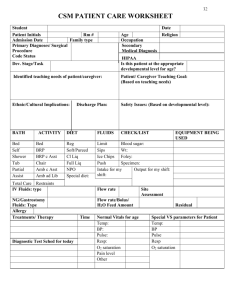
Savings through RESPs can be challenging due to
advertisement

Funded by the Government of Canada through the Canada Education Savings Program Our goal is to help families by providing clear and useful information about saving for your childs’ education after highschool (college/university/trade school etc.) We hope that families will feel more confident in their understanding of Registered Education Savings Plans’s (RESPs) and the government grant and bond (free money!!!!). Future trends in educational needs and work demands The Fact Is….. The work world is changing and there are fewer and fewer jobs today in Canada that don’t require some continuing education after high school. Those who have a trade, college or university degree will have a much better chance of finding a full time job and getting higher pay. Future Trend in Educational Demands Post Secondary Education: How much will it Cost? 59% of Canadians under-estimate the future cost of Post Secondary Education. By 2019: According to Statistics Canada, a fouryear univesity degree will cost about $74,000* and a three-year college diploma will total $45,000*. (*this includes tuition, books and living expenses) Cost-Benefit University graduates on average make $27,200 more per year (2005 figure) than high school graduates. By not going to university the cost saved (from tuition and lost wages) with interest for 35 years = $441,300 Graduating from university, potentially $27,200 more per year is made and if saved with interest for 35 years = $2,455,900 Start Saving Early While the costs of post-secondary schooling seems high, there are ways to help plan ahead and save some of the money that may be needed. Every little bit will help so your kids won’t have to start out their adult lives with a big student debt. It is important that your child knows that there is an opportunity to continue education after high school if they want. And it is not just about making more money, it is also about personal development, choices and opportunities. Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP): Questions to Consider • • • • • • What is it? Why open one? Who can open an RESP? When should you open an RESP? Where can you open an RESP? What do you need to do to open an RESP? • Do you need to deposit a minimum amount of money into an RESP? Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) ….continued • How much can you put into an RESP? • How long can an RESP account stay open? • How often do you have to put money into an RESP? • Can more than 1 RESP be opened for a child? • Can you open an RESP for yourself? • How is an RESP taxed? Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) ….continued • How is an RESP taxed if a child decides not to continue education after high school? • Does having a RESP account with savings effect Work Benefits or Disability Support Payments? • How do you get the money out to use for PSE or training? • What happens if one parent opens the RESP and then there is a divorce? Federal Government Programs Federal Government Programs There are two Federal Government PSE savings incentive programs: • The Canada Education Savings Grant (CESG) and the Additional CESG • The Canada Learning Bond Canada Education Savings Grant CESG • Who qualifies? – Anyone up to 17 yrs of age that has savings in an RESP • How much is the grant? – 20% added to a RESP contribution (up to $1000 grant maximum per year) Additional CESG – If the net family income is below $40,970 additional 20% will be added to the first $500 of contributions (for a max of $100 grant per year) $7,200 is the maximum CESG and additional CESG grant an individual can recieve CESG + Additional Net family Income Contribution ($ family adds) CESG adds CESG+ adds Total $40,970 or less $100 $20 $20 $140 $1000 $200 $100 $1300 Above $40,970 to $81,941 $100 $20 $10 $130 Above $81,941 $100 $20 n/a $120 Canada Learning Bond (CLB) • Who qualifies? – The CLB is available for if families • receives the National Child Benefit Supplement (NCBS) • the child (beneficiary) was born after December 31, 2003 • An RESP account has been opened however a deposit into that account is not required to qualify How Much is the Canada Learning Bond? • The first bond is $500 plus an additional $25 (to cover the expense of opening an RESP) • $100 per year thereafter up to the age of 15 and a maximum amount of $2,000 RESP Savings $8,000.00 Total in savings Savings over 10 years $7,000.00 $6,000.00 $5,000.00 Family contributions Family contributions CESG $4,000.00 CLB $3,000.00 $2,000.00 Total in savings CESG CLB $1,000.00 $0.00 Totals Contributions Canada Learning Bond Contributions Only with Annual $100 Deposits and Compounded Interest (rate at .04) 3500 3000 Dollar Value 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Years Bond Only Cumulative amount (bond & interest) 12 13 14 15 16 RESPs 101 An Introduction to the Types of Registered Education Savings Plans Individual Plan For 1 person The person doesn’t have to be related to you There are no age limits This RESP could even be for you or another adult. However, the CESG is only for children aged 17 or younger The CLB is only for children aged 15 or younger Some plan fees may apply Individual Plan continued…. Qualifying educational programs include apprenticeships, and programs offered at trade schools, CEGEP, college or university and foreign studies Usually, a qualifying educational program is a course of study that lasts at least 3 weeks in a row, with at least 10 hours of instruction or work each week. A program at a foreign educational institution must last at least 13 weeks Individual Plan continued…. • An Individual Plan may be a good choice if: – You want to save for a child who is or is not related to you – You want to decide how to invest the money, either on your own or with the help of a financial advisor – You don’t necessarily want to make regular monthly payments Family Plan You can name one or more children as beneficiaries The children must be related to you(your children, adopted children or grandchildren, brothers or sisters) Must be under 21 years Additional CESG payments available only if children are siblings CESG can be used for either child CLB can only be used for specific child May not require specific monthly payments Some plan fees may apply Group Plan You can name only one child in a group plan The child doesn’t have to be related to you Your savings are combined with those of other people Plans are provided by group plan dealers, who usually put money in low-risk investments Usually, you must make regular payments into the plan over a certain period of time Limited to full time studies, usually a minimum of 6 months per year and a 2 year program Fees apply!!!!!!! Group Plan continued…. A group plan may be a good choice if: – You can make regular payments into the RESP (there is a penalty if you don’t) – You prefer to have someone else decide how to invest the money for you – You are fairly sure that the child you are saving for will continue education after high school Documents needed for an RESP • Social Insurance Number (SIN) for the parent/legal guardian and one for the child • Child’s original document (birth certificate/birth registration) • A document that confirms that you are the legal guardian of the child OR authorization from the primary caregiver for you to open an RESP account for their child Who can apply for a Social Insurance Number (SIN)? 