The Spanish Encounter updated
advertisement

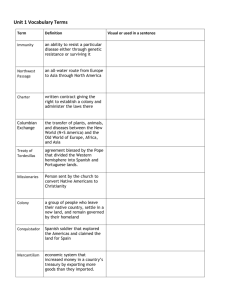
“The Spanish Encounter” A profound ‘event’ • “The biggest population shift of modern times has been the colonization of the New World by the Europeans, and the resulting conquest, numerical reduction, or complete disappearance of most of Native Americans…” -Jared Diamond, Guns, Germs, and Steel Peoples of the Americas ~1492 C.E. 1491: Europeans v. Americans Europe: about 60 million people (80 million before the Black Plague) Americas: population estimates range from 10 million to over 100 million. Many scholars take a mid-point of about 50-60 million people • Aztec Empire 6-10 million • Inca Empire: 10 million • Caribbean 225,000-6 million (probably on the higher end) REASONS FOR COLONIZATION AND EXPLORING THE NEW WORLD • Europeans are searching for a trade route to Asia for spices and silk • Christopher Columbus reaches the West Indies, a chain of islands near the Americas on October 12, 1492 Voyages of Columbus THE SPANISH:GOD • Spanish fought for hundreds of years against the Moors, Islamic rulers of Spain since 711 AD • For the Spanish it is a “Holy War” against non-Christians • The Spanish believe that it is their duty to spread Christianity to the world • When the Spanish conquer Native Americans they must be converted THE SPANISH: GOLD • Both the Incas and Aztecs have gold • The Spanish want gold in a big way to enrich themselves and pay for expansion of their empire • Spain is competing with other European countries THE SPANISH:GLORY • The Spanish come from a warlike tradition (hundreds of years of warfare against the Moors) • Spain is not a wealthy country and Spanish conquistadors are willing to take great risks to make a name and fortune for themselves in the New World • Many conquistadors are lower level nobles without an inheritance The Fall of Aztec & Inca Empires Spanish advantages – Superior and intimidating weapons • horses, guns, ships, steel – Divide and conquer; conflict in both Aztec and Inca empires • Subjects who were taxed heavily, treated badly – Fought to kill vs. to capture (particularly Aztecs) – Germs--Incas already reduced by smallpox and civil war, Aztec resistance is undermined by smallpox and other diseases. HERNANDO CORTES • In 1519, Hernando Cortes lands at Vera Cruz, Mexico with 600 soldiers • Cortes destroys the Aztec empire in 1521 The Incan Empire What do we know? Peoples of the Americas ~1492 C.E. The Incan Empire Theocratic Empire: • The ruler could only come from a family believed to be descended from the sun god. • Ruled over the largest empire in the Americas: 16 million people. The Incan Empire • Master builders and engineers. • Didn’t use the wheel • Llamas don’t pull plows. – Built by hand. Incan Labor system The Mita System: • All able bodied people had to work for the state for a certain number of days every year. • In exchange, the state supported old and sick people. • The state would send potatoes to areas that had poor harvests. Incan road system 14,000 miles of roads. Atahualpa v. Francisco Pizzaro Spanish defeat the Incas • In 1532 Francisco Pizarro at the head of fewer than 200 Spaniards entered the Inca Empire, ambushes the Incas at Carjamarca and kidnapped the Inca emperor Atahualpa. • Atahualpa offered to fill a room once with gold and twice with silver in exchange for his release. • After the Spaniards received the ransom, they strangled Atahualpa. • The Spanish then took control of the Inca capital, Cuzco, and ultimately the defeated the Incas in a series of battles Atahualpa captured Indians were not conquered immediately • Resistance to Spanish continued for 40 years, until 1572. Incas defeated Spanish several times in battle. • Incas adapted tactics to counter Spanish military advantages • Some Indians (Argentina and Chile) were not defeated until the late 1800s • After the death of the Inca, several of Atahualpa's generals took matters into their own hands. Quizquiz was especially notable for resisting the Spaniards at Cuzco, and Ruminahui burned Quito rather than let it fall into enemy hands. Nevertheless, the Spaniards were irrepressible, and within two years were seemingly in firm control. However, one of the "puppet" Incas that the Spaniards had enthroned was plotting against them. In 1536 Manco Inca Yupanqui, one of the many brothers of Atahualpa and Huascar, led over 100,000 Incan warriors in a revolt against the Spanish overlords. He besieged the city of Cuzco for over six months and killed one of the Pizarro brothers before being driven away by Spanish reinforcements. Manco Inca escaped and formed a rebel colony deep in the mountains which was not conquered by the Spanish for almost forty years. The Great Dying By 1650, only 5-8 million indigenous people remained A 90-95% reduction in population of the Americas in 150 years Population of Mexico after Spanish Encounter Treasure • Spain soon became the richest, most powerful nation in the world due to the American colonies. • 2 main areas of silver production-Mexico (Zacatecas) and Potosi (Peru) • In the 1500s, Spain extracted the equivalent of about $1.5 trillion (in 1990s $) in gold and silver from the Americas. • This new found wealth helped usher in the ‘Golden Age’ of Spain and made Spain the wealthiest nation in Europe Silver: The first truly global commodity Potosi-Cerro Rico “Rich Hill” 8 million dead Mercantilism Economic nationalism to build a wealthy and powerful state, especially in Europe 1600-1800. 1.Maintain strict government control of trade 2.Get as much gold, silver and other resources as you can 3.Establish a favorable balance of trade at the expense of other nations 4.Get colonies and exploit them. 5.Build a big navy The Columbian Exchange In your opinion, what are the two most important organisms that were involved in the Columbian Exchange? Birth of Spanish America Spanish POV • Spanish forced Indians to become Christians • Indians also forced to work the fields, clear forests, and work in the gold and silver mines • If the Indians did not submit they were punished and killed • Some Spaniards took Indian women as wives, their children known as mestizos (“mixed”) • Birth of Spanish America Indios POV • Indigenous people who survived adapted to Spanish rule: – Spanish language – Adopted Christianity (but with local influences) – Women intermarried with Spanish (mestizos) Encomienda • Labor system—Indians “awarded “ to Spanish landowners • indigenous labor for construction, servants, agricultural work, mining • Harsh working conditions, contributed to decline in Indian populations. • System fostered concentrated ownership of land. Cortes awarded 7,700 square miles of land in Mexico = almost 5 million acres. Opposition to Spanish rule • Spanish priests accompanied Spanish conquistadors and worked to spread Christianity in the Americas. • Many of they also pushed for a better treatment of Native Americans, speaking out against the cruelty towards the natives. • They criticized the encomienda system. Bartolome de las Casas • “There is nothing more detestable or cruel than the tyranny which the Spaniards use toward the Indians for getting of riches.” • Las Casas suggested the use of African labor. – “The labor of one is more valuable than that of four Indians.” – The Spaniards soon began to import Africa slaves to meet their growing labor needs. De las Casas The Colonial Class System Peninsulares Mestizos Native Indians Creoles Mulattos Black Slaves Coiote Casta system Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade