The Many Faces of Fascism
advertisement

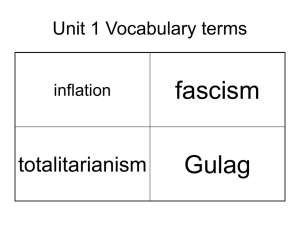
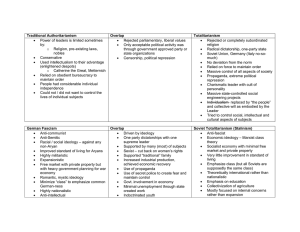
Ideologies 1920s, 1930s fascism was more of a movement than an ideology Fascism derived from Italian fascio, which means "bundle", group, or "union” ; Strength through Unity Fascists despised intellectualism and ideology Analysis of fascism as ideology has centered on historical actions of fascist regimes Theoretical Influences: Irrationalism: rejection of the application of reason and science to social problems and use myth, emotion,and hate as tool of manipulation Social Darwinism: social theories viewing life as a struggle for survival (Herbert Spencer, Charles Darwin) It defied key principles of liberal democracy a. individualism b. competition c. Quest for profit and material gain d. Social divisions, fragmentations, and particularisms (pluralism and cultural diversity) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. State is Supreme Ideological Indoctrination of Masses Single-Party State Social Interventionism and Patriarchy Personalized, charismatic Leadership Military Expansionism Individual is insignificant; everyone’s needs are subordinate to needs of the state Central Motto: “Everything within the State, Everything for the State, Nothing outside the State.” A New Society Needed to be fostered to create Unity and Cooperation: “Believe; Obey; Work; Fight.” Friedrich and Brzezinski list following criteria for Totalitarian State: 1. official, infallible ideology enjoying almost religious status 2. single party dominates regime, usually led by a single man 3. monopoly on the means of mass communication 4. terroristic policy force eradicating political dissent through coercion and intimidation 5. state possesses a monopoly of the weapons of armed combat 4. state control of major facets of economic life Empirical examples: Fascist Italy, Nazi Germany Active indoctrination of masses with ideology is paramount Ideology centers on nationalism and racism Nation becomes identified with a Race 1. 2. 3. 4. Racial segregation in living, working, and breeding Racial supremacy Hitler “Mein Kampf”: Racial Purity is Iron Law of Nature Anti-Semitism in Germany Extreme (exclusive) Nationalism: stresses membership in a group which is “closed” in terms of racial prerequisites Membership denied based on genetic, historical, and cultural reasons Anti-Immigrant Characteristic of a single-party state (one-party system) in which a single political party forms the government and no other parties are permitted to run candidates for election. Oppositional forces are eliminated Corporate state: government control over business and labor Italy: Nationalist Fascist Party (1922-1943) Germany: National Socialist German Worker’s Party (Nazi: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei) Endorsement of social interventionism dedicated to influencing society to promote the state's interests f.ex. Creation of a "new man" and a "new civilization" as part of their intention to transform society. Mussolini: “social revolution” for “remaking” the Italian people. Hitler: aimed to purge Germany of non-Aryan influences on society and create a pure Aryan race through eugenics. Eugenics: belief in the possibility of improving the qualities of the human species or a human population by means if controlling reproduction. Negative Eugenics: discouraging reproduction by individuals who have presumed defects or inheritable Positive Eugenics: encouraging reproduction by individuals who are believed to have inheritable desirable traits Fascism promotes principles of masculine heroism, militarism, and discipline Rejection of cultural pluralism and multiculturalism Fascist states revolve around a leader who is not only a dictator but the symbolic representation of the nation; the personal representative of the race People are moved by emotion, not reason Hitler (1933-1945) Franco (1939-1975) Peron (1946-1955) State seeks to aggressively prove superiority and strength of nation through military victories or conquests International Environment is harsh, and other states and nations threaten the purity and survival of the fascist state