Handout financial markets and agg demand
advertisement

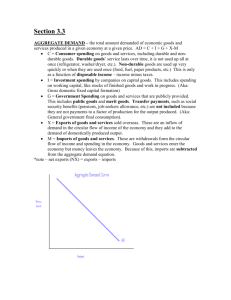
Handout Econ 101 Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a __________ rather than its __________ parts. The circular flow diagram demonstrates that we can measure GDP by looking at _________ or ___________. Aggregate demand consists of four parts. List the parts below and who is the purchaser. Component Agent 1 2 3 4 Wealth and Financial markets Wealth is accumulated savings. The three major ways to hold wealth are: (1)_________, (2)___________, and (3)_____________. The primary financial assets are ____________ and _____________. Stocks carry ___________in a company, while bonds are __________. In the case of bankruptcy who get paid first? _____________. Home ownership is probably the biggest component of ____________ for households. What is risk? If two projects have the same rate of return, the riskier project is the one with the _____variable returns. The two basic categories of risk are:__________ and ___________. What are the three ways and individual can protect against risk? Diversification can help protect against ___________ risk. The risk of bankruptcy is called ___________ risk. As interest rates fall business will increase their _____________. They do so because projects with lower _____________ become profitable to carry out. These projects become more profitable because at lower interest rates, the present value of the future benefits ___________. Money Economists consider money to be anything that is ___________ in exchange. Money is important to economic development because it breaks the _________________ and allows _________ trades to take place. Increased trading allows greater ____________ and ____________ which lower opportunity costs of producing goods and services. The two basic types of money are _________ money and __________ money. Money that is made of a something that has a valuable alternative use is called _________ money. Money that has no “backing” is called ______ money. Money serves what three functions: (1)_____________, (2)______________, and (3)_____________. When one is adding up the grocery bill, which function is money performing?_______________. If money is held in a safe it is performing its ______________ function. Most importantly money is used to carry out ____________. The amount of money people hold in their portfolio depends on what three variables? __________, ____________, and _____________. If the overall level of prices goes up people will have to hold _______to carry out transactions. If interest rates rise, the ____________ of holding money goes ________, so individuals will hold __________money. If individuals are holding too much money in their portfolios, they will either _________it or ________ it. If they spend it, ______________ goes up. If they lend it the supply of loanable funds __________ and interest rates __________. When interest fall ___________ investment __________. Exchange rates and the Value of the Dollar The exchange rate is the price of the dollar in other _____________. It can be expressed as how much a dollar buys of other currency or how much of the foreign currency is required to purchase a dollar. Economists prefer to use the former. So if the exchange rate with British pounds is .67. A dollar will buy .67 pounds (or it takes a $1.50 to buy one pound). If the US dollar buys less foreign currency it _____________. If it buys more foreign currency it ____________. The value of the dollar is determined by supply and demand in exchange markets. If US interest rates rise, foreigners, ceteris paribus, want to buy more U.S. financial assets, so the demand for dollars goes up and the dollar _____________. If US interest rate fall, the dollar ____________. The supply and demand for dollar also determines net exports. If the dollar appreciates foreign goods become_________ in the US so next exports will _________. If it depreciates, next exports will __________. Aggregate Demand Curve The demand curve is microeconomics is based on the substitution and income effects. The ____ warns us that what is true for the individuals is not necessarily true for the whole. The substitution effect is based on one good become cheaper, but if the price level falls in macro _____ price tend to fall. Instead, as the price level falls, the real value of people’s money holding ___________. This causes them to have excess liquidity in their portfolios and they will _____ or _______ it. If they spend it ____ increases; if they lend it, the supply of loanable funds ________ and __________ fall. This encourages business to increase ___________. Also, if interest rates in the US fall, the demand for $ will fall in foreign currency markets. This will cause the US $ to ___________ and increase _______. The result is that as the price level fall aggregate __________ increases. These three effects are called: ________,_________, and____________. They explain why the aggregate demand curve is ____________ just like the demand curve in micro. The aggregated demand curve shifts because of spending change in either the ________ sector of the ________ sector. In the private sector, _____________sentiment is important and depends on such things as ___________ and ___________. ____________ sentiment is important in determining investment spending and includes such things as __________ and ___________. Lastly, changes in ROW spending patterns can affect _____________. In the public sector, increased government spending, decreased taxes, or increases in the money supply will shift the aggregate demand curve _________. Aggregate Supply Aggregate supply is upward sloping because of wage stickiness. Wages that are not adjusted for the price level or inflation are called _______ wages. Once we divide these wages by the price level, we have the _________wage. As prices rise, wages generally don’t go up as fast as a producer’s____________. Therefore, the real wage or the real cost of labor will ___________ and producer’s will increase __________. Wages tend to go up faster the closer employment is to __________employment or as the unemployment rate goes ____________. So the aggregate supply curve has three ranges, but it is ________ sloping. Short-run Fluctuations in Output SR changes in output and prices are caused by shifts in _____________ and ___________. Until the early seventies, most change in output and prices were caused by change in aggregate ___________. This is apparent because prices and output tended to move in _____________ direction during the business cycle. The create depression was caused by a large drop in aggregate demand and unemployment grew to q high of ________%. Output can also fluctuate because of a change in aggregate supply. If the aggregate supply decreases the _________ will rise and output will _________. This is known as stagflation. The first major bout of this economic malady occurred in the 19__s. The ____________ sector determinants of aggregate demand can be used to potentially offset changes in spending patterns in the _______ sector. These types of policies are called ________ policies. If the work to reduce the fluctuations in prices and output they are called _____-cyclical policies if they exacerbate the fluctuations they become ____cyclical. The Great Depression was first caused by a drop in aggregated demand because of the _________. It was made worse when the Federal Reserve allowed banks to _______ and the money supply to ______. This was compounded by the federal government raising ___ and cutting ____________. Recessions can help discipline irresponsible ________-taking. If such individuals are overly protected, __________ suggest they will undertake ________ risky behavior. Insurance companies have to be concerned about __________ and __________, both of which contribute to risk. The current US economic situation has its origins in the __________ action to prevent a recession after the ______ crisis. The Fed ___________ liquidity to prevent a decline in ___________. Individuals reduced they excess liquidity by __________ and __________. These behaviors contributed to the creations of the _________ bubble. The bubble was exacerbated by irresponsible ___________. Also, during this time new financial instruments that bundled _________ were created called __________. These were insured by large ____________ banks. As housing prices began to ____________, many of the institutions involved in these financial instruments became increasingly ____________. The Fed responded by _________ liquidity. Banks are currently holding unprecedented levels of ___________. Interestingly, the ____________it mechanism appears to be constrained because banks are worried that borrowers _______________. They also worry about the increased __________ of bank regulators.