The Modern Middle East
advertisement

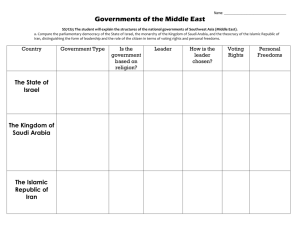
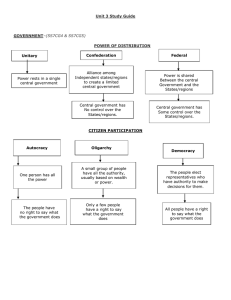
The Modern Middle East Chapter 16 Section 4 Middle East Middle East Religions and Ethnic Groups Most people are Muslim There are also Christians, and Jews in Israel Most countries have large ethnic or religious minorities The Kurds are an example of an ethnic minority Kurds live in Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey Kurds have been frequently discriminated against Distribution of Kurds Israel The Holocaust created worldwide support for a Jewish homeland after World War II In 1947, the UN drew up a plan to divide Palestine into an Arab and a Jewish state Arabs rejected the plan; Jews accepted the plan In 1948, Jews proclaimed the independent state of Israel Arab countries sent their armies to crush Israel beginning in 1948 Arabs believe that all of the land belongs to them UN Partition Plan Israel has fought four wars against her Arab neighbors in 1948, 1956, 1967, 1973, and other minor conflicts since Israel declared statehood in 1948. In each war, Israel’s military has successfully defeated the Arab countries. The goal of the Arab countries is to destroy and wipe Israel off the map. Israel, since 1948, has concluded peace treaties with Egypt and Jordan. Insurgents (rebels) still launch rockets from the Gaza Strip and Syria. Israel (continued) The wars between Arabs and Israel forced 700,000 Palestinians from their homes The Arab countries invited many Palestinians to join the fight to destroy Israel after Israel declared independence in 1948 After Israel defeated the Arabs, the Arab countries refused to accept the return of the Palestinians Many Palestinians become refugees and demand their own country Despite the ongoing conflicts, Israel has developed rapidly due to a skilled workforce and a modern democracy Kibbutzim work on what is called a kibbutz, or collective farm (Mr. Tilles lived on a kibbutz in the 1970s) State of Israel Resources and Religion Resources and religion have led to conflicts in the Middle East The Middle East has the world’s largest oil and gas reserves Consequently, it has strategic importance because the world operates on petroleum Some Middle Eastern countries have adopted secular, or non-religious, government and laws Oil Resources and Religion However, many Muslim leaders argue that a renewed commitment to Islamic doctrine is needed In Iran and Saudi Arabia, women are required to wear hejab, the traditional Muslim garments Many Islamic countries make their laws based on Islamic doctrine and beliefs. These countries are secular (religious). Iran and Saudia Arabia are two examples of secular countries. These two countries are anti-democratic. Egypt Most populous Arab country in North Africa Egypt controls the Suez Canal Under Gamal Abdel Nasser, Egypt fought two unsuccessful wars against Israel Nasser wanted to nationalize (control) the Suez Canal Nasser’s successor, Anwar Sadat, made peace with Israel Islamists were angry about government corruption and the failure to end poverty In 1981, Muslim fundamentalists assassinated Sadat Suez Canal Egypt Nasser, the Egyptian leader, wanted to nationalize (control) the Suez Canal, a vital waterway that links the Mediterranean Sea with the Red Sea. Iran In Iran, Shah Mohammed Reza Pahlavi ruled with the support of the United States, which helped oust one of his opponents, Mohammad Mosaddeq The shah’s secret police terrorized critics In the 1970s, the shah’s enemies rallied behind Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, a radical Islamic cleric Radical Iranian, anti-American students stormed and overtook the U.S. embassy in Tehran, Iran (1979) Protests forced the shah into exile, and Khomeini established an Islamic theocracy, or government ruled by religious leaders Ayatollah Khomeini A radical Islamic cleric who became the leader of Iran following the Islamic Revolution and ouster of the Shah (king). Mohammad Mossadeq The Shah Saudi Arabia Has the world’s largest oil reserves The location of Islam’s holy city (Mecca) is located in Saudia Arabia Kings from the Sa’ud family have ruled Saudi Arabia since the 1920s Fundamentalist Muslims have criticized Saudi Arabia’s close ties to Western nations like the USA Some opponents have adopted violent tactics that threaten to disrupt the Saudi oil industry Saudi Arabia Powerpoint Questions (16 points) 1. What is the dominant religion in the Middle East? 2. What two other religions originate and exist in the Middle East? (2 points) 3. What discriminated ethnic group resides in Iran, Iraq, Turkey, and Syria? 4. What was the U.N. plan in 1947 toward Palestine? 5. In what year did Israel proclaim itself a state? 6. What is a kibbutz? Powerpoint Questions (16 points) 7. What natural resource does the Middle East have? 8. Another word for non-religious is ??? 9. What are Muslim women required to wear? 10. What body of water flows through Egypt? 11. Who was the Egyptian leader who wanted to nationalize the Suez Canal? Powerpoint Questions (16 points) 12. What Egyptian leader was assassinated by Muslim fundamentalists? 13. What is a theocracy? Explain. 14. What Iranian leader established a theocracy in Iran? 15. What country has the world’s largest oil reserves? The End