Progressive Legislation - Woodbridge Township School District
advertisement

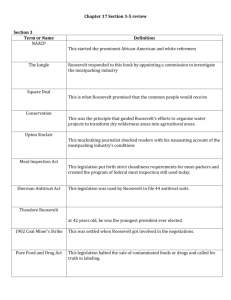
Progressivism - reform movement that responded to social challenges caused by industrialization, urbanization, & immigration in 1890s & 1900s. Progressives believed honest & efficient gov’t social justice. Mainly from middle class logic and reason for reform Honest gov’t change End corruption Gov’t must respond to ppls needs Use modern ideas & science to improve society • corrupt pol machines • trusts & monopolies • inequities • safety • city services • women’s suffrage Middle class progressives wanted gov’t to bust the trusts formed in Gilded Age Help create more econ opportunities for the middle class Progressive wanted to attack problems Gap between rich & poor Poor living conditions Poor labor conditions in factories & mines Improve the city slums Jacob Riis used flash photography to show the conditions in city slums Dirty No running water Full of disease The naturalist novel portrayed the struggle of common people. Upton Sinclair’s novel The Jungle provided a shocking look at meatpacking in Chicago’s stockyards. Walter Rauschenbusch believed religion Social Reform He blended ideas of German Socialism & American Progressivism Social Gospel Use the Bible to lead reform Shorter work weeks No child labor Limit trust power Jane Addams led the settlement house movement. Hull House – Chicago; urban community center social services for immigrants and the poor Taught English Offered nursery schools YMCA – rel org 2/3 of states abolished child labor in 1907 Massachusetts started minimum wage in 1912 Florence Kelley founded the Women’s Trade Union League which worked for a federal minimum wage and a national eight-hour workday. Progressives succeeded in reducing child labor and improving school enrollment. The United States Children’s Bureau was created in 1912. John Dewey pushes for a school system the forces thinking creatively Teach history, geography, cooking, and carpentry March 25, 1911 500 women were working at the Triangle Shirtwaist Company They were located on the top floors of a ten story building in New York A fire broke out and quickly spread The women tried to escape but found the doors locked from the outside Employers did not want employees leaving for breaks Some women filed on to a fire escape Their weight collapsed the fire escape causing them to fall to their death Fire truck ladders could not reach the top floor 146 workers died After the fire a Jewish immigrant from Poland named Rose Schneiderman fought for change Fire inspectors Fire drills Unlocked fire proof exits Automatic sprinklers Some employers create disability or other compensation for workers and their families in case of accidents State governments are allowed to make laws based on workers safety Muller v. Oregon women laundry workers can not work more then 10 hours a day Municipal means city Municipal reformers opposed political bosses They had trouble defeating big machines like Tammany Hall Disaster caused municipal change 6,000 people were killed during a hurricane in Galveston Texas in1900 causing the city to create an emergency commission to rebuild The commission became a part in their city government Galveston Texas in1900 Mantoloking NJ After Hurricane Sandy City mayors fought for control of utilities to end utility monopolies Parks, homeless shelters, and kindergartens were added to some cities Wisconsin Gov Robert M. La Follette establishes a direct primary Creation of Initiative Referendum Recall Direct election of senators by the ppl Could not vote Rarely educated Paid poor wages if they worked Believed men spent earnings on alcohol Alcohol made men neglect families and beat wives The Women’s Christian Temperance Movement grew in popularity and helped pass the 18th amendment in 1919 banning alcohol. Margaret Sanger founded the American Birth Control league Ida B. Wells founded the National Association of Colored Women Since 1860 Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton had worked for women’s suffrage The right to vote In 1919 the 19th amendment gave women the right to vote Immigrants coming to America were forced to assimilate to American culture This Americanization advised immigrants to wear clothing of middle class white Americans Replace the foods and customs of there homeland Stop serving alcohol at dinner, especially to children Prejudice against non-whites Plessy v Ferguson allowed segregation to spread through the South Booker T. Washington and W.E.B. Du Bois wanted equality for African Americans 1909 National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) forms Youngest president to date The Teddy bear was named after him Became president after McKinley was assassinated Known for his Square Deal which meant he promised fairness and honesty in government Mine workers went on strike and owners refused to negotiate Teddy told each side to submit to arbitration He threatened take the mines over with the army Arbitrators granted workers a 10% raise and a 9 hour workday instead of 10 Roosevelt called it a “square deal” Roosevelt passed 42 antitrust actions He broke up monopolies including Standard Oil He wanted trusts regulated by the government The Elkins Act in 1903 allowed the government to fine railroads that gave special rates to favored shippers, a practice that hurt farmers In 1906 he passed the Hepburn Act creating the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) which set and limited railroad rates Teddy used the Sherman Antitrust Act to stop large companies from bullying smaller companies or cheating consumers. After reading The Jungle He past the Pure Food and Drug Act as well as the Meat Inspection Act It required labeling of ingredients and strict sanitary conditions and a system for rating meat He set aside 100 million acres for national forests, mineral reserves, and water projects Roosevelt closed off more than 100 million acres of forestland. Taft defeats William Jennings Bryan in 1908 He was not a strong leader like Roosevelt He angered conservationists because his Secretary of the Interior did not favor conserving federal land The Republican party became split between progressives and non-progressives Taft believed monopolies were acceptable as long as they didn't’t squeeze out smaller companies Roosevelt campaigned for progressive candidates He called his new plan for progressive change New Nationalism Democrats won control of the house Taft - Republican Woodrow Wilson – Democrat Theodore Roosevelt – Bull Moose Party Roosevelt runs under the “Bull-Moose Party” On October 14 Roosevelt is shot in the lung and then gives a one hour speech Wilson was Governor of New Jersey He challenged Big Business and Big Government Wilson wins the election Reduced Tariffs Underwood Tariff Act of 1913 reduced tariff rates from 40% to 25% Made federal income tax a law in1913 He wanted to end monopolies In 1914 he passed the Clayton Antitrust Act which stated certain activities businesses could not do The Clayton Antitrust act also legalized unions, strikes, peaceful picketing, boycotts The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) was established to enforce the law He passed the Federal Reserve Act in 1913 It created the Feral Reserve System which divided the country into 12 districts with their own Federal reserve Bank Wilson would win the presidency again in 1916 on the slogan of keep the US out of the World War The US would eventually enter the war and the Progressive era would come to a close