Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
advertisement

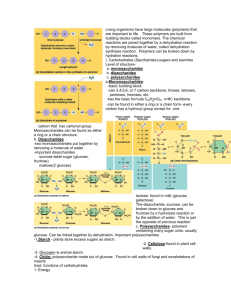
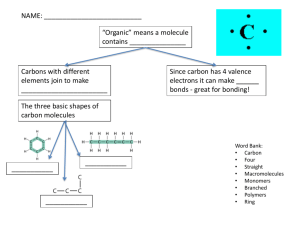
Cell Biology: Cell Compounds and Biological Molecules Lesson 3 – Carbohydrates and Lipids (Inquiry into Life pg. 31-36) Today’s Objectives Analyze the structure and function of biological molecules in living systems, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids Demonstrate a knowledge of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis applied to organic monomers and polymers Differentiate among carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids with respect to chemical structure Recognize the empirical formula of a monosaccharide List the main functions of carbohydrates Differentiate among monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides Differentiate among starch, cellulose, and glycogen with respect to function, type of bonding, and level of branching Describe the location, structure, and function of the following in the human body: neutral fats, steroids, phospholipids Compare saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in terms of molecular structure 2.4 Organic Molecules Always contain: Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) A carbon atom may share electrons with another carbon atom Can form long carbon chains (below) Carbon Rings Can also form carbon rings when a carbon chain turns back on itself Called a ring compound Functional groups can be attached to carbon chains or rings Macromolecules Many molecules of life are macromolecules. (macromolecules contain many molecules joined together) Monomers: Simple organic molecules that exist individually Can also be called “unit molecules” Polymers: Large organic molecules form by combining monomers Macromolecules Organic Molecules A meal containing carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. Dehydration and Hydrolysis Reactions Cells have mechanisms of joining monomers to build polymers Dehydration Reaction: an -OH and -H are removed as a water molecule Hydrolysis Reaction: the components of water are added Dehydration and Hydrolysis Reactions Dehydration and Hydrolysis Reactions Ex) dehydration of glucose Practice Pg. 42-43, #12, 17 Organic Molecules The 4 main types of organic polymers that we will be looking at are: Carbohydrates Lipids (fats) Proteins Nucleic Acids All are essential to life 2.5 Carbohydrates Some Functions: Quick fuel* Short-term energy storage* Structure of organisms * foremost function Molecules characterized by presence of the grouping H-C-OH Ratio of H to O is 2:1 Monosaccharides Simple Carbohydrates Monosaccharides are sugars with 3 - 7 carbon atoms Sugars are vital fuel nutrients for cells Pentose refers to a 5-carbon sugar All occur as ring structures with the formula C5H10Ox Hexose refers to a 6-carbon sugar Glucose – found in our blood Fructose – found in fruits Galactose – found in milk All occur as ring structures with the formula C6H12O6 Exact shape of ring differs, as does arrangement of the –H and –OH groups attached Monosaccharides - Glucose Three ways to represent the structure of glucose. Monosaccharides GLUCOSE FRUCTOSE GALACTOSE Disaccharides Disaccharides contain two bonded monosaccharides Have a common formula C12H22O11 Common disaccharides: Maltose - two molecules of glucose Sucrose – one glucose, one fructose Lactose – one glucose, one galactose Polysaccharides Polysaccharides are long polymers that contain many glucose subunits. basic formula (C6H10O5)n n= dozens to thousands of glucose units Three main types: Starch is the storage form of glucose in plants. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals. Cellulose can be found in the cell walls of plants. Polysaccharides Glycogen Starch Cellulose Starch Storage form of glucose in plants Few side chains of glucose Linkage between glucose units are the same Figure 2.17 pg. 33 Glycogen “animal starch” stored in the liver and muscle tissue Storage form of glucose in animals Many side chains of glucose Linkage between glucose units the same Figure 2.18 pg. 33 Cellulose Gives plants its structure Found in the cell walls of plants No side chains of glucose Different linkages between glucose units Fig. 219 pg. 33 Cellulose Our digestive system is unable to digest