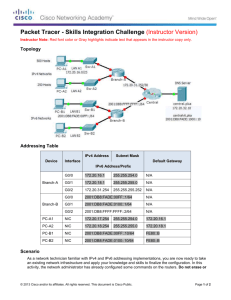
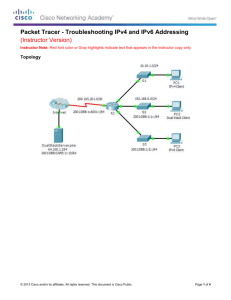
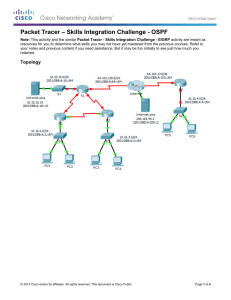
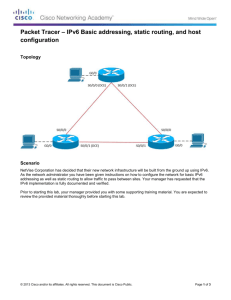
An IPv4-to-IPv6 Transition Approach
advertisement
Broadband Forum Focus: IPv6 Home Network David Miles david.miles@alcatel-lucent.com Disclaimer The views in this presentation do not represent the opinion of the Broadband Forum or its members. All document are Work In Progress. 2 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 1 What is the Broadband Forum? 3 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 The Broadband Forum Vision Develop the full potential of broadband around the world. Mission The Broadband Forum is a worldwide organization committed to rapidly creating specifications for communication service providers and vendors that Accelerate the development and deployment of broadband networks, Foster successful interoperability, Manage and deliver advanced IP services to the customer. http://www.broadband-forum.org/about/mission.php Forum History The Broadband Forum is a global consortium of nearly 200 leading industry players covering telecommunications, equipment, computing, networking and service provider companies. Established in 1994, originally as the ADSL Forum and later the DSL Forum, the Broadband Forum continues its drive for a global mass market for broadband, to deliver the benefits of this technology to end users around the world over existing copper telephone wire infrastructures. http://www.broadband-forum.org/about/forumhistory.php 4 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 2 IPv6 for Consumer Deployment Options 5 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Native IPv6 IPv6 Home Network IPv6 Gateway IPv6 Internet Softwires from Client in the Home Network IPv6 Home Network Softwire Client L2TP Tunnel DSL Router (Existing) IPv4 Internet IPv6 Internet Softwire Concentrator Native IPv6 using L2TP IPv6 Home Network L2TP PPPoA IPv6 Gateway LAC IPv6 Internet IPv6 LNS Host Access using PPPoE L2TP PPPoE IPv6 Internet Bridge LAC IPv6 LNS Host Access using Softwires L2TP Tunnel PPPoE IPv4 Router IPv4 Internet IPv6 Internet Softwire Concentrator 3 IPv6 for Consumer Broadband WT-177 and WT-187 11 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Routing Home Network Subnet A Internet Subnet B IPv4 NAT Function UDP TCP TCP UDP IPv4 IPv4 Ethernet Ethernet IPoE IWF Ethernet RFC 2684 ATM DSL IPv4 802.1ad 802.1ad Ethernet Ethernet 802.3 PHY 802.3 PHY IPv6 Routing IPv6 Ethernet Ethernet RFC 2684 ATM DSL 12 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 IPoE IWF Ethernet IPv6 802.1ad 802.1ad Ethernet Ethernet 802.3 PHY 802.3 PHY Routed Gateway with PPPoE WAN (1) Subnet A Subnet B Routed Gateway BNG RADIUS PPPoE PADI – PADO – PADR - PADS PPP LCP ConfReq ConfReq: MRU, Magic Number PPP LCP ConfReq ConfReq: MRU, Magic Number, Auth=PAP PPP LCP ConfAck ConfReq: MRU, Magic Number, Auth=PAP PPP LCP ConfAck ConfReq: MRU, Magic Number PAP Authenticate-Request Username (Peer-ID)+ Password RADIUS Access-Request User-Name, Password, Service-Name VSA Service-Type=Framed, Framed-Protocol=PPP RADIUS Access-Accept Delegated-IPv6-Prefix, IPv6-DNS, (IPv6-Address/Framed-IPv6-Pool) 13 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Routed Gateway with PPPoE WAN (2) Subnet A Subnet B Routed Gateway BNG RADIUS PAP Authenticate-Ack IPv6CP ConfReq Interface-Id= 64-bit Interface ID/Client PPP Phase