Chapter 9b IPv6 Subnetting
advertisement
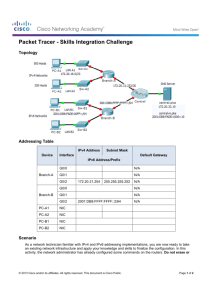
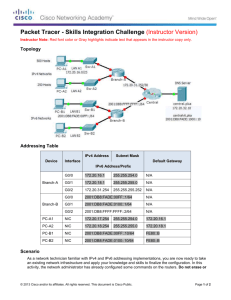
Chapter 9b Intro to Routing & Switching Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to: Identify an IPv6 address Identify the prefix, subnet ID, and interface ID Explain how to borrow bits Identify a subnetted IPv6 address Explain how IPv6 address assignments are implemented in a business network. 9.3 How many bits in an IPv6 address? How many hextets in an IPv6 address? 16 What are the 3 portions of the address? 8 How many bits in a hextet? 128 Prefix, subnet, interface How many addresses are available in IPv6? 340 undecillion How many bits is the interface ID? 64 What is the prefix ID? 2001:db8:4a7d:1f:1234:acad:abe5:115f/48 2001:db8:4a7d:: What 1234:acad:abe5:115f What is the interface ID? is the 1f? Subnet ID Why? It’s not even needed! For design only, NOT for conserving addresses Hierarchy (order) Borrowed bits from the interface ID Remember: Nibble /68 /72 /76 /80, etc. 1 hex digit is 4 bits Packet Tracer Lab 9.3.1.4 Subnetting an IPv6 Network Your network administrator wants you to assign five /64 IPv6 subnets to the network shown in the topology. Your job is to determine the IPv6 subnets, assign IPv6 addresses to the routers, and set the PCs to automatically receive IPv6 addressing. Your final step is to verify connectivity between IPv6 hosts. 9.2 Prevent Each host/port needs a unique IP Keep documentation Assign static addresses Servers & printers need to be accessed They can’t have random IPs! Monitor duplicate addresses performance Proper planning of network (separating subnets, making them smaller) makes for less bottlenecks Name Set some things… a pattern for each group Clients- DHCP assignment Servers & Printers Email & web Public IP Switches & WAPs Set statically for access Servers that access Internet Automatic within a set range Leased addresses can change For management Assigned manually Router ports Static 1st or last address pattern 9 VLSM Lab 9.2.1.4 Paper or 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer VLSM Lab 9.4.1.2 Packet Tracer As a network technician familiar with IPv4 and IPv6 addressing implementations, you are now ready to take an existing network infrastructure and apply your knowledge and skills to finalize the configuration. The network administrator has already configured some commands on the routers. Do not to erase or modify those configurations. Your task is to complete the IPv4 and IPv6 addressing scheme, implement IPv4 and IPv6 addressing, and verify connectivity. Worth 2 100 test grades! Complete Take the study guide handout the quiz on netacad.com Jeopardy review Chapter 9b Intro to Routing & Switching