this linkage. Cellulose passes through our system as fiber or roughage. May be important for good health and prevention of colon cancer Summary of Carbohydrates 1) Source of short-term energy for all organisms: Animals – glycogen Plants – starch Energy is released as the carbohydrates are broken down by hydrolysis 2) Structural molecules in plants - cellulose Practice Pg. 42-43, #7, 9, 29 2.6 Lipids Include: Fats and Oils Phospholipids Steroids We eat lipids as part of our food. Our bodies are capable of producing them as well as metabolizing them Next to glucose, fats are the second most important energy molecule for us Unfortunately, we store them in adipose (fat) cells Lipids Some functions: Long-term energy storage Insulation against heat loss Protection of major organs Primary component of the cell membrane Molecules also contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but the H:O ratio is greater than 2:1 Lipids do not dissolve in water (non-polar) Lipids are electrically neutral Lipids Fats and Oils Fats (saturated fats) Usually of animal origin Solid at room temperature Fats provide long-term energy storage, insulate against heat loss, and protect major organs Ex.) lard, butter Oils (unsaturated fats) Usually of plant origin Liquid at room temperature Ex.) vegetable oils Formation of Fats Fats and oils form when one glycerol molecule reacts with three fatty acid molecules A fat molecule is sometimes called a triglyceride because of its three-part structure The term neutral fat is sometimes used because the molecule is non-polar Neutral Fat Structure Synthesis and degradation of a fat molecule Fatty Acids Saturated and Unsaturated Fatty Acids Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains that end with an acidic group -COOH. Saturated fatty acids: No double covalent bonds between carbon atoms Carbon atoms are “saturated” with as many hydrogen atoms as they can hold Unsaturated fatty acids: Have some double bonds between carbon atoms (wherever the number of hydrogens is less than two per carbon atom) Fatty Acids Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty Acid -COOH acidic group Carbon double bond Phospholipids Phospholipids are a variation of a triglyceride where one of the 3 fatty acids is replaced with a phosphate and nitrogen-containing group Primary components of cellular membranes Phospholipids The phosphate group creates a polar region on one end of the phospholipid This allows phospholipids to mix with both polar (hydrophilic) and non-polar (hydrophobic) materials Phospholipids The heads of the phospholipids are polar and are said to be water loving (hydrophilic) The tails of the phospholipids are non-polar and are said to be water fearing (hydrophobic) Phospholipid Structure Cell Membrane The structure of phospholipids make them a very important part of cells as they form much of the cell membrane Steroids Assist in protein synthesis Insoluble in water All steroids have four adjacent carbon rings. Examples: Cholesterol Testosterone important part of the cell membrane Protective cover around nerve fibers Precursor of sex hormones Male sex hormone Estrogen Female sex hormone Structure of Steroids All steroids have four adjacent carbon rings, but their attached groups differ. The effects on the body largely depend on the difference in the attached groups (shown in blue) Cholesterol Formed by the body and also enters body as a part of our diet Important part of the cell membrane and protective cover around nerve fibers Cholesterol is important but often results in fatty deposits inside arteries which narrows the pathway for blood to the heart Can result in high blood pressure Summary of Lipids 1) Source of long term energy storage 2) Insulate against heat loss 3) Protect internal organs 4) Saturated and Unsaturated fatty acids 5) Include fats and oils, phospholipids, and steroids Practice Pg. 42-43, # 15, 28 Review Quiz Organic Molecules always contain which elements? What reaction joins monomers to form polymers? Unit molecules The unit molecules of carbohydrates are? Hydrolysis Monomers are also known by which name? Dehydration synthesis What reaction breaks down a polymer into monomers? C and H Monosaccharides (such as glucose) The unit molecules of lipids are? Glycerol and 3 fatty acids