IPv6CP ConfAck Interface-Id= 64-bit Interface ID/Client IPv6CP ConfReq Interface-Id= 64-bit Interface ID/BNG IPv6CP ConfAck Interface-Id= 64-bit Interface ID/Client RADIUS Accounting-Request Start, User-Name, Service-Name VSA Service-Type=Framed, Framed-Protocol=PPP 14 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Routed Gateway with PPPoE WAN (3) Subnet A Subnet B Routed Gateway BNG Multicast Router Advertisement Numbered: M=1,O=0, No PIO Un-numbered: M=0, O=1, No PIO DHCPv6 SOLICIT IA_PD-Option, (IA_NA-Option), DNS-Servers Option DHCPv6 ADVERTISE DHCPv6 Phase IA_PD-Option + Prefix, (IA_NA) DHCPv6 REQUEST IA_PD-Option, (IA_NA-Option), DNS-Servers Option DHCPv6 REPLY IA_PD-Option + Prefix, (IA_NA) 15 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 RADIUS Routed Gateway with Ethernet WAN (1) Subnet A Subnet B Routed Gateway BNG RADIUS Multicast Router Advertisement Numbered: M=1,O=0, No PIO Un-numbered: M=0, O=1, No PIO DHCPv6 SOLICIT IA_PD-Option, (IA_NA-Option), DNS-Servers Option RADIUS Access-Request User-Name, Password, Service-Name VSA Service-Type=Framed DHCPv6 Phase RADIUS Access-Accept Delegated-IPv6-Prefix, IPv6-DNS, (IPv6-Address/Framed-IPv6-Pool) DHCPv6 ADVERTISE IA_PD-Option + Prefix, (IA_NA) DHCPv6 REQUEST IA_PD-Option, (IA_NA-Option), DNS-Servers Option DHCPv6 REPLY IA_PD-Option + Prefix, (IA_NA) 16 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Bridged Home with PPPoE Host Internet IPv4 IPv4 PPPoE Bridge Ethernet Ethernet RFC 2684 ATM DSL 802.1ad 802.1ad Ethernet Ethernet 802.3 PHY 802.3 PHY IPv6 IPv6 PPPoE Bridge Ethernet RFC 2684 ATM DSL 17 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Ethernet 802.1ad 802.1ad Ethernet Ethernet 802.3 PHY 802.3 PHY Bridged Home with PPPoE Host (1) PPPoE Client Bridge BNG RADIUS PPPoE PADI – PADO – PADR - PADS PPP LCP ConfReq ConfReq: MRU, Magic Number PPP LCP ConfReq ConfReq: MRU, Magic Number, Auth=PAP PPP LCP ConfAck ConfReq: MRU, Magic Number, Auth=PAP PPP LCP ConfAck ConfReq: MRU, Magic Number PAP Authenticate-Request Username (Peer-ID)+ Password RADIUS Access-Request User-Name, Password, Service-Name VSA Service-Type=Framed, Framed-Protocol=PPP RADIUS Access-Accept IPv6-DNS, Framed-IPv6-Prefix 18 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Bridged Home with PPPoE Host (2) PPPoE Client Bridge BNG RADIUS PAP Authenticate-Ack IPv6CP ConfReq Interface-Id= 64-bit Interface ID/Client IPv6CP ConfAck Interface-Id= 64-bit Interface ID/Client PPP Phase IPv6CP ConfReq Interface-Id= 64-bit Interface ID/BNG IPv6CP ConfAck Interface-Id= 64-bit Interface ID/Client RADIUS Accounting-Request Start, User-Name, Service-Name VSA Service-Type=Framed, Framed-Protocol=PPP 19 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Bridged Home with PPPoE Host (3) PPPoE Client Bridge BNG RADIUS Anti-Spoofing Installed Multicast Router Advertisement M=0, O=1 Prefix Information Option: from Framed-IPv6-Prefix DHCPv6 INFORMATION-REQUEST DNS-Servers Option DHCPv6 REPLY DNS-Servers Option 20 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Optional DHCPv6 Stateless Phase 4 Prefix Size Broadband Subscribers 21 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 IPv4 and IPv6 Routing Gateways Internet IPv4 NAT Function UDP TCP TCP UDP IPv4 IPv4 Ethernet Ethernet IPoE IWF Ethernet RFC 2684 ATM DSL IPv4 802.1ad 802.1ad Ethernet Ethernet 802.3 PHY 802.3 PHY IPv6 Routing IPv6 Ethernet Ethernet RFC 2684 ATM DSL 22 