Physical Science Vocabulary BINGO-Unit 2
advertisement

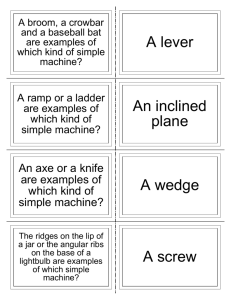
PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY BINGO- UNIT 2 B I N G O force Newton inertia Newton’s 3rd law of motion balanced forces net force unbalanced forces weight mass gravity friction velocity acceleration lever pulley wedge compound machine work distance mechanical advantage screw inclined plane Newton’s 2nd law of motion static friction motion PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY BINGO- UNIT 2 B I N G O wedge mechanical advantage inertia Newton’s 3rd law of motion velocity net force unbalanced forces weight distance gravity friction balanced forces motion lever force pulley screw work mass Newton compound machine inclined plane Newton’s 2nd law of motion static friction acceleration PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY BINGO- UNIT 2 B I N G O force Newton balanced forces friction inertia inclined plane unbalanced force motion mass Gravity Newton’s 3rd Law of motion velocity acceleration lever pulley wedge compound machine work distance mechanical advantage net force screw Newton’s 2nd law of motion static friction weight PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY BINGO- UNIT 2 B I N G O screw inclined plane inertia static friction motion net force gravity weight mass unbalanced forces friction pulley compound machine lever velocity wedge acceleration work distance mechanical advantage force Newton Newton’s 2nd law of motion Newton’s 3rd law of motion balanced forces PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY BINGO- UNIT 2 B I N G O weight mass friction Newton’s 3rd law of motion balanced force net force unbalanced force force Newton Motion inertia velocity acceleration work pulley wedge compound machine lever distance Screw Mechanical advantage inclined plane Newton’s 2nd law of motion static friction gravity PHYSICAL SCIENCE VOCABULARY BINGO- UNIT 2 B I N G O force Newton’s 2nd law of motion wedge Newton’s 3rd law of motion unbalanced forces net force balanced forces friction mass lever velocity weight acceleration gravity compound machine inertia pulley inclined plane distance motion screw work Newton static friction mechanical advantage Definitions for BINGO Unit 2: force- a push or a pull Newton’s 2nd law of motion- force is equal to the mass times the acceleration wedge-a simple machine that is made up of two inclined planes and that moves; often used for cutting Newton’s 3rd law of motion- for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction unbalanced forces- when all forces acting on an object have a value other than zero and causes motion. net force-the sum of all forces acting on an object balanced forces-when all forces acting on an object have a value of zero and no motion occurs. static friction- the force that resists the initiation of motion between two surfaces that are in contact and at rest friction- a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact mass- this and distance are the two main things that affect the force of gravity lever- simple machine that consists of a bar that pivots at a fixed point called a fulcrum velocity- the speed of an object in a particular direction weight-a measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object; its value can change with the location of the object in the universe acceleration-the rate at which velocity changes over time; an object accelerates if its speed, direction, or both change gravity-a force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses and that decreases as the distance between the objects increases compound machine-a machine made of more than one simple machine inertia-an object in at rest tends to stay at rest; an object in motion tends to stay in motion pulley-a simple machine that consists of a wheel over which a rope, chain, or wire passes inclined plane-a simple machine that is a straight, slanted surface, which facilitates the raising of loads; a ramp motion-an object’s change in position relative to a reference point screw-a simple machine that consists of an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder work-the transfer of energy to a body by the application of a force that causes the body to move in the direction of the force Newton-the SI unit for force; the force that will increase the speed of a 1 kg mass by 1 m/s each second that the force is applied (symbol, N) mechanical advantage- a number that tells how many times a machine multiplies force; it can be calculated by dividing the output force by the input force