1. Canadian citizens 2. Newcomers 3. Temporary residents 4. Children under 12 through a parent or legal guardian Health Care Premium Subsidy National Child Benefit Supplement Canada Child Tax Benefit Guaranteed Income Supplement Seniors Benefit Filing an Income Tax Return could entitle you to some or all of these credits Income for Severely Handicapped Rent Subsidy GST Tax Credit Day Care Subsidy Banking Terms Basic Banking Info It is important to understand some basic banking concepts and products such as: Compound interest GIC’s, mutual funds Compound interest is the concept of adding interest made back to the principal ($ you added), so the interest becomes part of the earnings to make more interest. However, if it is a loan (not savings), it too may have interest compounded every month. In this case, a loan with $100 principal and 10% interest per month would have a balance of $110 at the end of the first month so you are now paying interest on $110. Guaranteed Investment Certificate’s (GIC’s) • You may have to invest at least $500 • You agree to keep your money in the GIC for a certain amount of time, such as six months, one year, two years, or up to 10 years. • Most GICs pay you interest. A GIC may pay a higher interest rate than savings accounts, but not always. GIC’s cont… • In most cases, the longer you agree to put your money in a GIC, the more interest you will make • The amount that you originally invested is guaranteed by the government • With some GICs, if you need to get your money back sooner than you agreed, you won’t earn any interest. In fact, you may have to pay a fee or penalty How do Mutual Funds Work? • When you put your money in a mutual fund it is added to many other investments, creating a large pool of money that can be invested. • The company that runs the mutual fund puts a professional in charge(fund manager)of investing the money. This person decides where to invest the money and also decides when to buy and sell. Mutual Funds cont… • You can choose a fund that buys the kinds of investments that will help you meet your goals. • Is the most important thing to keep your money safe? Grow your money? The fund you choose must be right for you. How do you make money from a Mutual Fund? • If the price of your units go up and you sell, you will make money. If they are have gone down and you sell, you will lose money. Tax Free Savings Account Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA) Most banks and credit unions now offer a tax free savings account where you can deposit up to $5000 a year and earn interest tax free. Some differences between RESPs and TFSAs: 1. An RESP is specific to education savings. 2. With a TFSA you don’t pay tax on the money earned. With an RESP you pay tax when you take it out but it is taxed at the rate of the students earnings (or rolled into an RRSP). 3. You have to close an RESP after 36 years. There is no time limit for contributing to a TFSA. 4. With a TFSA you can name your spouse or common-law partner as a beneficiary. The money will roll over to them upon your death. But with an RESP, if the account is transferred over taxes still have to be paid. 5. *The Canada grant and bond program only applies to RESPs* Saving Tips Saving Behaviours Attitudes about savings and actual savings behaviour is strongly related to what kids see is done in the household (Do you talk about finances with your children (age appropriately)? Did your parents talk to you?) Financial planning is a key to gaining wealth (in whatever form) Learning to Save Things to consider: • What is your short term goal (achievable in a year)? • What are your long term objectives (next 5 years)? • What are your strategies to achieve the short term goal? The long term goal? • Who can assist you with your planning? Saving cont… Important things to know: • Monthly Income • Monthly Expenses • Emergency and unexpected costs Saving cont… Taking the steps: • Calculate your monthly/yearly expenses and earnings • Make a budget (plan to set aside $ on a regular basis to meet your goals) • Write it all out • Is it working? Is it doable? Are you miserable?(review on a regular basis and revise if necessary). Sharing Ideas • Ways to save? • What motivates you to save? • What keeps you on track? • How do you or will you engage your family in saving? Tips for Saving • Save before you spend. Ask your bank to take money from your pay and put it into a savings account for you. Even saving small amounts each month will add up. • Leave your credit and debit card at home and shop around for the best prices. Don’t buy the first thing you see. Plan your purchases to take advantage of sales. • Small amounts of cash or loose change are too easy to spend. Start a money jar for loose change instead and deposit it in a savings account at the end of each month. Tips cont’d… • Take a set amount of cash out each month, and put that debit and credit card away! • Ask a bank for a low cost bank account. • Stay away from Money Mart etc.! They can charge up to 150% interest on loans..it’s robbery. • Look for ways to save at home. For example, home-cooked or homemade is usually cheaper and often better than store-bought. Tips cont’d… • Every time you spend money, write it down. You'll be surprised how much you can save by getting rid of a few small things. • Start saving for your children’s education early. Take advantage of government grants to add to your savings. • Know the difference between what you need and what you want and educate your family about it. Have fun being the recycle/reuse/save the planet and save your money family! Making it Work