Esters
advertisement

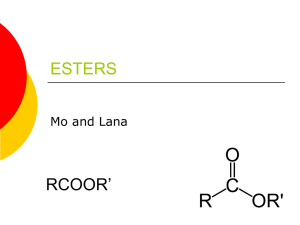
Esters Ben, Scott, Rachel, Parker 1st Period Esters basic structure Characteristics Colorless “volatile” liquids Gives off pleasant aroma Used for food flavorings Occur as animal fats and vegetable oils Nomenclature IUPAC rules for naming esters: Systematic names of esters are based on the name of the corresponding carboxylic acid. The alkyl group is named using the -yl ending. This is followed by a space. The acyl portion of the name is named by replacing the -ic acid suffix of the carboxylic acid with -ate. CH3COOH + ------------- Ethanoic Acid (Acetic acid) isopropyl alcohol (isopropyl acetate) isopropyl ethanoate Nomenclature Here are some more examples: Mechanisms Esterification is typically used to convert carboxylic acids to their ester forms Hydrolysis is the process by which Esters are broken down into their parent compounds. Mechanisms con… Amide Preparation: amide compounds are formed from esters using heat and an amine compound (NH) Dacron Polymerization- polyester- large chains of molecules formed from smaller molecules. Examples of Esters Fruits Perfume Flowers Soap Sodium Propanoate Isopentyl Acetate Methyl Propanoate What can esters be used for? Esters are organic compounds formed when an acid and an alcohol combine and release water. Larger esters, which are formed from long-chain carboxylic acids, can be animal and vegetable fats, oils, and waxes. Plexiglas, which is a stiff transparent plastic, is made from long chains of esters. Esters and the real world Smaller esters create the fragrances and flavors of many flowers and fruits. Esters can also be used for food flavorings. Esters are known for their sweet fragrance and taste. Esters can be used for the artificial flavoring of pineapple. Pears, oranges, bananas, pineapple, apple, and strawberry are helped by esters to get their pleasant aroma or taste. Without esters many of these fruits would not taste or smell nearly as good and fruits are vital to a healthy body. Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following is esters general structure? A. C. B. D. Multiple Choice Questions Which of the following is a characteristic of ester? A. Has a Color B. Causes blindness C. Used for food flavorings D. Gives off an unpleasant aroma 2. Multiple Choice Questions Hydrolysis is the process by which Esters A. are separated by their parent compounds. B. destroy their parent compounds. C. are broken down into their parent compounds. D. None of the above 3. Multiple Choice Questions Which of the following is NOT a rule for naming ester? A. The acyl portion of the name is named by replacing the -ic acid suffix of the carboxylic acid with -ite B. The alkyl group is named using the -yl ending C. . Systematic names of esters are based on the name of the corresponding carboxylic acid. D. All of the above 4. Multiple Choice Questions Which of the following is NOT an example of ester? A. Fruits B. Flowers C. Soap D. Salt 5. Work Cited http://www.enotes.com/chemistry/q-and-a/what-volatileliquids-252818 http://www.thefreedictionary.com/ester http://butane.chem.uiuc.edu/cyerkes/Chem104A_BFA05/ Genchemref/nomenclature_rules.html http://www.chemvip.com/index/products_index/all_products/ all_products_solvents/product-isopropyl_acetate.htm http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/carey/student/olc/c h20reactionsesters.html