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 IPoE IWF Ethernet IPv6 802.1ad 802.1ad Ethernet Ethernet 802.3 PHY 802.3 PHY IPv4 and IPv6 Routing Gateways Internet IPv4 NAT Function UDP TCP TCP UDP IPv4 IPv4 Ethernet Ethernet RFC 2684 ATM DSL IPv6 Routing IPv6 Ethernet Ethernet RFC 2684 ATM DSL 23 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Network Address Translation Customer-selected addresses on LAN IPoE IWF Ethernet IPv4 802.1ad 802.1ad Ethernet Ethernet 802.3 PHY 802.3 PHY IPv6 Routed IPoE IWF addresses on the LAN IPv6 Provider-assigned 802.1ad Ethernet 802.1ad Ethernet Ethernet 802.3 PHY 802.3 PHY IPv6 Prefix Delegation •Allows the routing gateway to receive a range of IPv6 addresses (a prefix) that are valid for that subscriber. The gateway must manage the assignment of individual addresses to hosts outside the scope of Prefix Delegation. Routing Gateway BNG DHCPv6 Solicit IA_PD Option DHCPv6 Advertise IA_PD: Prefix Option: <prefix> DHCPv6 Request IA_PD: Prefix Option: <prefix> DHCPv6 Reply IA_PD: Prefix Option: <prefix> 24 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Contents of the Prefix Delegation Option 0 16 32 Option IA_PD option-length IAID Timer 1 Timer 2 Option IAPREFIX option-length Preferred Lifetime Valid Lifetime prefix-length IPv6 Prefix IPv6 Prefix 25 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Contents of the Prefix Delegation Option 0 16 Option IA_PD 32 option-length IAID Contact the delegating router at this time to extend Contact _any_ delegating router at this time to extend Option IAPREFIX option-length Preferred Lifetime of addresses derived from this prefix Valid Lifetime of addresses derived from this prefix prefix-length IPv6 Prefix IPv6 Prefix 26 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 How Small? If Stateless Address Auto-Configuration (SLAAC) is to be supported, the prefix-length of any IPv6 link must be exactly 64-bits ::/64 RFC 4862: “If the sum of the prefix length [in the PIO] and the interface identifier length is not equal to 128 bits, the Prefix Information option MUST be ignored” RFC 2464: IPv6 over Ethernet The Interface Identifier is 64-bits and is based on the EUI-64 format. 27 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 How Big? Single Subnet Internet Subnet A Two Subnets Subnet A Internet Subnet B Cascading Routers Subnet A Subnet B 28 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Subnet C Internet The views http://www.apnic.net/policy/ipv6-guidelines.html An LIR can assign a /64 to /48 to an end site customer network based on their requirements. The following guidelines may be useful: /64 where it is known that only one subnet is required. /56 for small sites where it is expected only a few subnets will be required within the next two years. Subscribers can receive a /56 when connecting through on-demand or always-on connections such as small office and home office enterprises. /48 for larger sites, or if an end site is expected to grow into a large network. An LIR must submit a second opinion request to APNIC if it plans to assign more than a /48 to a single end site Assignments for networks equal to or greater than /48 must be registered. 