Reading-guide-Atomic
advertisement
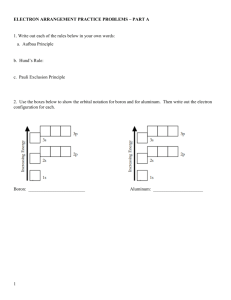
Chem. Reading Guide Topic: Atomic Orbitals Name:_______________________ Wilbraham et al: Page 131-136 Part I: Before Reading: 1. What background information do you already know about Characteristics of Elements? Question Answer What is an Element? An element is a type of atom with a specific number of ____________, that do NOT change. What part of an element never changes? ____________ never change in an element. That is what makes each element unique on the periodic table. What parts of an element are in the nucleus? ___________ and ______________ are found in the nucleus of an atom. What parts of an atom are floating around the outside of an element? _____________ are floating around the protons and neutrons in the nucleus. What did Erwin Schrödinger add to the Cloud Model of an atom? What is a property of an element? Erwin Schrödinger made a _______________ model to determine the most likely _______________ of an electron. A property of an element is a way to ______________ an element based on its physical ___________ and how it chemically __________ without elements, when it undergoes a chemical change. During Reading: Read to answer the following essential questions, and answer them at the end: Essential Question to think about when you are reading How are electrons related to the properties of elements? To organize the important information in this section, use the following note-taking guide: Study Questions: Atomic Orbitals Answer 1. According to Schrödinger, Each electron can have different ____________ ____________. what does each electron have? 2. What is an atomic orbital? An atomic orbital is a region of _____________ in which there is a high 3. What tells each energy level in an atom? 4. What does each energy sublevel correspond to? 5. What is used to represent the different atomic orbitals, which have different shapes? _______________ finding an electron. Each energy level in an atom are labeled by _____________ __________ _____________. Each energy sublevel corresponds to an ____________ of a different ____________, which describes _________________________________. Different atomic orbitals are represented by ________________. orbital Describe the shape Draw a picture of the shape Write the number of orbitals at each energy level s 6. What are the shapes of the orbitals? p d f Study Questions: Electron Configurations 7. What is the interaction between the nucleus and the electrons that are around it? 8. What is an electron configuration? 9. What is the Aufbau Principal? 10. What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle? 11. What is Hund’s rule? 12. How do you write the Answer (in your own words) Electrons and the nucleus interact to… Electron configurations are… Electrons occupy the… Each orbital can have… Each orbital must have opposite ___________. Hund’s rule says that ____________ electrons enter each orbital until… orbital filling diagram for the element, Flourine? 13. What is the shorthand way to write the electron configuration of oxygen? F: _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ 1s 2s 2px 2py 2pz 3s The shorthand method for showing the electron configuration of oxygen is… Study Questions: Answer (in your own words) Exceptional Electron Configurations 14. What are more stable, filled energy levels or partially filled energy levels? Study Questions: Electron Answer (in your own words) Configurations in Groups 15. What plays a key role in determining the property of elements? ****AFTER reading this section: return to your essential question, and answer it. *** How are electrons related to the properties of elements?

![6) cobalt [Ar] 4s 2 3d 7](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009918562_1-1950b3428f2f6bf78209e86f923b4abf-300x300.png)