Accounting for a Merchandising Business
advertisement

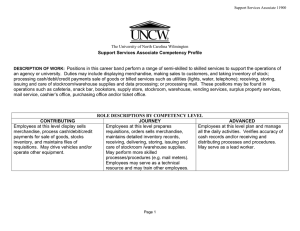
Accounting for a Merchandising Business Required Reading: Chapter 11 Terms • Service Business – Business that sell services rather than goods. Example: Dentist, Roofer, Travel Agent. To this point in the course, we have only looked at service businesses. • Merchandising Business – Business that buys goods and then sells them at a profit. Example: Clothing Store, Car Dealer. Merchandising Terms • Manufacturer – A business that converts raw materials to finished goods. • Wholesaler – A business that buys finished goods from a manufacturer and sells them to retailers. Otherwise called a “distributor” or a “middleman”. • Retailer – A business that buys finished goods from wholesalers and sells them to the public. Service vs. Merchandising • Services are not tangible. Therefore, there is no inventory kept. Once the opportunity to sell a service is past, it is gone forever. • Merchandise is tangible. Therefore, inventory that is not sold today can be sold at a later point, even if that means taking a reduced price. Therefore….. • Merchandise inventory has value and it is owned – it must be accounted for as an ASSET on the BALANCE SHEET AND… • Merchandise inventory represents an outflow of resources to produce revenue, so it must be accounted for on the INCOME STATEMENT. Inventory + = = Beginning Inventory Merchandise Purchased Total goods available for sale Merchandise Sold Ending Inventory The inventory figure here will go on the balance sheet as a current asset. AND… + = Cost of beginning inventory Cost of merchandise purchased Cost of ending inventory Cost of merchandise sold This figure will go to the income statement in a new section called “Cost of goods sold”.