29 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 What is the impact? Using a prefix longer than a ::/56 does not affect your allocation. HD-Ratio is calculated against ::/56 prefixes. The use of a shorter prefix does not increase the number of routes or FIB entries in Service Provider infrastructure. In the minimum /32 LIR allocation, there are: 16,777,216 ::/56 6,183,533 ::/56 at HD-Ratio 0.94 30 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 How many subnets is enough? With cascading routers we must support at least two subnets. The closest nibble is a /60, with 16 subnets. WT-187 and WT-177 Requirement: R-xx: A minimum delegation of a ::/60 to a Routing Gateway. R-xx: A recommended delegation of a ::/56 to a Routing Gateway. 31 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 5 IPv6 Addressing Importance of Persistent Addresses 32 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Impact of Valid & Preferred Lifetimes 0:00:00 Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred Host links can come up before the broadband connection. Impact of Valid & Preferred Lifetimes 0:01:00 DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation T1: 30 min T2: 48 min IA_PD: 2001:db8:1::/64 Preferred: 3600 Valid: 43200 Router Advertisement PIO: 2001:db8:1::/64 Preferred: 3600 Valid: 43200 Autonomous, On-Link Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 3,600 43,200 Preferred DHCPv6-PD options used in Router Advertisements. Impact of Valid & Preferred Lifetimes 0:01:30 Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 3,570 43,170 Preferred Lifetimes are tracked by the Host and decremented. Impact of Valid & Preferred Lifetimes 0:01:35 Router Advertisement PIO: 2001:db8:1::/64 Preferred: 3565 Valid: 43165 Autonomous, On-Link Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 3,565 43,165 Preferred And the RG also tracks lifetimes so that any RA are accurate. Impact of Valid & Preferred Lifetimes 0:01:40 Router Advertisement ROUTER LIFETIME: 0 PIO: 2001:db8:1::/64 Preferred: 3560 Valid: 43160 Autonomous, On-Link Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 3,560 43,160 Preferred If the Broadband Link goes down, set Router Lifetime to zero (0) so that the RG is not used as default router. Impact of Valid & Preferred Lifetimes 0:02:40 Router Advertisement ROUTER LIFETIME: 0 PIO: 2001:db8:1::/64 Preferred: 3500 Valid: 43100 Autonomous, On-Link Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 3,500 43,100 Preferred Prefixes are still valid even when link is down. RA continue to be sent. Impact of Valid & Preferred Lifetimes 1:02:40 Address Valid Lifetime Preferred Lifetime State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 0 39,500 Deprecated Impact of Valid & Preferred Lifetimes 1:05:00 DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation T1: 30 min T2: 48 min IA_PD: 2001:db8:1::/64 Preferred: 3600 Valid: 43200 Router Advertisement PIO: 2001:db8:1::/64 Preferred: 3600 Valid: 43200 Autonomous, On-Link Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 3,600 43,200 Preferred Whenever DHCPv6-PD provides the RG new lifetimes these are reflected in the RA Impact of Changing Prefixes 1:06:00 Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 3,540 43,140 Preferred Impact of Changing Prefixes 1:07:00 DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation T1: 30 min T2: 48 min IA_PD: 2001:db8:2::/64 Preferred: 3600 Valid: 43200 Router Advertisement PIO: 2001:db8:2::/64 Preferred: 3600 Valid: 43200 Autonomous, On-Link Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 3,540 43,140 Preferred 2001:db8:2::aaaa 3,600 43,200 Preferred Source Address Selection is NOT deterministic, however the Broadband