Units 1 - biologyatstabs
advertisement

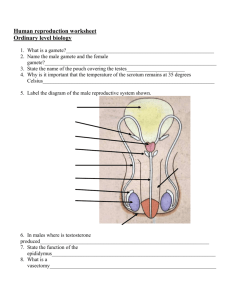
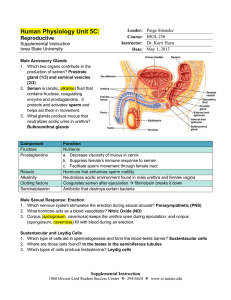
Higher Human Biology: Homework Questions Topic 1: Health and Physiology Mark Sub-Topic 2a: Reproduction Name ____________________________________________ Class ____________________________________________ Sub-Unit 1: REPRODUCTION 1. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A B C D sperm testosterone seminal fluid follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) 2. The sperm counts of a sample of men taken between 1940 and 2000 are shown in the graph below. What is the average reduction in sperm count per year? A B C D 0.67 million/cm3/year 0.75 million/cm3/year 0.92 million/cm3/year 45 million/cm3/year 3. From which structure in the female reproductive system does a corpus luteum develop? A B C D Endometrium Graafian follicle Fertilised ovum Unfertilised ovum 4. Which of the following forms of contraception causes thickening of cervical mucus? A B C D Mini-pill Barrier methods Morning-after pill Intra-uterine device 5. The graph below shows the growth in length of a human fetus before birth. What is the percentage increase in length of the fetus during the final 4 months of pregnancy? A B C D 33.3 60.0 62.5 150.0 6. The table below contains information about four semen samples Semen Sample A B C D Number of sperm in sample (millions/cm3 ) Active sperm (percent) Abnormal sperm (percent) 40 30 20 60 50 0 75 40 30 65 10 70 Which semen sample has the highest number of active sperm per cm3 7. The diagram refers to human reproduction. OVARY TESTIS gamete mother cells gamete mother cells Process X Process X Ovum 9. One function of the seminal vesicles is to A B C D produce testosterone allow sperm to mature store sperm temporarily produce nutrients for sperm 10. The graph below shows changes in the concentration of hormones X and Y in the blood during the menstrual cycle. Sperm Process Y Zygote Which of the following correctly identifies hormones X and Y? Process Z Embryo cells Which of the following correctly identifies processes X, Y and Z? A B C D X mitosis meiosis meiosis mitosis Y meiosis fertilisation mitosis fertilisation Z fertilisation mitosis fertilisation meiosis 8. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? Hormone X LH Oestrogen Oestrogen Progesterone A B C D Hormone Y Oestrogen FSH Progesterone Oestrogen 11. Changes in the ovary during the menstrual cycle are described below. 1 2 3 4 5 Corpus luteum forms Ovulation occurs Progesterone is produced Corpus luteum degenerates Graafian follicle develops The sequence in which these changes occur following menstruation is A B C D 2, 3, 1, 5, 4 2, 1, 3, 4, 5 5, 3, 2, 1, 4 5, 2, 1, 3, 4 12. The graph below shows the growth in length of a human fetus before birth. 14. The diagram below shows the blood flow in the umbilical cord. Which line in the table below identifies correctly blood vessel X and the blood it carries? What is the percentage increase in length of the fetus during the final 4 months of pregnancy? A B C D 33.3 60.0 62.5 150.0 A B C D The diagram shows the stages of development when major and minor malformations of organs may occur if there is exposure to nicotine. Key A B C D 0.67 million/cm3/year 0.75 million/cm3/year 0.92 million/cm3/year 45 million/cm3/year Blood carried in X deoxygenated oxygenated deoxygenated oxygenated 15. Nicotine is a chemical which may affect pre-natal development. 13. The sperm counts of a sample of men taken between 1940 and 2000 are shown in the graph below. What is the average reduction in sperm count per year? Blood vessel X vein vein artery artery major malformation minor malformation For how many weeks during pregnancy is there a possibility of major malformations to organs during development? A B C D 6 7 9 13 16. The diagram below represents part of the mechanism which controls ovulation. Pituitary Stimulating hormone Inhibiting hormone Ovaries The hormones indicated above are A B C D Stimulating hormone Inhibiting hormone FSH Progesterone Oestrogen LH Oestrogen FSH LH testosterone 17. On which day in the following menstrual cycle could fertilisation occur? A B C D Day 30 Day 17 Day 14 Day 2 18. The diagram shows a section through the reproductive organs of a man. (a) (i) State he site of sperm production within the testis. __________________________________ (ii) 1 State one function of the secretions from the seminal vesicles and prostrate gland. ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ (b) (i) (ii) During a male sterilisation operation (vasectomy), a tube is cut. Draw a letter X on the diagram to indicate the likely position of the cut. 1 Why is the transport of testosterone from the testes unaffected by this operation? ______________________________________________________ 1 19. The diagram shows stages in the development of a human embryo from fertilisation to implantation. (a) Name the parts labelled A and B. A ___________________________ B _________________________ 1 (b) What term is used to describe he first few divisions of the zygote? _______________________________________ 1 (c) Name a hormone which is involved in preparing the endometrium for implantation and state where it is produced. Hormone ______________________ Produced by ___________________ 1 (d) What organ will develop from the tissue labelled C? _________________________________________ (e) Sometimes twins develop in the uterus. Distinguish between the formation of monozygotic and dizygotic twins. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 1 20 The diagram shows part of the reproductive system of a woman in early pregnancy. (a) Place an X on the diagram to show where fertilisation occurred. 1 (b) Structure P produces progesterone at this stage in pregnancy. (i) Name structure P. _______________________________ (ii) 1 State one function of progesterone during early pregnancy. ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ 1 (c) Structure Q will develop into the placenta. Name the processes involved in the transfer of oxyen, glucose and antibodies across the placenta. Oxygen ___________________ Glucose ___________________ Antibodies ___________________ 2 (d) In the early stages of pregnancy the cells of the embryo are starting to differentiate. Describe what happens during differentiation. ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ 1 (continued) 21 (e) Name a stage of embryo development that comes between fertilisation and differentiation. ________________________________ 1 (e) A woman gives birth to monozygotic twins. State whether monozygotic twins are identical or non-identical and give a reason for your answer. Monozygotic twins ___________________________ Reason ________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 1 Questions 22 and 23 refer to the following list of hormones. A Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) B Luteinising Hormone (LH) C Oestrogen D Progesterone 22 Which hormone stimulates the production of testosterone by the testes? 23 Which hormone is produced by the corpus luteum? 24 Which of the following will not normally pass through the placenta between the mother and fetus? A B C D Oxygen Minerals Glucose Red blood cells 25 The flowchart summarises the processes involved in the production of semen. Hormone X LH Tissue Y Testosterone Sperm Mother Cells Structure Z Mature sperm cells Semen SEMINIFEROUS TUBULES (a) Name Hormone X and tissue Y. Hormone X _________________ Tissue Y ________________________ (b) Semen contains substances secreted by structure Z. (i) Identify structure Z. __________________________________ 1 (ii) Describe how a named substance from structure Z aids fertilisation. Substance __________________________ Description ______________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 1 (c) Complete the table to show the percentage of each type of cell which would contain a Y chromosome. Cells Sperm mother cells Mature sperm cells Percentage of cells containing A Y chromosome 26 The diagrams represented gamete production in an ovary and part of a testis. (a) (i) Which letter represents a mature ovum? 1 (ii) Identify one labelled part of each organ which is affected by FSH. Letter Name (iii) Describes the effect of testosterone on the testes of an adult. ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ (b) 1 Oxytocin is a hormone which is secreted during and after childbirth. (i) State where oxytocin is produced in the body __________________________________ 1 (ii) Synthetic oxytocin can be used to induce labour Describe how it brings about birth. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 1 The diagram below shows a section of a woman’s breast shortly after she has given birth. 27 (a) (i) Name the hormone that stimulates the secretory glands to start producing milk. ____________________________ 1 (iii) The cells lining the secretory glands are particularly rich in ribosomes. Suggest a reason for this. ______________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ (b) 1 Fluid is not usually released from the breast until the baby suckles. (i) What name is given to the first fluid that the baby receives from the breast? (ii) Describe one way in which this first fluid differs from the breast milk Produced a few days later. _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 1 (iii) Suckling and crying are examples of non-verbal communication used by a baby. Why is non-verbal communication important to both the mother and baby? _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 1 28 The graphs below show that plasma concentrations of certain hormones throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle. Graph 1 shows the concentration so FSH and LH. Graph 2 shows that concentration of two other hormones, X and Y. 29 (a) Where in the body are FSH and LH produced? __________________________________________________ (b) 1 Name