Unit 3 Study Guide: Government, Economics, Environment
advertisement
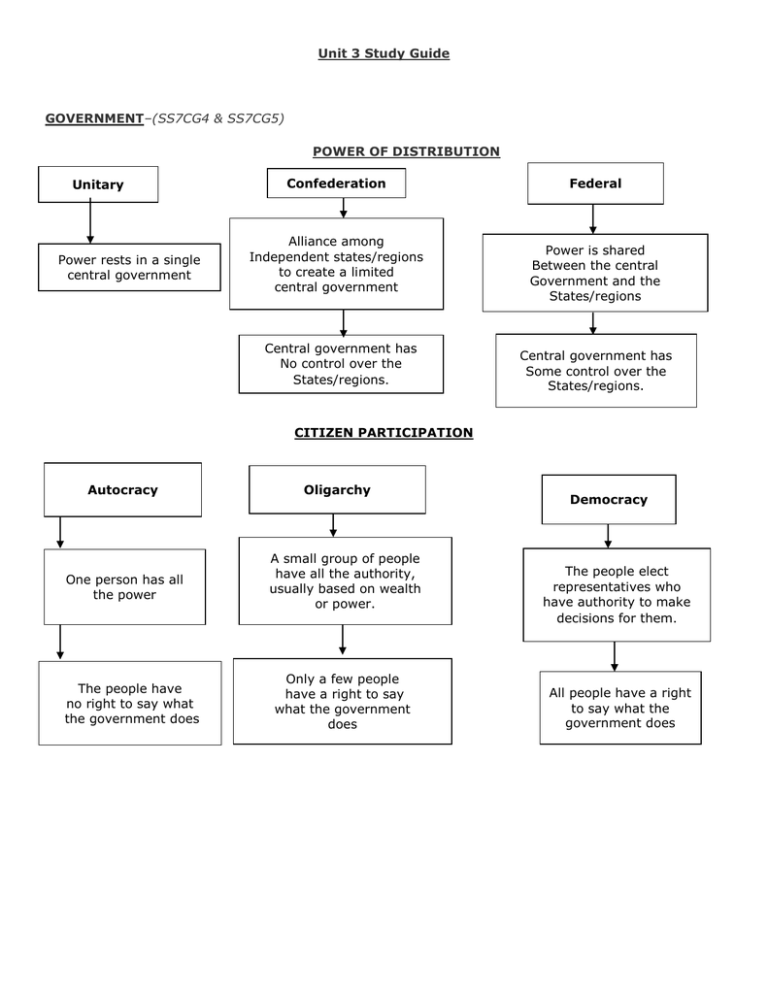
Unit 3 Study Guide GOVERNMENT–(SS7CG4 & SS7CG5) POWER OF DISTRIBUTION Unitary Power rests in a single central government Confederation Alliance among Independent states/regions to create a limited central government Central government has No control over the States/regions. Federal Power is shared Between the central Government and the States/regions Central government has Some control over the States/regions. CITIZEN PARTICIPATION Autocracy One person has all the power The people have no right to say what the government does Oligarchy A small group of people have all the authority, usually based on wealth or power. Only a few people have a right to say what the government does Democracy The people elect representatives who have authority to make decisions for them. All people have a right to say what the government does Democracy Representative Direct Ancient Athens Presidential System Parliamentary System Power vested in The legislature Power vested in Separate institutions Prime Minister chosen By the legislature New England Town Halls Native American Societies President chosen By the people ** Ranking in order greatest citizen participation to least citizen participation in government decisions are as follows: 1) Presidential Democracy, 2) Parliamentary Democracy, 2) Oligarchy, and 4) Autocracy** COMPARISON OF GOVERNMENTS OF ISRAEL, SAUDI ARABIA, AND IRAN Government Prime Minister, Parliament Israel (Parliament is the Legislative Branch of government, so Prime Minister is head of the Legislative Branch of the government) Monarch, Saudi Arabia no written constitution, no elected legislature (Ruler must be a direct descendant of the prior leader of the country) Theocracy, Iran Elected president and legislature. An expert on Islamic law is the supreme leader. (Religious leaders have the most influence.) ECONOMICS - (SS7E5, SS7E6, & SS7E7) **Each economic system must answer the following 3 basic questions: 1) What to produce? 2) How to produce? 3) For whom to produce? ECONOMIC SYSTEMS COMMAND MARKET Government controls production, wages, and prices. People can own and operate a business with little government interference. People have no say as to what the government does. Laws of supply and demand determine production, wages, and prices. TRADITIONAL Society or culture determines what is produced or sold. Children usually follow in the occupation of their family members. Both consumers and the market decide what will be sold and at what price. ** Most countries have a mixed economy in order to be successful and protect consumers. ** Israel Type of Economy Mixed Saudi Arabia Mixed Turkey Mixed What to produce? High tech manufacturing, financial services, & agriculture (Israel does not invest in oil – no oil reserves in Israel) World’s leading producer of oil. Government invests in industrial production. Large service, manufacturing, and agricultural economy. How to produce? Substantial government ownership but is privatizing companies - Over 95% of the oil industry is operated by the governme nt. - 1/3 of the labor force Since the 1980’s has gradually moved from a government directed economy to more private enterprise. For whom to produce? Produce goods and services for domestic and international markets 1/3 of GDP is based on exports to other countries. (oil) 1/5 of Turkey’s production is exported. Remainder is consumed by domestic consumers and government. ** Israel is the most economically free country at 68% market economy. Saudi Arabia is next most economically free at 64% market economy. Turkey is least economically free out of these three countries – 62% market economy. Iran is mostly a command economy.** SPECIALIZATION AND TRADE Specialization Currency Exchange Tariff Quota Embargo Production of what country does best at lowest opportunity cost. (** Iran and Saudi Arabia specialize in oil and petroleum products.) Exchanging from one country’s currency to another – countries must be able to exchange currency in order to trade. Trade Barriers Tax placed on imported goods Set a limit on the amount of certain goods that can be imported into a country. Quotas impact the supply and price of the product that is produced and traded. An order that stops the importing or exporting of goods. Sometimes embargos are placed on another country’s government to pressure that government to change its actions. (OPEC stopped all sales of oil and gas in 1973.) **OPEC – Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries – controls supplies and pricing of oil in the world market.** Land Labor Capital - Human - Physical Entrepreneurship Factors of Production Land provides raw materials and natural resources needed for production. Does the “hands on” and transforms raw materials into a product. (GDP may go down if workers are not properly trained.) Human made goods which are used in production of other goods. Education and on-the-job training of workers. Machinery, tools, factories, and technology used in production Risk takers who combine all factors to create their own business ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES - (SS7G6) Water Distribution o o Water is unevenly distributed Turkey and Iraq share Tigris and Euphrates River systems. Israel, Syria, and Jordan share the Jordan River. Saudi Arabia has NO water! As a result. . . SWA must use irrigation to farm and raise animals. Underground aquifers – trap water runoff underground from rain Fossil Water – dig wells that tap into water down very deep Drip Irrigation o Used by Israel and Saudi Arabia o Uses computers to determine the amount of water each plant requires o Very expensive to use Desalination – removing salt and chemicals from seawater to provide useable water o Requires high technology o Very expensive Conflict between countries over water rights!!!!! o Dams To create lakes Hydroelectric Power Irrigation Problems arise Countries further downstream get less water due to stop of water flow in the rivers. Water Pollution o o Farmers use of chemical fertilizers have contaminated water supplies Overuse of rivers and streams has led to water pollution