File
advertisement

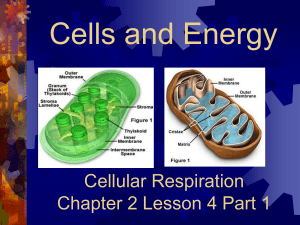
Biology Fermentation lab Metabolism • The scientific term for obtaining and using energy Cellular respiration • the process through which our cells get the energy to perform their functions. Since all living things are made of cells, and all cells need energy to perform life's functions, cellular respiration is necessary for all living things. There are two types of cellular respiration: aerobic and anaerobic • During aerobic respiration, oxygen is present, and this results in a larger amount of energy. Even though anaerobic cellular respiration lacks the presence of oxygen, it is still able to produce energy, just smaller amounts of it. This process is called fermentation. Aerobic respiration • the process by which a cell uses O2 to "burn" molecules and release energy ATP • Is considered to be the 'energy currency' of cells. During cellular respiration, food molecules are broken down from sugar molecules to energy molecules. • All organisms produce ATP by releasing energy stored in glucose and other sugars. • Plants make ATP during photosynthesis. • All other organisms, including plants, must produce ATP by breaking down molecules such as glucose. Krebs Cycle • http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072 507470/student_view0/chapter25/animation_ _how_the_krebs_cycle_works__quiz_1_.html • https://youtu.be/JPCs5pn7UNI glycolosis • (glyco = sugar; lysis = breaking) • Goal: break glucose down to form two pyruvates • Who: all life on earth performs glyclolysis • Where: the cytoplasm Fermentation • is a metabolic process that converts sugar to acids, gases or alcohol. It occurs in yeast and bacteria, but also in oxygen-starved muscle cells, as in the case of lactic acid fermentation. Variables • Independent – The thing you change. There can only be one. It is listed first on a data table. • Dependent – Can be measured, can be more than one. The “what happened”. • Control – a constant, no changes made to it.