLS
• In many-celled organisms, the cell are often quite DIFFERENT from each other
• Cells are specialized to perform specific functions
• Cells ---- Tissues ---- Organs ---- Organ Systems