Network Gateway is only expecting traffic sourced from 2001:db8:2::/64 Better Behaviour 1:07:00 DHCPv6 Prefix Delegation Router Advertisement T1: 30 min T2: 48 min IA_PD: 2001:db8:2::/64 Preferred: 3600 Valid: 43200 PIO: 2001:db8:1::/64 On-Link PREFERRED: 0 Valid: 43080 Autonomous, On-Link PIO: 2001:db8:2::/64 Preferred: 3600 Valid: 43200 Autonomous, On-Link Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 0 43,080 Deprecated 2001:db8:2::aaaa 3,600 43,200 Preferred Instead, let us Deprecate the old addresses. We cannot invalidate because of DoS-protection rules. Better Behaviour 1:07:30 Router Advertisement PIO: 2001:db8:2::/64 Preferred: 3540 Valid: 43140 Autonomous, On-Link Address Preferred Life Valid Life State fe80::aaaa Infinite Infinite Preferred 2001:db8:1::aaaa 0 43,020 Deprecated 2001:db8:2::aaaa 3,540 43,140 Preferred Source Address Selection will now prefer the new address space. 6 IPv6 Addressing Minimising Prefix Changes 45 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Address Hierarchy @ BNG – Day 2 2001:db8:0:0::/56 2001:db8:0:100::/56 Route table -----------------------------------------------------------2001:db8::/39 aggregate lo0 2001:db8:0:0::/56 2001:db8:0:100::/56 ... subscriber subscriber eth1 eth1 2001:db8:0:200::/56 2001:db8:0:300::/56 2001:d8b::/39 2001:db8:0:400::/56 2001:db8:0:500::/56 2001:db8:200:0::/56 Route table -----------------------------------------------------------2001:db8:200:/39 aggregate lo0 2001:db8:200:0::/56 2001:db8:200:100::/56 ... subscriber subscriber eth1 eth1 2001:db8:200:100::/56 2001:db8:200:200::/56 46 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 2001:d8b:200:/39 Address Hierarchy @ DSLAM – Day 1 2001:db8:0:0::/56 Route table -----------------------------------------------------------2001:db8::/46 aggregate lo0 2001:db8:4::/46 aggregate lo0 2001:db8:8::/46 aggregate lo0 2001:db8:0:100::/56 2001:db8:0:200::/56 2001:d8b::/46 2001:db8:4:0::/56 2001:db8:4:100::/56 2001:db8:4:200::/56 2001:d8b:4::/46 2001:db8:8:0::/56 2001:db8:8:100::/56 2001:db8:8:200::/56 2001:d8b:8::/46 47 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 2001:db8:0:0::/56 2001:db8:0:100::/56 ... subscriber subscriber eth1 eth1 Address Hierarchy @ DSLAM – Day 2 Route table -----------------------------------------------------------2001:db8::/46 aggregate lo0 2001:db8:4::/46 aggregate lo0 2001:db8:0:0::/56 2001:db8:0:100::/56 2001:db8:0:0::/56 2001:db8:0:100::/56 ... 2001:db8:0:200::/56 subscriber subscriber eth1 eth1 2001:d8b::/46 2001:db8:4:0::/56 2001:db8:4:100::/56 2001:db8:4:200::/56 2001:d8b:4::/46 2001:db8:8:0::/56 2001:db8:8:100::/56 2001:db8:8:200::/56 2001:d8b:8::/46 48 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 Route table -----------------------------------------------------------2001:db8:8:/46 aggregate lo0 2001:db8:8:0::/56 2001:db8:8:100::/56 ... subscriber subscriber eth1 eth1 Address Hierarchy Prefix Delegation The BNG should aggregate subscriber /56 prefixes into supernets within the service provider domain. The aim is to reduce the size of the service provider routing table. Logically group prefixes by the largest logical device (switch, DSLAM, etc) that is persistent regardless of normal network rearrangement. Recommend: Each access node should be represented by its own unique prefix-pool when DHCPv6 PD is in use 49 | Presentation Title | Month 2007 www.alcatel-lucent.com Thank You 50 | Presentation Title | Month 2007