I. Energy in Ecosystems
advertisement

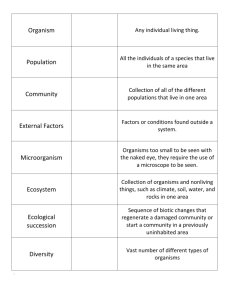
Name: ____________________________________ Date: _______________ Env. Science Period: _____ Unit 1: Ecology (Ch. 5) I. Energy in Ecosystems ** The ____________________ of ____________________ through an ecosystem is one of the most important factors that determines the system’s capacity to sustain life. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) What is ATP comprised of? ___________________, ____________________, and _________________ Where is energy stored in ATP? How is energy released? ______________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Interactions and Interdependence in Ecology Ecology is the study of ___________________ and relationships between __________________ and their environment. What non-living things in their environment do organisms interact with? _______________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ In what ways are these nonliving things essential to organisms? ______________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ ________________ contains the combined portions of the planet in which all of life exists, including land, water, and air (atmosphere). Name the levels of organization within the biosphere (start from the smallest level to the largest level) __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ __________ Producers What is the main energy source for life on earth? ______________________________________ Producers are also known as __________________. How do they get food? ___________________________________________________________ Name the two types of producers: __________________ and __________________ o Photo-autotrophs use __________________ in the process of photosynthesis. o Chemo-autotrophs use __________________ __________________. Where do most producers get their energy from? ____________________ Photosynthesis is the process by which producers use ___________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6CO2 + 6H2O Light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 On land, _____________ are the main autotrophs but in freshwater ecosystems, _____________ are the main autotrophs. Cellular respiration is the process by which both autotrophs & heterotrophs ___________ energy from food to do cellular work; it is the OPPOSITE of photosynthesis. C6H12O6 + 6O2 energy + 6CO2 + 6H2O Consumers Consumers are also known as __________________. These are organisms that reply on other organisms for their _______________ and food supply. Consumers use the sun’s energy _______________. The five (5) types of consumers/heterotrophs are: 1. _______________ - eat plants. Ex: rabbits 2. Carnivores — eat other ________________________. Ex: Lions, Sharks 3. Omnivores — eat BOTH _______________ and _______________. Ex: _____________ 4. ______________ — eat plant and animal _______________ called detritus. Ex: vultures 5. Decomposers — ______________________ down organic matter. Ex: bacteria & fungi Feeding Relationships Energy flows through an ecosystem in _______________ _____________________. Sunlight Producers Consumers Energy Transformations Only ______ of the energy at each _______________ _______________is passed on to the next. Primary – 1st Secondary – 2nd Trophic levels Tertiary – 3rd Quaternary – 4th The other ______is lost as _____________when consumers burn food during cellular respiration; this is good because it helps us to maintain our body temperature (homeostasis). Food Chain What is a food chain? ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ What does a food chain begin with? ___________; where do producers store energy? _________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Stored energy is passed on to ________________________ when they eat __________________ or other consumers. Ex: Sun Producer ___________________ Secondary Consumer _____________________ (Grass) (Grasshopper) (Snake) (Hawk) Decomposer (Fungi) Food Web What is a food web? _________________________ _________________________________________ ________________________________________ Ecological Pyramids An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows the relative amounts of __________________ or matter contained within each ________________ ________________ in a food chain. There are three (3) types of ecological pyramids: o Energy Pyramid - ________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ o _______________ _______________- represents the amount of living organic matter at each trophic level. Usually, the greatest biomass is at the base (bottom) of the pyramid. o Pyramid of Numbers - ____________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Recycling in the Biosphere Matter and energy move __________________ through the __________________. Energy flows __________________ way. Some energy is lost as ________________, only _______________ of energy is used directly by organisms at each _______________ _______________. Matter is __________________ through the ecosystem. o Law of Conservation of Matter o Matter can be _________________ II. Ecosystems, Communities & Population Growth Factors in an Ecosystem Biotic factors: __________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ o Examples: insects, plants, Abiotic factors: _________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ o Examples: sunlight, wind, soil Community Interactions ___________________ occurs when organisms attempt to use an ecological resource in the same place and at the _______________ time. o A ________________ is any necessity of life. Examples are: water, nutrients, light, food, space What is predation? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ o Ex.: lions hunt deer so lions are the predators and deer are the prey There are three (3) main types of Symbiosis. These are ____________, _____________, and _______________. o Mutualism - _______________ organisms benefit from the relationship. Ex: ______________________________________________________________ o _______________ - one organism _______________ while the other organism is neither helped nor _______________. Ex: ______________________________________________________________ o Parasitism - _______________ organism _______________ at the expense of the other organism which is harmed. Ex: ______________________________________________________________ Ecological Succession Ecological succession is ___________________ changes that occur in a community over time. Primary succession: _____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ o Ex: after a volcanic explosion where the land is covered with lava/ashes o Pioneer species is ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Secondary succession: ___________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ o Ex: wildfires, plowing, logging industry Population Growth Population growth is affected by three (3) factors: _______________, _______________, and number of organisms arriving or leaving (immigration or emigration). _______________ and immigration increase the population. Death and _______________ decrease the population. There are two ways growth can occur in a population: exponential growth and logistic growth. o Exponential growth occurs when organisms in a population _______________ at a _______________ _______________; J-shaped curve. Exponential growth tends to happen when resources are _______________. o Logistic growth happens when resources become _______________ available so growth will _______________ or _______________; S-shaped curve. Logistic growth happens when a population reaches its carrying capacity due to _______________ _______________.