chemical kinetics hw
advertisement

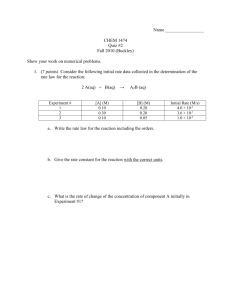
HOME ASSIGNMENT –CLASS:XII-UNIT - IV (CHEMICAL KINETICS)MARKS : 5 Prepared By : A.P. Singh, PGT- Chemistry , KV Aliganj,Lucknow 2.1. What do you understand by the ‘order of a reaction’ ? Identify the reaction order from each of the following units of reaction rate constant : (i) L─1mol s─1 (ii) L mol─1s ─1(2012,11,09) 2.2. A reaction is of second order with respect to a reactant .How will the rate of reaction be affected if the conc .of the reactant is : (I) doubled (II) reduced to Half ? (2012,09) 2.3. Express clearly what you understand by ‘ rate expression ‘ and ‘rate constant ’ of a reaction. (2011) 2.4. Define the following : (i) order of a reaction (ii)Rate of a reaction (iii) Molecularity of a reaction (iv) Elementary step in the reaction (v) Activation Energy of a reaction (2011,10) 2.5. A reaction is of first order in reactant A& of second order in reactant B .How is the rate of this reaction affected when (I) conc. Of B alone is increased for 3 times. (II) the cone. of A as well as B are doubled (2013,10,09,08) 2.6. The rate constant for a reaction of Zero order in A is 0.0030 molL─1 s─1 . How long will it take for the initial conc.of A to fall from 0.10 M to .075 M ? (2010) 2.7. A first order reaction takes 40 minutes for 30 % completion . calculate its t1/2 value. (2008,13) 2.8. What is meant by a pseudo order reaction ? Giver an example of a pseudo order reaction . (2008) 2.9. The rate constant for a first order reaction is 60 s–1. How much time will it take to reduce the initial (2013) concentration of the reactant to 1/10th of its initial value? 3.1. For the reaction : 2NO (g) + Cl2 (g) ------------- 2NOCl (g) , The following data were collected . All measurement were taken at 263 K Experiment No. Initial [NO] (M) Initial [Cl2] (M) 1 2 3 4 0.15 0.15 0.30 0.25 0.15 0.30 0.15 0.25 Initial rate disappearance Cl2 (M/ min) 0.60 1.20 2.40 ? of of (a). Write the expression for rate law. (b). Calculate the value of rate constant and specify its units. (c). What is the initial rate of disappearance of Cl2 in experiment 4.(2012) 3.2. The reaction , N2 (g)+ O2 (g) --------- 2 NO (g) contributes to air pollution whenever a fuel is burnt in air at a high temperature . At 1500 K , eqlb. constant K for it is 1.0 x 10─5 . Suppose in a case [N2]= 0.80 mol L─1and [O2] = 0.20 mol L─1 before any reaction occurs. Calculate the eqlb. concentrations of the reactants and the products after the mixture has been heated to 1500 K. (2012) 3.3. A first order reaction has a rate constant of 0.0051 min─1 . If we begin with 0.10 M conc. of the reactant, how muchconc. of the reactant will remain is solution after 3 hrs? (2011,09) 3.4. Nitrogenpentoxide decomposes acc. to the eqn. : 2N2O5 (g) ------- 4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g) This first order reaction was allowed to proceed at 40 oC [N2O5] M Time (min) data given below were collected : 0.400 0.00 (i) (i)Calculate the rate constant of the reaction . 0.289 20.00 (ii) (ii) Calculate the initial rate of reaction. 0.209 40.00 (iii)After how many minutes will [N2O5] be equal to 0.350 M ? 0.151 60.00 0.109 80.00 and the 3.5.The thermal decomposition of HCOOH is a first order reaction with a rate constant of 2.4 x 10─3s ─1 at a certain temperature. Calculate how long will it take for three-fourth (3/4) of initial quantity of HCOOH to decompose ? (log 0.25 = − 0.6021 ) (2011) 3.6The decomposition of phosphine PH3. Proceeds acc. to following eqn: 4 PH3 (g) --->P4(g) + 6H2 (g) ; It is found that he reaction follows the following rate equation: Rate = K [PH3] ; The half lite of PH3 is 37.9 S at 1200C (1) How much time is required of 3/4th of PH3 to decompose ? (2) What fraction of original sample of PH3 remains behind after 1 minute ? (2010,09) 3.7. The rate of a reaction increases 4 times when the temperature changes from 300 K to 320 K. Calculate the energy of activation of reaction, assuming that it does not change with the temp. (R=8.314 JK─1mol−1). (2013,10,08) 3.8..For a decomposition reaction the values of rate constant K at 2 different temperature one given below K1 = 2.125 X 10─8at 650 K & K2= 2.39 X 10−7 at 700 K Calculate the value of Energy of activation for this reaction . (R=8.314 JK─1mol−1) (2009) 3.9.H2O2(l) decomposes to H2O (l) and O2 (g) in a reaction that is first order in H2O2 (l) and has a rate constant K = 1.06 x 10─3 min─1 . (a) How long will it take 15 % of sample of H2O2 to decomposes ? (b) How long will it take 85 % of sample of H2O2 to decomposes ? (2009) ─1 3.10. The rate constant of a first order reaction is 60 s .How much time will it take to reduce the initial concentration of the reactant to 1/16 of its initial conc. (2008) 3.11. Thehalf- life of radioactive C-14 is 5730 years .A wooden part of an archaeological artifact has only 80 % of the C-14 activity found in fresh wood . Calculate The Age Of The Artifact. (2008) 3.12. Sucrose decomposes into glucose and fructose in acid solution following first order reaction wheret1/2= 3 hours. What % of Sucrose sample will remain after 8 hrs.? (2011 sample) 3.13. When the temperature of a first order reaction is increased from 350 K to 400 K, if it is found that its rate constant becomes 5 times. Calculate the energy of activation.(2011 sample) 3.14. (a) For a reaction A + B P, the rate law is given by, r k[A]1/ 2 [B]2 . What is the order of this reaction? (2013) –14 –1 (b) A first order reaction is found to have a rate constant k = 5.5 × 10 s . Find the half life of the reaction. 3.15. For a chemical reaction R P, the variation in the concentration ln [R] vs. time t plot is given as For this reaction (i) what is the order of the reaction? (ii) what is the slope of the curve? (iii) what is the unit of rate constant ‘k’? (2013) 5.1 (a) For a first order reaction, show that time required for 99% completion is twice the time required for the completion of 90% of reaction. (b) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation: 1 Where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for log k vs. , a straight line with a slope of 𝑇 – 4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction. (R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1) (2013) HOTS QUESTIONS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8