Cell Test Study Guide 1. Identify the contributions of the following
advertisement

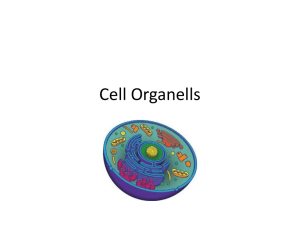
Cell Test Study Guide 1. Identify the contributions of the following people: a. Robert Hooke – saw 1st cell – cork cell; named cells b. Anton van Leeuwenhoek – saw 1st living cells (animalcules) c. Matthias Schleiden – “plants are made of cells” d. Theodor Schwann – “animals are made of cells” e. Rudolph Virchow – “cells come from cells” 2. List the three parts of the Cell Theory: 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. 3. Identify the function of the following: a. cell membrane – controls what enters and leaves the cell b. cell wall – support and structure c. chromosomes – genetic material, DNA d. nucleus – “control center” e. nucleolus – makes ribosomes f. cytoplasm – liquid background part of cell g. mitochondria – “powerhouse of cell” h. endoplasmic reticulum (ER): “highway system” 1. smooth ER – no ribosomes are present 2. rough ER – ribosomes are present i. vacuoles – “storage bins” j. ribosomes – “protein factories” k. centrioles – animal cell reproduction l. chloroplasts – contains chlorophyll; photosynthesis m. golgi complex – “UPS/Fed X” – packaging/shipping n. lysosomes – “clean up crew” 4. Identify differences between the structure of plant and animal cells. plants: rectangular, cell wall, chloroplasts, large vacuoles animals: circular, small vacuoles, centrioles, no cell wall 5. How are the cells of eukaryotes and prokaryotes different? eukaryotes – more complicated cell design, nucleus, membrane bound organelles, larger, unicellular or multicellular prokaryotes – simpler cell design, no nucleus, unicellular, bacteria 6. Identify the following organelles: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. rough ER mitochondria ribosomes Golgi bodies smooth ER nucleus cytoplasm nucleolus centrioles outer layer of cell – cell membrane 7. What does the structure and function of a cell mean? The structure of a cell is how it is designed, put together. The function of a cell is what the cell does for the organism, its purpose. 8. Explain the structure and function of a unicellular organism. A unicellular organism is made up of one cell. The cell is not specialized. The one cell is able to support all of the needs of the organism. 9. Explain the structure and function of a multicellular organism. A multicellular organism is made up of several cells that are specialized. The structure and function of the cells are different. A group of cells working together form tissues, which form organs, which form organ systems, which form an organism. 10. Compare the structure and function of a leaf cell, red blood cell and a nerve cell. Cell Leaf Red blood cell Nerve cell Structure Chloroplast Cell wall Gets rid of nucleus Long fibers Function Photosynthesis support Carries oxygen Receive/send messages