Forces and Motion Interactive Powerpoint
advertisement
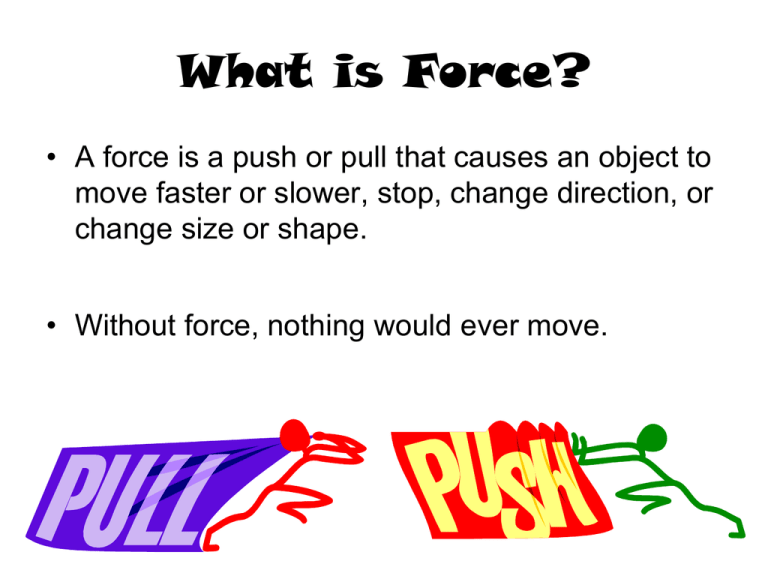
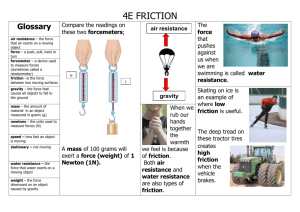
What is Force? • A force is a push or pull that causes an object to move faster or slower, stop, change direction, or change size or shape. • Without force, nothing would ever move. Let’s review information about forces! http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resources/parkworldplot/flash/concepts/allabo utforces.htm Magnetic Force Magnetism is the force of pushing or pulling between magnetic poles. It acts at a distance and cannot be seen. Materials that create this force are said to be magnetic and are called magnets. When like poles of magnets are near each other, a repulsive force exists, and the magnets move away from each other if the force is great enough. When opposite poles of magnets are near each other, an attractive force exists and the magnets move toward each other if the force is great enough. The closer the objects, the greater the magnetic force. The magnetic force is greatest at the poles of magnets. http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resources/parkworldplot/flash/concepts/magneticforces.htm Let’s look at what we already know about forces. What would happen with these pairs of magnets? Will they attract or repel each other? Write and draw what you think will happen, and then we will see if you are correct. 1. 2. 3. Gravitational Force • Gravity is a force that pulls all objects toward each other. http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resources/parkworldplot/flash/concepts/gravity.htm •The force of gravity causes two objects of different weights to fall to the ground at the same time. •The force of gravity is a pull that attracts objects to each other. This attraction is not noticeable unless one of the objects is very large (like a planet, moon, or the Sun). The force of gravity between Earth and anything on it is extremely noticeable because the mass of Earth is so large. •The pull of Earth’s gravity makes any object fall to the ground. As The Moon goes around Earth, its gravity pulls on Earth causing water in the oceans to move toward the Moon. •Earth’s gravity also pulls on the Moon. This force of gravity keeps the Moon moving around Earth. Similarly, the pull of the Sun’s gravity keeps Earth moving around the Sun. http://www.seed.slb.com/en/scictr/watch/skydiving/galileo_pisa.htm Which will hit the ground first? They travel at the same speed! The size of the mass does not change the rate of speed that objects fall. Which will hit the ground first? The paper was slowed by air getting trapped under as it fell. Shape of object may affect the speed in which it falls! Frictional Forces • Friction is the force that is applied by a surface as an object moves across it. • It is always present when two surfaces rub together. • Friction is affected by the nature of the surface (bumpy, smooth) and upon the degree to which they are pressed together . http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resources/parkworldplot/flash/concepts/friction.htm Friction Some forces can be seen when a moving object is touching another object, for example, a toy sliding across a table and slowing down. Friction is the force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. The rougher the surfaces are, and the harder they press together, the more friction there will be. Friction Friction can be reduced by using lubricants (like motor oil, wax, or grease), by making surfaces smoother, or by using rollers. Friction occurs in liquids and gases as well as between solids. Without friction, it would be very hard to slow or stop the motion of objects. high high low low low low The effect of friction can be changed in the following ways: • The rougher the surface, the greater the friction. • Smooth surfaces reduce friction. So, carpets have more friction that tile floors. Soles of shoes have rough textures to increase friction between the shoes and the floor so that it is possible to walk without slipping Amount of Surface Area • The greater the surface area, the greater the friction. • If more surface of an object touches another object, the friction will be greater. If tires of a car or truck are larger, more surface area of the tire will touch the road making friction greater. Trucks have larger tires to make it easier for them to stop or slow down. Lubrication • Lubricants- a substance put on a surface to reduce friction We use oil in a car to reduce friction on the motor. Without lubrication, moving parts of machines would slow down or stop very quickly. Motion • The motion of an object can be described by its position, direction of movement, and speed. How do we know this flag is in motion? Speed • One way to describe motion is speed. • Speed is a measure of the distance an object moves in a certain amount of time. • Speed is a measure of how fast an object is moving. • Motion is the change in position of an object over time when compared with a reference point. Position The position of an object is its location relative to another object (the reference point). For example, we can use the words “above”, “below”, “beside”, “behind”, “ahead of” plus the distance from the other object. The distance (length) from the reference point changes when the object moves. Point of Reference • Point of referenceyour point of motion when you observe a motion Starting Position • Speed, ramp height, length, and surface type can affect motion. • The higher the position, the greater the speed and distance will be in the object’s motion. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resourc es/parkworldplot/flash/concepts/balanceda ndun.htm Balanced Forces • Balanced forces are forces equal in size and opposite in direction. • Neither object moves because it is equal in both directions. Unbalanced Force Unbalanced forces occur when one force is greater than its opposite force. They cause the object’s motion to speed up, slow down, or stop. The object moves in the direction applied by the greater force. Unbalanced forces cause a non-moving object to start moving. They affect the rate and direction of motion in objects. Unbalanced Force Think of the game tug-of-war: If you are the only one pulling on your side, and on the other side there are three people pulling, the forces are unbalanced because it is three pulling against one. However, if three people were on each side, the forces would be more balanced, making the rope move less quickly. The Jeep pulling the car is another example of an unbalanced force because the Jeep has a bigger and more powerful force. If the Jeep was pulling another Jeep, the forces would be balanced and neither would move very far because the force being used is the same amount. Rate of motion Rate of motion is the speed of the object or how fast or slow the object is moving. Unbalanced forces can cause the speed or the rate of motion to change by increasing, decreasing, or stopping the motion. Direction If the total force is unbalanced the forces acting on an object are not equal in all directions. Thus, the unbalanced force causes a change in the direction of the motion as follows: The object moves away from the unbalanced force if it is a push, or toward the unbalanced force if it is a pull. The object will move in the direction of the greatest force acting on it. • Speed of an object is the measure of the distance (change in position) an object moves in a given amount of time. • Speed is distance divided by time, so you can take the value on the Y axis and divide it by the value on the X axis. Slower Speed The line on the graph is a flatter line, illustrating a slower speed Faster Speed Speed Stopped The line on the graph is a steeper line, illustrating a faster speed The line illustrates a constant speed from 0-5 seconds. From 5 to 10 sec, the line is flat with no increase in position. This graph illustrates an object that is stopped between 5 and 10 seconds. A change in force or mass affects the motion of an object as follows: Force • As the force increases, the speed of an object increases. • As the force applied to an object is decreased, the object will move slower than the object that was given a greater push or pull. • If there is no friction (for example, in outer space), an object that is already moving does not need a force to keep it moving. • Because of friction, however, an object slows or stops eventually. Mass • As the mass increases, the speed of an object decreases if the force remains the same. • The speed decreases as the object’s mass increases. • It is much harder to change the speed of a heavy object than a light object. • An object with a small mass is easier to stop or cause a change in motion than an object with a large mass. All About Forces • http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resourc es/parkworldplot/flash/concepts/allaboutfor ces.htm