hormones X and Y. X _______________________ Y _______________________ (c) What is the maximum concentration of hormone Y? _______________ Units (d) 1 On which day did ovulation occur? Give a reason for your answer. Day ______________ Reason ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________ (e) 1 During her next cycle, the woman became pregnant. Describe any differences which would occur in the concentrations of FSH and hormone Y after day 25. FSH ______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 1 Hormone Y _________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 1 30 The graph below shows the concentration of two ovarian hormones in a woman’s blood during her menstrual cycle. (a) Name hormone X. ________________________________________________________ 1 (b) What effect does oestrogen have on the following structures? (i) The uterus between days 4 and 12 in the cycle. ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ (ii) 1 The pituitary gland on day 12 of the cycle. ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 1 (c) Describe one way in which the graph would be different if the woman became pregnant during this cycle. _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 1 30 (continued) (d) The diagrams below show sections through two structures found in the ovary at different times in the menstrual cycle. P (i) Q Name structures P and Q P ______________________ Q ___________________ (ii) 1 What key event in the menstrual cycle occurs before P develops Into Q? __________________________________________________ 1 31 The graph below shows the relative concentrations of three hormones in the Plasma of a woman during a normal 28-day menstrual cycle. Hormone A Luteinising Hormone (LH) Increasing Hormone concentration Follicle stimulating Hormone (FSH) 2 (a) 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 Days of cycle 24 26 28 Name hormone A. __________________________ (b) 1 What is the effect of the sudden increase in concentration of luteinising hormone? ________________________________________________ (c) During which time period is the endometrium likely to reach maximum thickness? Underline the correct answer. 0 – 4 days (d) 1 12 – 16 days 22-26 days 1 In what way would the line showing the concentration of FSH be different if fertilisation took place during this cycle? Give an explanation for your answer. Difference ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 1 Explanation _________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 1 32. The graphs below show changes in the volume and composition of milk produced by a woman in the first week following the birth of her child. Graph 1 – changes in the volume of milk produced Graph 2 – Changes in the concentration of lactose sugar and IgA antibody in milk 32. (continued) (a) (i) What name is given to milk produced in the first few days after birth? ______________________________________________ (ii) 1 from Graph 2, describe two ways in which the composition of milk produced in the first three days after birth differs from milk produced later 1.______________________________________________ 2. _____________________________________________ (b) What was the volume of milk produced on day 3? _________________ (c) 1 (i) 1 Between days 2 and 3 this woman produced a constant mass of IgA. Explain why the concentration of IgA in her milk decreased during this time. ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ (ii) 1 Express, as a simple whole number ratio, the concentration of IgA Compared to the concentration of lactose produced on day 6. (1g = 1000mg) Space for calculation _______:_______ IgA Lactose (d) 1 Using Graphs 1 and 2, calculate the mass of lactose produced on day 5. Space for calculation __________g 1 33. The concentration of progesterone in the blood of a woman over a 40 week period of time during which she became pregnant is shown on the graph below. (a) Draw a vertical line on the graph to indicated the time of ovulation. 1 (b) Describe the changes in progesterone concentration during the first 32 weeks. ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ (c) (d) 2 Where is progesterone produced (i) during the first weeks of pregnancy? _________________ 1 (ii) during the later stages of pregnancy? ________________ 1 The decrease in the level of progesterone shown on the graph stimulates the production of prolactin. What is the effect of prolactin? ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ 1 34. The sperm counts of 30 men taken between 1940 and 2000 are shown in the graph below. A line of best-fit has been drawn, to indicate the trend over the 60 year period. (a) Using the line of best-fit, calculate the percentage decline in sperm count over the 60 year period. Space for calculation ___________ % (b) 1 From the graph, what is the maximum sperm count for any one individual recorded during this period? __________million/cm3 (c) Some insecticides are thought to influence sperm production. Explain why animals at the end of food chains are more likely to be affected by insecticides. ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 1 (d) Name the pituitary hormone which stimulates the production of sperm. ________________________________________________ 1 34. (continued) (e) Name a gland which adds fluid to sperm during ejaculation and describe one function of this fluid. Gland _____________________________ 1 Function of fluid ____________________________________ _________________________________________________ (f) 1 Two treatments sometimes used for infertility are artificial insemination and in vitro fertilisation. Describe briefly what is meant by these terms. Artificial insemination ________________________________ _________________________________________________ In vitro fertilisation __________________________________ _________________________________________________ 35. The diagram below shows the influence of the pituitary gland on testosterone production. Pituitary gland Hormone X produced Testes stimulated Testosterone produced What is hormone X? A. Luteinising hormone B. Follicle stimulating hormone C. Oestrogen D. Progesterone 2 36. Which of the following changes indicate ovulation is likely to have taken place? Cervical mucus A B C D 37. Which of the following describes correctly the exchange of materials between maternal and fetal circulations? A B C D 38. Becomes sticky Becomes sticky Becomes watery Becomes watery Body Temperature Rises Falls Rises falls Glucose In to fetus by active transport In to fetus by active transport In to fetus by pinocytosis In to fetus by diffusion Antibodies In to fetus by active transport In to fetus by pinocytosis In to fetus by active transport Into mother by pinocytosis The diagram below presents the appearance of a testis when viewed under a microscope. (a) Name Structure X: ____________________________________ (b) State which cells are produced in structure X: _______________ (c) What is the name of cells labelled Y? _____________________ (d) Explain the role of cells labelled Y in the production of male sex cells. ___________________________________________________ 39. Luteinising hormone is involved in the control of the menstrual cycle in female mammals. (a) Name the gland which produces luteinising hormone ___________________________________________________ (b) Name another hormone produced by this gland which controls the menstrual cycle ____________________________________________________ (c) Progesterone is a hormone produced from within the ovary. (i) Name the structure from within the ovary which produces progesterone. _______________________________________________ (ii) State one function of progesterone during the menstrual cycle. _______________________________________________ (iii) As the menstrual cycle continues, progesterone levels decrease. State the effect this will have on the uterus. ________________________________________________ 40. (a) Decide if each of the following statements about treatments for infertility is TRUE or FALSE and tick () the correct box. If the answer is FALSE, write the correct word(s) in the Correction box to replace the word(s) underlined in the statement. Statement If mature sperm are defective or very low in number IVF can be used Ovulation can be stimulated by drugs that prevent the negative feedback effect of progesterone on FSH secretion Donor sperm can be used in artificial insemination of the male partner is sterile. True False Correction ICSI Intracytoplasmic sperm injection oestrogen ¶ (b) the table below refers to semen samples take from five men. Semen Sample Number of sperm in sample (millions/cm3) Number of normal sperm in sample (millions/cm3) (i) A B C D E Identify which man has the lowest percentage of normal sperm. Letter: _________________________________________________ (ii) A man is fertile if at least 60% of his sperm are normal Identify which man/men is/are infertile. Letter(s): _______________________________________________ 41. (a) (b) A variety of techniques can be used to monitor the health of the mother and the developing foetus. State what each of the following is used for: (i) Ultrasound imaging _________________________________ (ii) Dating scans ______________________________________ A sample of fluid which surrounds the embryo can be extracted from the mother using a syringe. What is the name given to this technique? ______________________________________________________ Give ONE advantage and ONE disadvantage in using this technique. Advantage: _____________________________________________ Disadvantage: ___________________________________________ Postnatal screening can be carried out involving diagnostic testing for metabolic disorders. Name a metabolic disorder which can be tested for using postnatal screening techniques. Name: __________________________________________________ End of Sub-Unit 1 : REPRODUCTION