Syllabus - nikeths.resources
advertisement

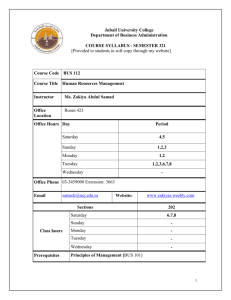
Royal Commission for Jubail and Yanbu Jubail University College Academic Affairs Department Department of Business Administration FX-ACA-057 Issue 0 Rev. 0 April 21, 2015 i COURSE SYLLABUS SEMESTER _361_ Course Code & Number: BUS 338 Course Title: MARKETING CHANNEL Prerequisite: BUS 231-PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING Section Number(s): 201 Instructor: MRS. SABITHA NIKETH Office Location: Room 423 Office Hours: Sunday – 3, 6 Monday – 3, 4, 5, 6 Tuesday – 3, 6, 7, 8 Wednesday – 2 Thursday – 3, 6 Class Hours: 201-Mon 1, 2 Thurs 6 Instructor’s Office Phone: 03-3459000 Extension: __3666__ Instructor’s Email: NIKETHS@ucj.edu.sa Course Description Course Objectives Methods of Instruction Required Textbooks Proposed Websites Grading Scheme Marketing channels are analyzed as systems of interrelated and interdependent organizations engaged in making goods and services available for consumption by industrial, institutional, and household consumers. This course emphasizes the means by which effective and efficient distribution networks (comprising manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, transportation firms and other actors in the distribution process) can be constructed. Cases are used for illustrative and analytical purposes. By the end of this course, students will be able to demonstrate knowledge of analyzing marketing channels as systems of interrelated and interdependent organizations engaged in making goods and services available for consumption by industrial, institutional, and household consumers. They will demonstrate skills in constructions of effective and efficient distribution networks. Lecture sessions, Tutorials, Self-learning with the use of library and internet resources, Homework, assignments, Case studies and Group activities Marketing Channels, 7/e Coughlan, Anderson, Stern & ElAnsary©2006 | Prentice Hall | Paper; 624 pp | | ISBN-13: 9780131913462 www.mymktlab.com. 2 major quizzes Assignment Mid Term Examination Final Examination Total 20% 20% 20% 40% 100% Course Outline Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Topics & Activities Marketing Channels: Structure and Functions CHAPTER 1: What Is a Marketing Channel? Why Do Marketing Channels Exist and Change? What Is the Work of the Marketing Channel? Who Belongs to Marketing Channel? , A Framework for Channel Analysis. Segmentation for CHAPTER 2:End-User Channel Preferences, Marketing Channel Service Outputs, Segmenting the Market by Service Design: Service Outputs Output Demands, Meeting Service Output Demands, The Role of Service Output Demand Analysis in Marketing Channel Design. Supply Side Channel CHAPTER 3: Channels Flows Defined, Analysis: Channel Flows Describing the Current Channel with the Efficiency and Efficiency Analysis Template, Using Channel Flow Concepts to Design a Zero-Based Channel, Matching Normative and QUIZ 1-10% Actual Profit Shares. Gap Analysis CHAPTER 5: Sources and Types of Channel Gaps, Closing Channel Gaps, Pulling it Together: The Gap Analysis Template. Managing Conflict to CHAPTER 7: Assessing the Degree and Nature of Increase Channel Channel Conflict, The Consequences of Conflict, Coordination Major Sources of Conflict in Marketing Channels, Clash of Market Domains, Fueling Conflict, Conflict Resolution Strategies: How They Drive The Conflict and Shape Channel Performance. MID TERM EXAMINATION (20 %) Strategic Alliances in Distribution 10 11 12 Retailing QUIZ 2-10% Wholesaling 13 14 15 16 Notes Franchising Logistics and Supply Chain Management CHAPTER 8 : Strategic Alliances: Their Nature and the Motives For Creating Them, Building Commitment by Creating Mutual Vulnerability, Building Commitment by the Management of Daily Interactions, Decision Structures That Enhance Trust, Moving a Transaction Through Stages of Development to Reach Alliance Status. CHAPTER 10: Retailing Defined, Choosing a Retail Positioning Strategy, Strategic Issues in Retailing. CHAPTER 11: Introduction, An Overview of The Wholesaling Sector, What the Independent Wholesale Sector Offers: The Essential Tasks, Federations of Wholesalers, Voluntary and cooperative Groups, Consolidation, Export Distribution Channels, The Future of WholesalerDistributors. CHAPTER 12: What Is Franchising? Why Become a Franchisee? Why Become a Franchisor? CHAPTER 13: The Impact of Logistics and Supply Chain Management, Responding efficiently, Responding Rapidly, Putting it All Together: What Is the Right Supply Chain? 17 18-19 Revision (Attendance is Mandatory) FINAL EXAMINATION (40 % ) Jubail University College Policies Attendance 1. Attending at punctual time: Present otherwise the student is absent. 2. Late attendance 0 < 5 minutes: is late 3. Late ≥ 5 minutes: is absent Notes: (i) Every 3 late are counted as 1 absent 3 (ii) Every × total semester contact hours + 1 is DN 15 Grading 1. Quality point: is the result of multiplying the credit hours by the grading points. 2. Semester GPA: is the result of dividing total quality points achieved in all courses at that semester by total graded credit hours of all courses in that semester. 3. Cumulative GPA in a semester: is the sum of total quality points achieved in all courses up to that semester divided by the total credit hours graded for all courses up to that semester Plagiarism & Cheating 1. Cheating is a serious offence and will be punished by the JUC. 2. Talking, looking at your colleagues’ exam papers or any other suspicious act is considered cheating during exam. 3. Student will fail the subject if caught cheating.