Perception
advertisement

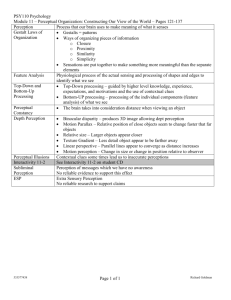
Chapter 6 Perception The process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting sensory information, which enables us to recognize meaningful objects and events. 2 Selective Attention Perceptions about objects change from moment to moment. We can perceive different forms of the Necker cube; however, we can only pay attention to one aspect of the object at a time. Ex: Cocktail Party Phenomenon Experiment - Video Necker Cube 3 Inattentional Blindness Daniel Simons, University of Illinois Inattentional blindness refers to the inability to see an object or a person in our midst. Simmons & Chabris (1999) showed that half of the observers failed to see the gorillasuited assistant in a ball passing game. 4 Change Blindness Change blindness is a form of inattentional blindness in which a majority of individuals giving directions failed to notice a change in the individual asking for directions. Experiment - Video © 1998 Psychonomic Society Inc. Image provided courtesy of Daniel J. Simmons. 5 Perceptual Illusions Illusions provide good examples in understanding how perception is organized. Studying faulty perception is as important as studying other perceptual phenomena. Line AB is longer than line BC. 6 Illusions • Physical • Paradoxical/Perceptual 7 Perceptual Organization Visual Capture Vision vs. other senses? Vision usually wins GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY -A movement formed in Germany in the 1920s and ’30s -The study of how people organize the world visually into meaningful units and patterns. - “The whole is more important than the sum of the parts” - In other words, when we perceive something, properties emerge from the object that are not found in any particular component. 8 Gestalt: Form Perception • People ALWAYS organize the visual field into 2 parts – ___________: stands out from the rest of the environment – ___________: the background SOMETIMES… Your eyes have trouble distinguishing FIGURE and GROUND GESTALT PRINCIPLES • 1. _______________ – Things that are near each other, tend to be grouped together • For Example… GESTALT PRINCIPLES • 2. Connectedness – In order to complete forms, the brain FILLS IN THE GAPS • For Example… GESTALT PRINCIPLES • 3. _______________ – Things that are alike in some way (e.g. color, shape, size) tend to be perceived as belonging together • For example… GESTALT PRINCIPLES • 4. _________________ – Lines and patterns tend to be perceived as continuing in time or space • For Example… Depth Perception Innervisions Depth perception enables us to judge distances. Gibson and Walk (1960) suggested that human infants (crawling age) have depth perception. Even newborn animals show depth perception. Visual Cliff 24 Binocular Cues Retinal disparity: Images from the two eyes differ. Try looking at your two index fingers when pointing them towards each other half an inch apart and about 5 inches directly in front of your eyes. You will see a “finger sausage” as shown in the inset. 25 Binocular Cues Convergence: Neuromuscular cues. When two eyes move inward (towards the nose) to see near objects and outward (away from the nose) to see faraway objects. 26 Monocular Cues See Characteristics of Perception assignment we did in library and/or homework. 27 Apparent Motion Phi Phenomenon: When lights flash at a certain speed they tend to present illusions of motion. Neon signs use this principle to create motion perception. Two lights one after the Illusion other. of motion. One light jumping from flashing one point to another: 28 Perceptual Constancy Perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal images change. Perceptual constancies include constancies of shape and size. Shape Constancy 29 Size Constancy Stable size perception amid changing size of the stimuli. Size Constancy 30 Size-Distance Relationship The distant monster (below, left) and the top red bar (below, right) appear bigger because of distance cues. Alan Choisnet/ The Image Bank From Shepard, 1990 31 Size-Distance Relationship Both girls in the room are of similar height. However, we perceive them to be of different heights as they stand in the two corners of the room. Both photos from S. Schwartzenberg/ The Exploratorium 32 Ames Room The Ames room is designed to demonstrate the sizedistance illusion. 33 What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… What is your perception of… Perception: Nature or Nurture? Perceptual Interpretation: Restored Vision Blind adults w/ restored vision: could differentiate figure and ground relationships, but had difficulty distinguishing a circle and a triangle (Von Senden, 1932). Others struggled w/ facial recognition & expressions. Perceptual Interpretation: Sensory Deprivation Kittens raised without exposure to horizontal lines later had difficulty perceiving horizontal bars. 47 Perception: Nature or Nurture? Perceptual Adaptation Courtesy of Hubert Dolezal Visual ability to adjust to an artificially displaced visual field, e.g., prism glasses. 48 Perception: Nature or Nurture? Perceptual Set A mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another. What you see in the center picture is influenced by flanking pictures. From Shepard, 1990. 49 Perception: Nature or Nurture? Perceptual Set Other examples of perceptual set. Dick Ruhl Frank Searle, photo Adams/ Corbis-Sygma (a) Loch ness monster or a tree trunk; (b) Flying saucers or clouds? 50 FILL IN THE FOLLOWING WORDS? 1. Goose Swan D_ck 4. Wager Gamble B_t 7. Bonnet Derby _at 2. Bear Wolf _ox 5. Sinful Evil B_d 8. Shoot Kill H_nt 3. Artist Brush P_int 6. Courage Brave _old 9. Tractor Crops _arm FILL IN THE FOLLOWING WORDS 1. Sam Pete M_ke 4. Base Ball B_t 7. Cat Mouse _at 2. Package Carton _ox 5. Pillow Sheet B_d 8. Help Suggest H_nt 3. Needle Sharp P_int 6. Bend Crease _old 9. Hurt Punish _arm Perception: Nature or Nurture? Schemas Schemas are concepts that organize and interpret unfamiliar information. Courtesy of Anna Elizabeth Voskuil Children's schemas represent reality as well as their abilities to represent what they see. 53 Schemas: Recognizing a Face 54 55 56 Features on a Face Face schemas are accentuated by specific features on the face. Kieran Lee/ FaceLab, Department of Psychology, University of Western Australia Students recognized a caricature of Arnold Schwarzenegger faster than his actual photo. 57 Eye & Mouth Eyes and mouth play a dominant role in face recognition. Courtesy of Christopher Tyler 58 Perception: Nature or Nurture? Cultural & Context Effects Context instilled by culture alters perception. What do you see in this picture? To an East African, the woman sitting is balancing a metal box on her head, while the family is sitting under a tree. 59 Perception: Nature or Nurture? Perception = Biopsychosocial 67 Perception & Human Factors Human Factor Psychologists design machines that assist our natural perceptions. Courtesy of General Electric Photodisc/ Punchstock The knobs for the stove burners on the right are easier to understand than those on the left. 68 Is There Extrasensory Perception? Perception without sensory input is called extrasensory perception (ESP). A large percentage of scientists do not believe in ESP. 1. Telepathy: Mind-to-mind communication. One person sending thoughts and the other receiving them. 2. Clairvoyance: Perception of remote events, such as sensing a friend’s house on fire. 3. Precognition: Perceiving future events, such as a political leader’s death. 69 Putting ESP to Experimental Test In an experiment with 28,000 individuals, Wiseman attempted to prove whether or not one can psychically influence or predict a coin toss. People were able to correctly influence or predict a coin toss 49.8% of the time. 70 Premonitions or Pretensions? Can psychics see the future? Can psychics aid police in identifying locations of dead bodies? What about psychic predictions of the famous Nostradamus? The answers to these questions are NO! Nostradamus’ predictions are “retrofitted” to events that took place after his predictions. 71